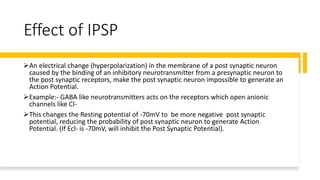
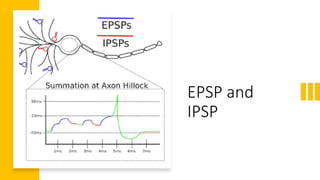
EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic potential that occurs when a neurotransmitter like glutamate binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, making its membrane permeable to sodium ions and depolarizing the neuron. IPSP is an inhibitory postsynaptic potential that occurs when GABA binds to receptors, making the membrane permeable to chloride ions and hyperpolarizing the neuron. EPSPs can summate and cause the neuron to generate an action potential, while IPSPs make action potential generation less likely. Together, the balance of EPSPs and IPSPs control whether a neuron will fire an action potential.