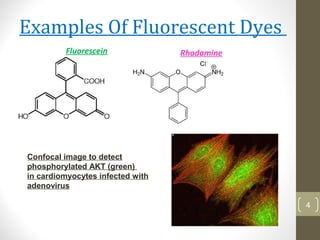
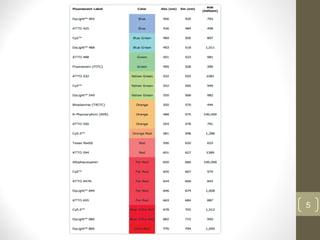
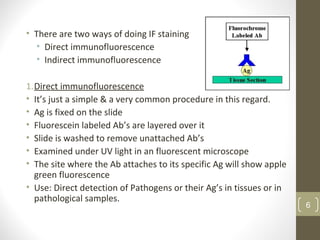
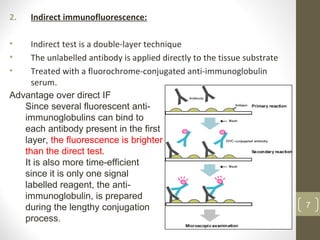
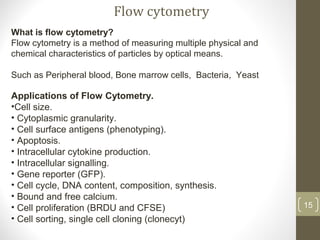
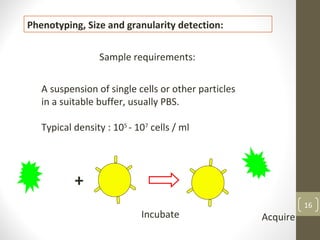
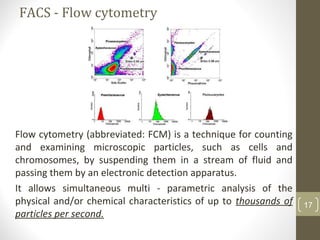
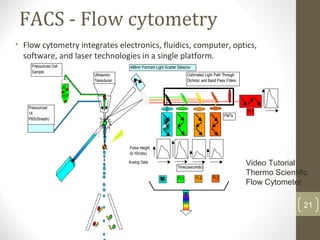
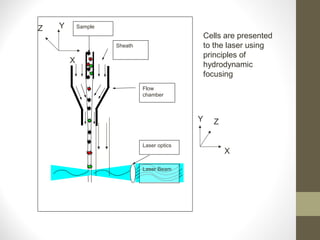
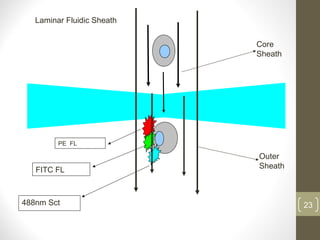
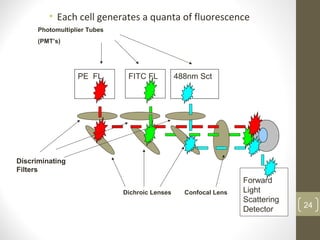
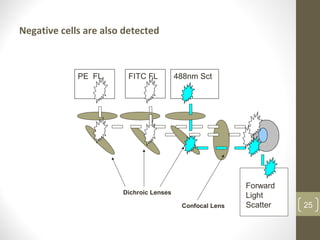
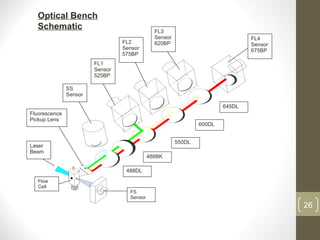
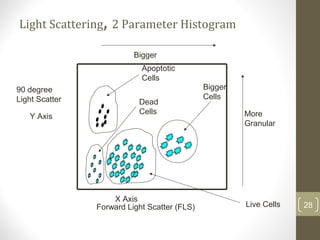
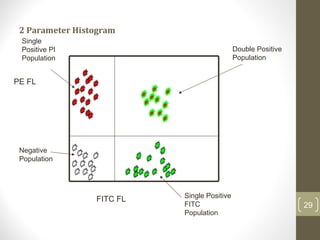
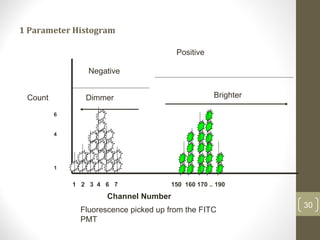
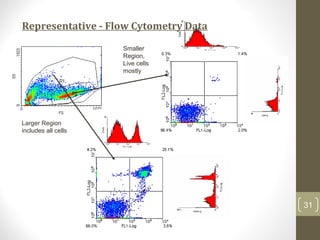
This document provides information about immunofluorescence and fluorescence microscopy techniques. It discusses immunofluorescence, which uses fluorescent-labeled antibodies to detect target antigens. It describes direct and indirect immunofluorescence methods. It also discusses fluorescence microscopy, including different types of fluorescent dyes, fluorescence microscopes, applications such as visualizing viral plaques and detecting proteins in cells, and considerations for effective immunofluorescence applications. Flow cytometry is also summarized, which uses fluorescence to examine particles like cells that are passed through a flow chamber.