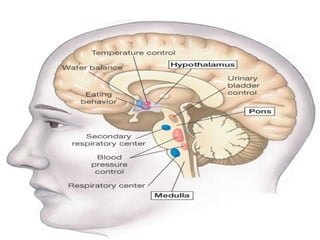
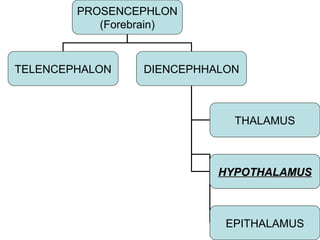
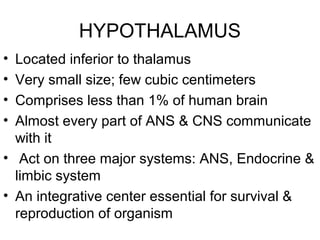
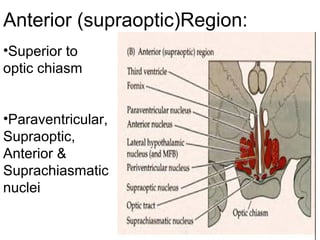
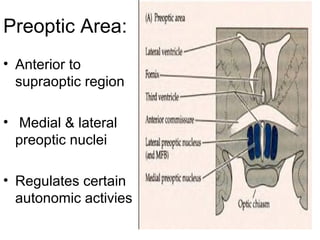
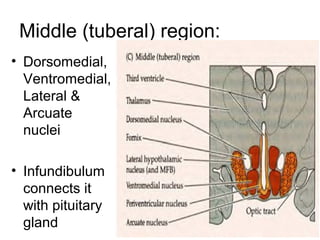
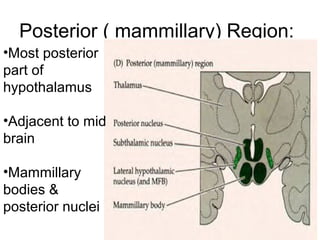
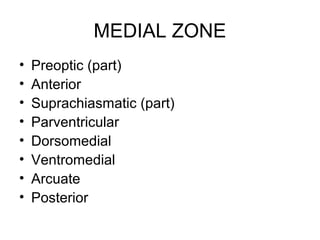
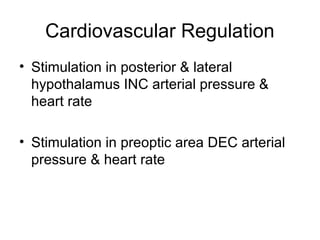
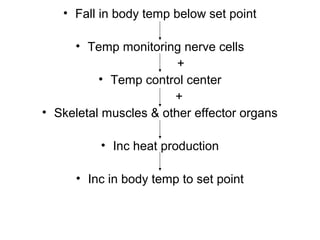
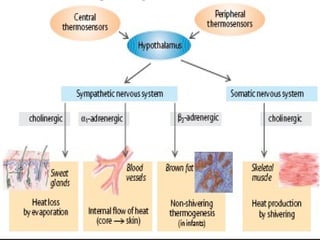
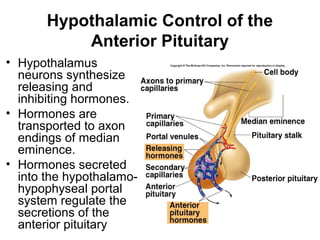
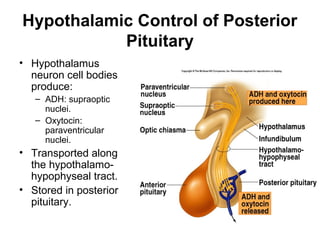
The hypothalamus is a small region located inferior to the thalamus that regulates many essential body functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, hunger, and hormone secretion through the autonomic nervous system, endocrine system, and limbic system. It is divided into anterior, middle, and posterior regions that control different processes like circadian rhythms, reproduction, feeding, and emotional responses. The hypothalamus communicates with the pituitary gland to regulate hormone release and various homeostatic mechanisms in the body.