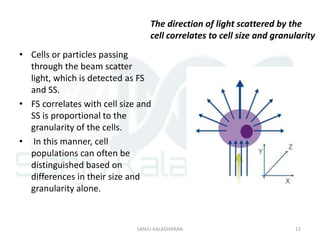
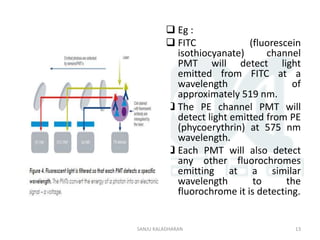
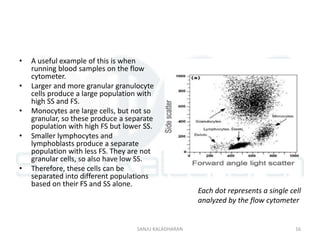
Flow cytometry is a technique that uses laser-based technology to count, sort, and profile cells in a fluid mixture. A flow cytometer passes cells in single file through a laser, and measures light scatter and fluorescence to obtain quantifiable data on physical and chemical characteristics of cells. Key components include a fluidic system to hydrodynamically focus cells through the laser, an optics system using lasers and detectors to measure light signals, and an electronics system to convert these signals into electronic data that can be analyzed. Common applications include immunophenotyping, apoptosis measurement, and cell sorting.