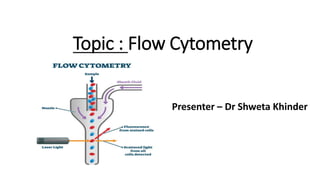
Flow cytometry is a technique that uses lasers to detect and measure physical characteristics of cells or particles in a fluid mixture. Cells passing through the laser beam scatter light and may fluoresce if stained with fluorescent antibodies. Forward scatter detects cell size while side scatter detects internal complexity. Fluorescence identifies protein or nucleic acid expression. Data is converted to electrical signals and analyzed by a computer. Flow cytometry is used in clinical applications like detecting malignancy and monitoring treatment response. It provides information about cell phenotypes that helps diagnose hematological conditions.