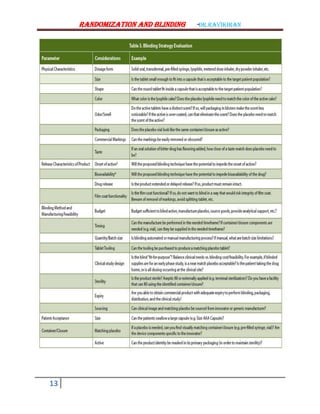
The document discusses randomization and blinding in clinical trials. It defines randomization as a process that assigns participants to experimental and control groups randomly to reduce bias. Randomization ensures groups are similar and comparable. Blinding refers to keeping participants and investigators unaware of group assignments to prevent bias in assessing outcomes. The document outlines various randomization techniques like simple randomization and stratification. It also discusses types of sampling and limitations of non-randomized trials in comparing interventions. In summary, the key points are that randomization and blinding are important design elements in clinical trials to reduce bias and ensure validity of results.