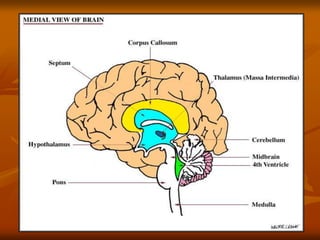
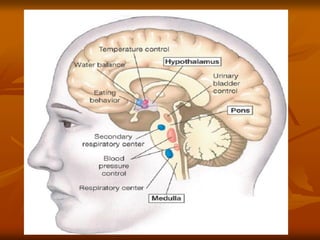
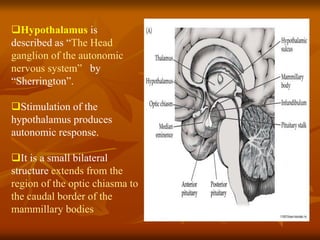
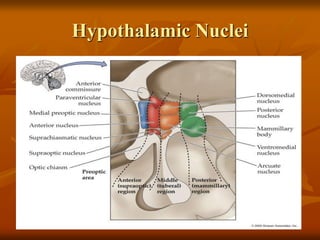
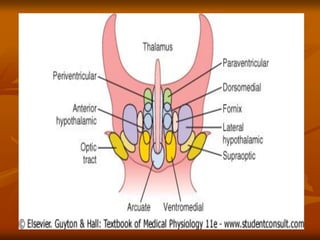
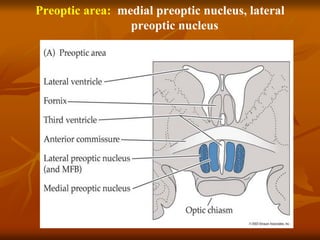
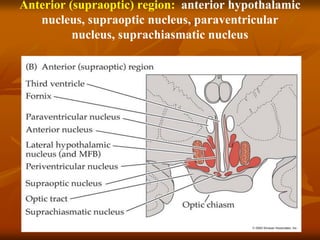
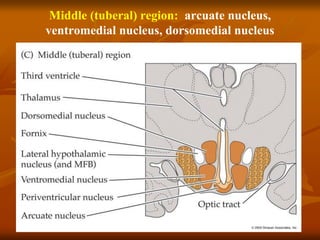
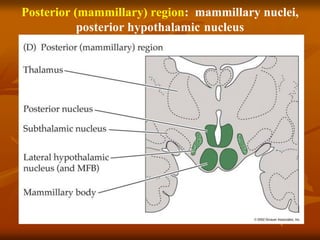
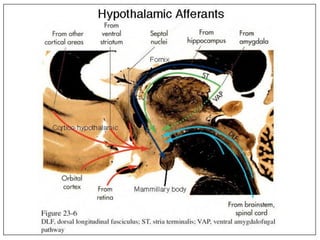
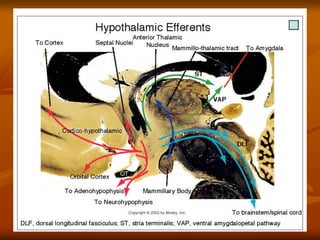
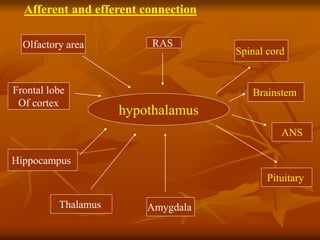
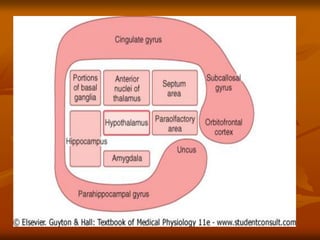
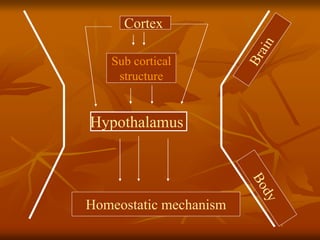
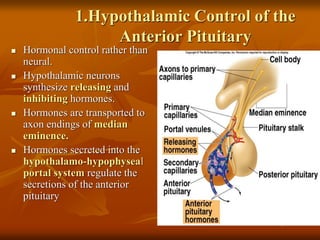
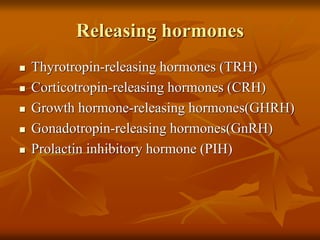
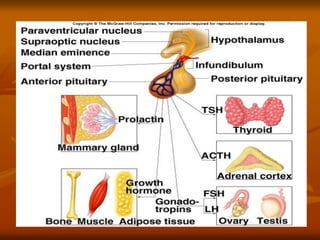
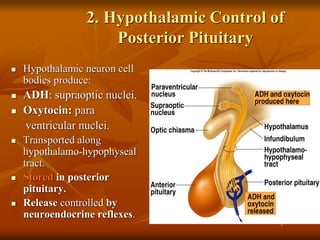
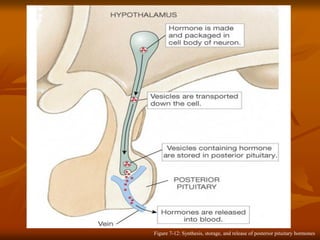
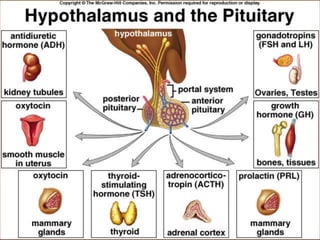
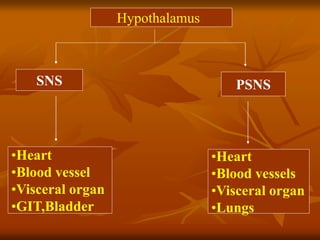
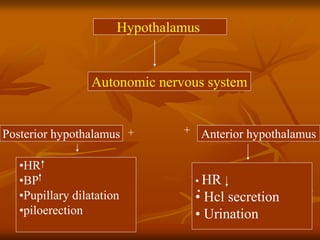
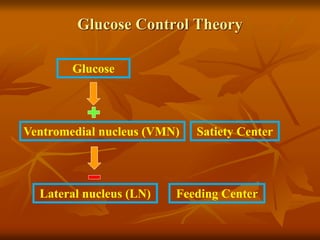
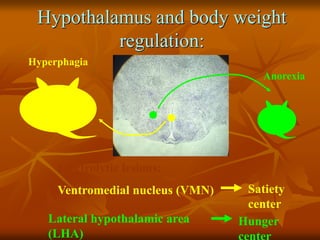
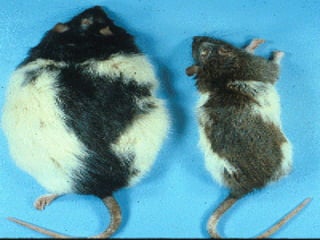
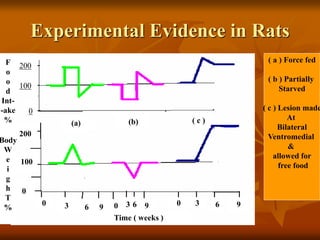
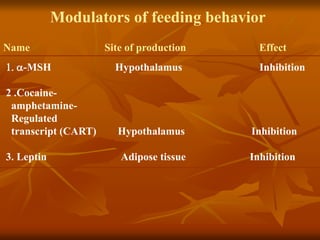
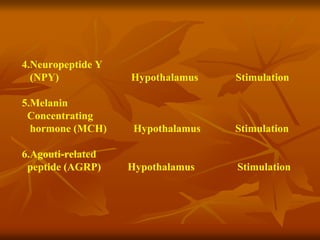
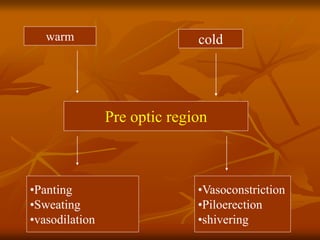
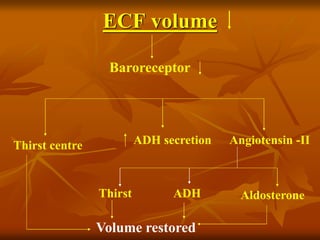
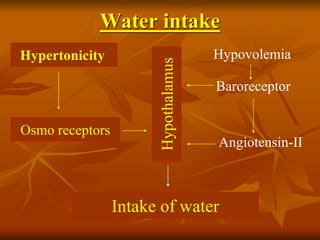
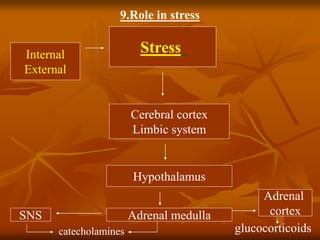
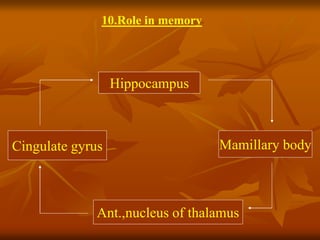
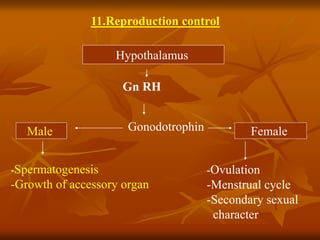
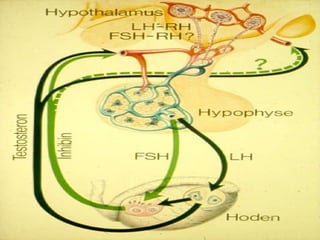
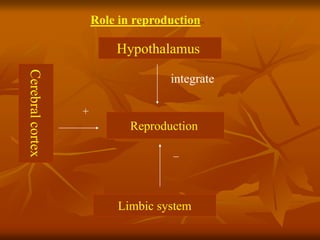
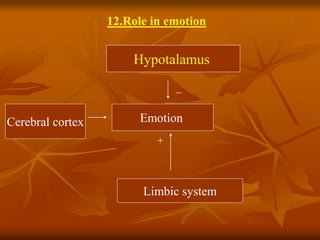
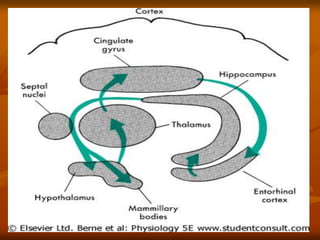
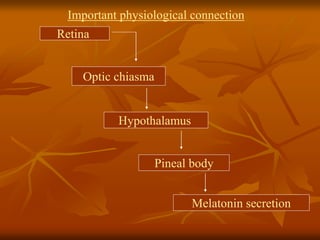
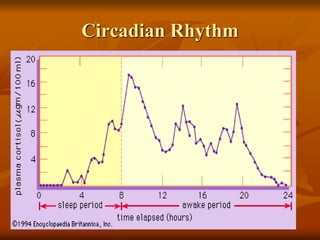
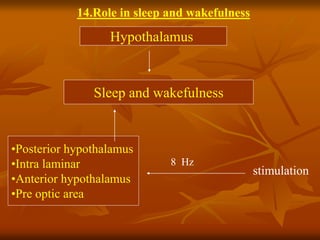
The hypothalamus is a small brain structure located below the thalamus that regulates many homeostatic functions including body temperature, hunger and thirst, circadian rhythms, hormone secretion, and the autonomic nervous system. It contains several nuclei that control these functions. The hypothalamus receives input from the limbic system and senses changes in the body to regulate the autonomic nervous system and pituitary gland to maintain homeostasis. Disorders of the hypothalamus can disrupt functions like sleep, emotions, temperature regulation, and hormone secretion.