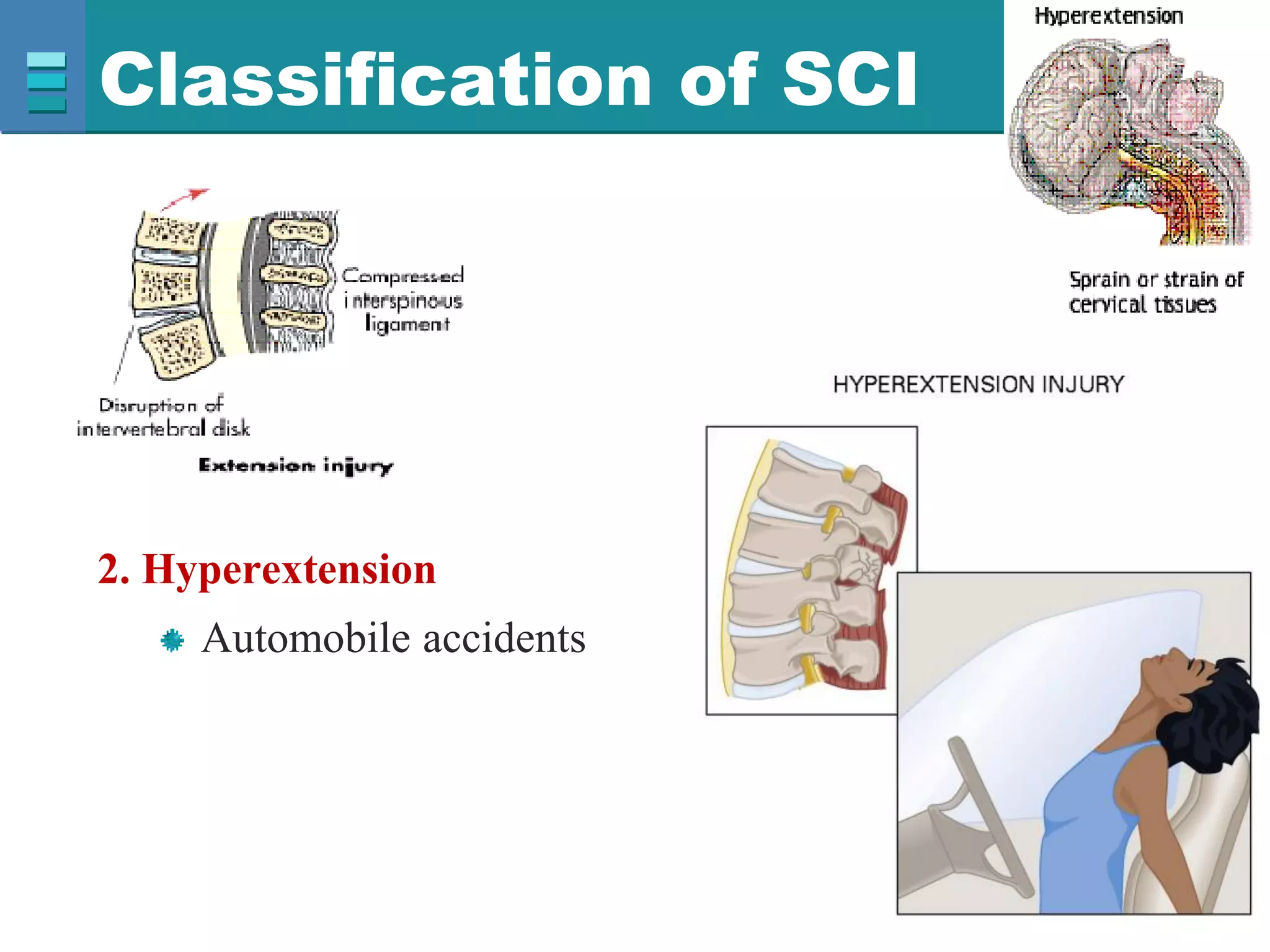
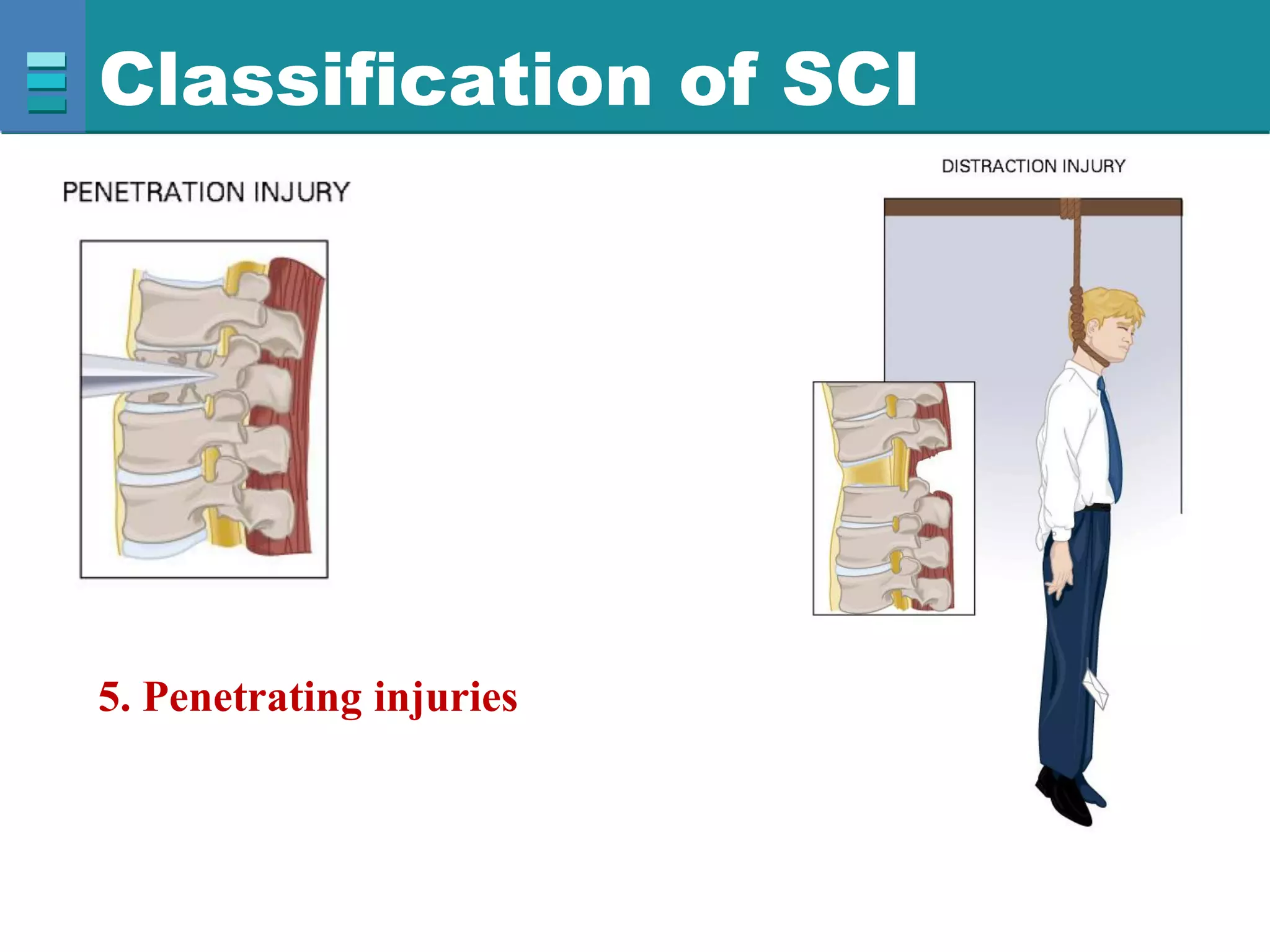
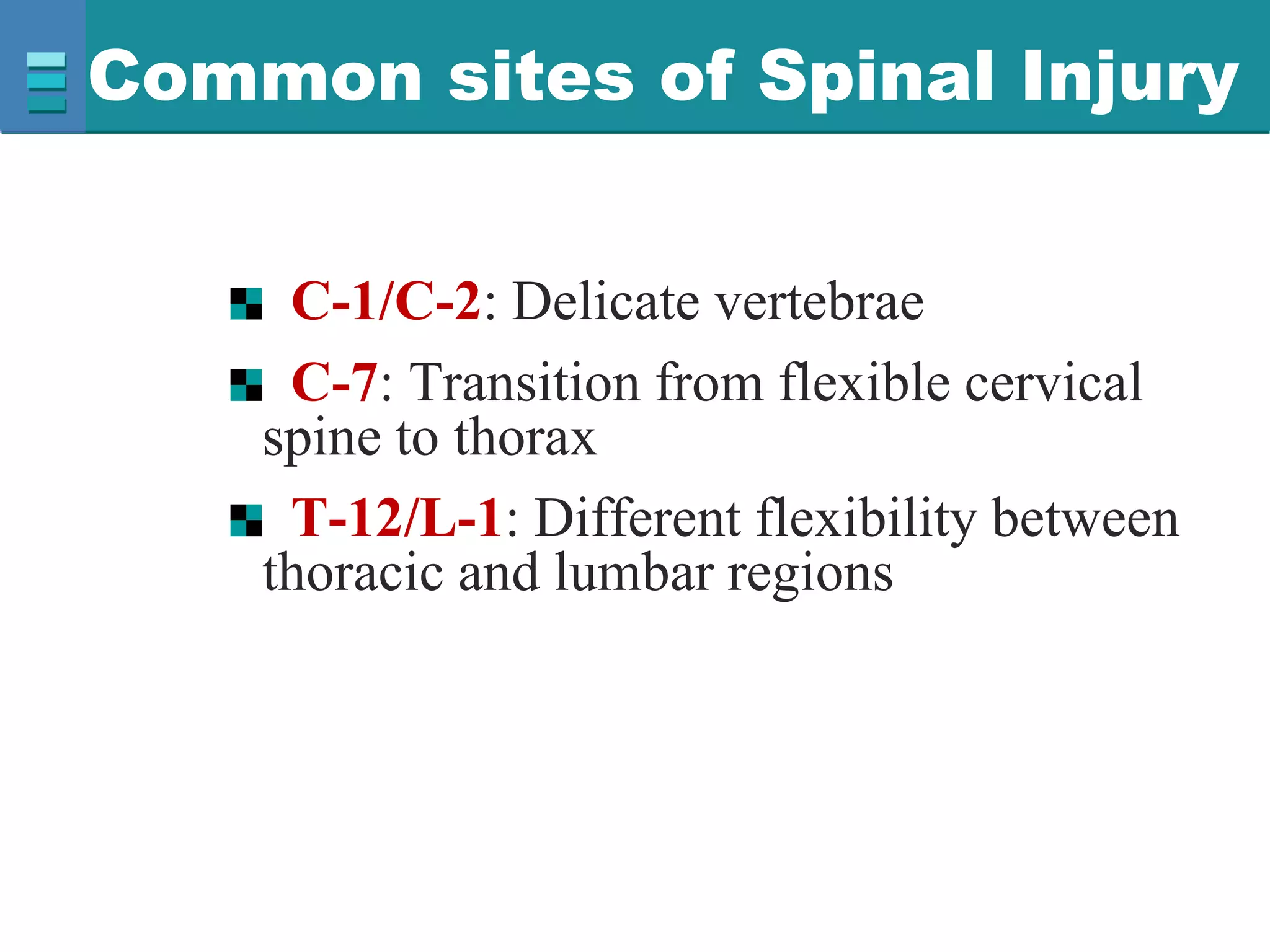
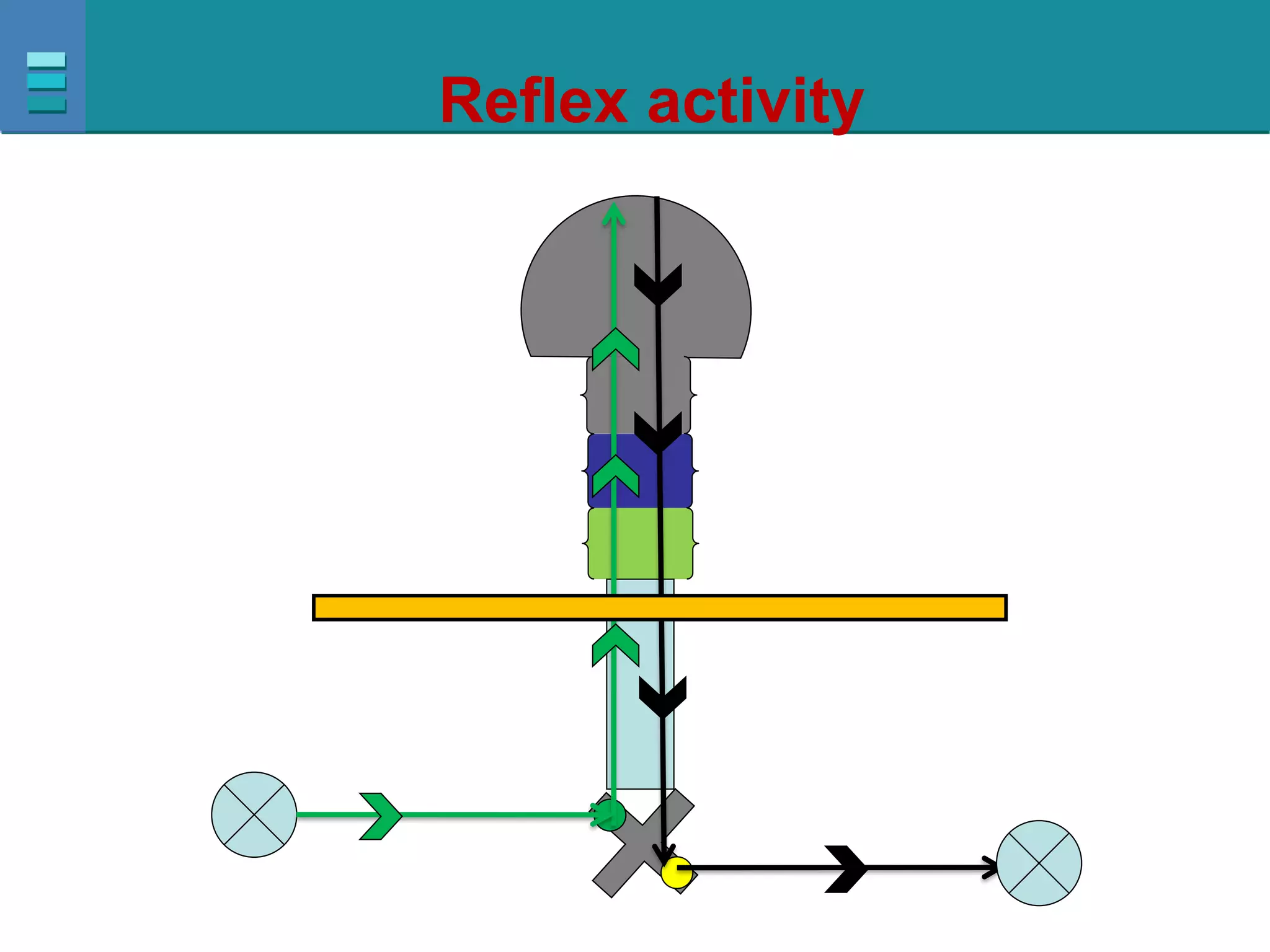
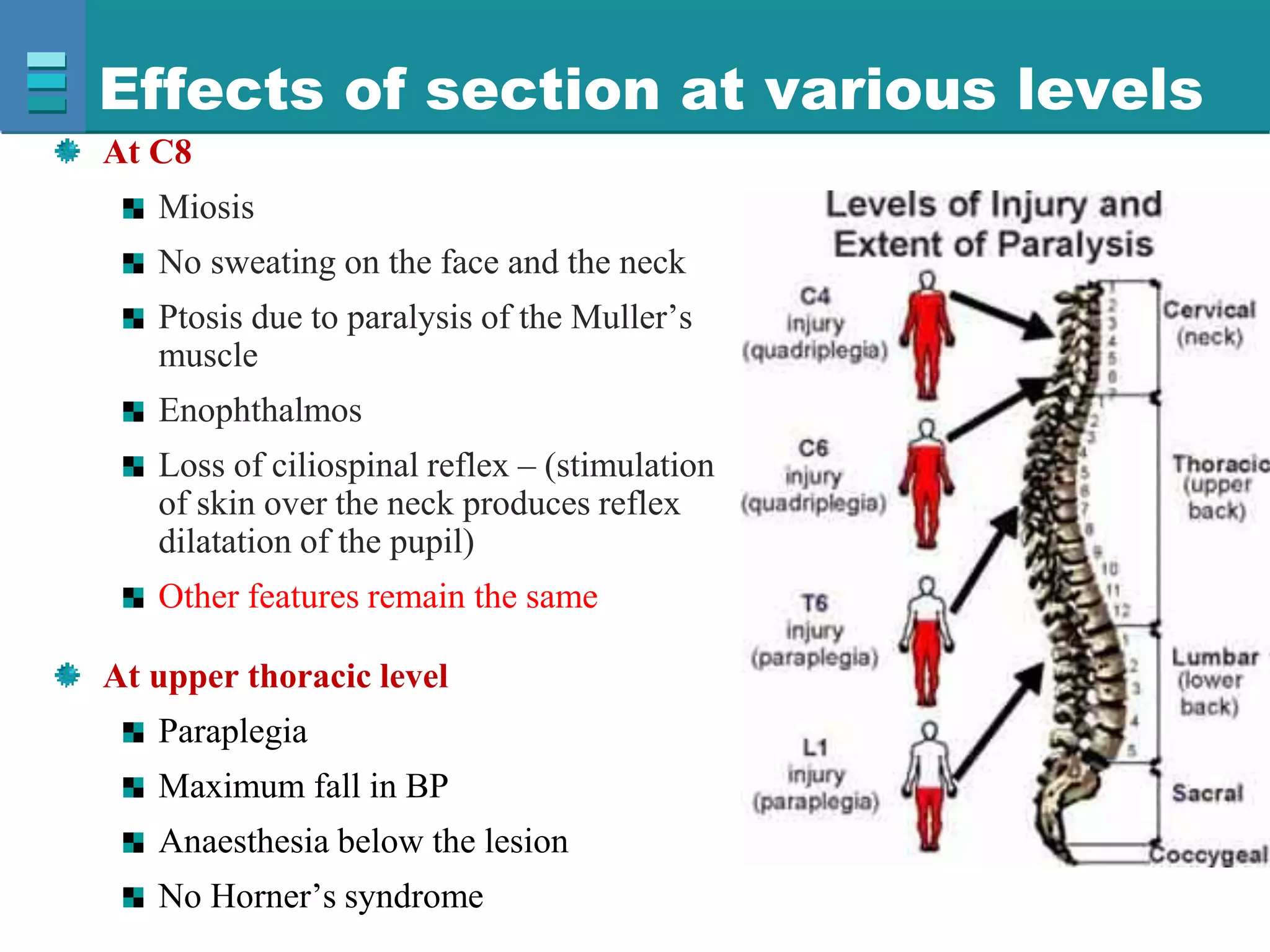
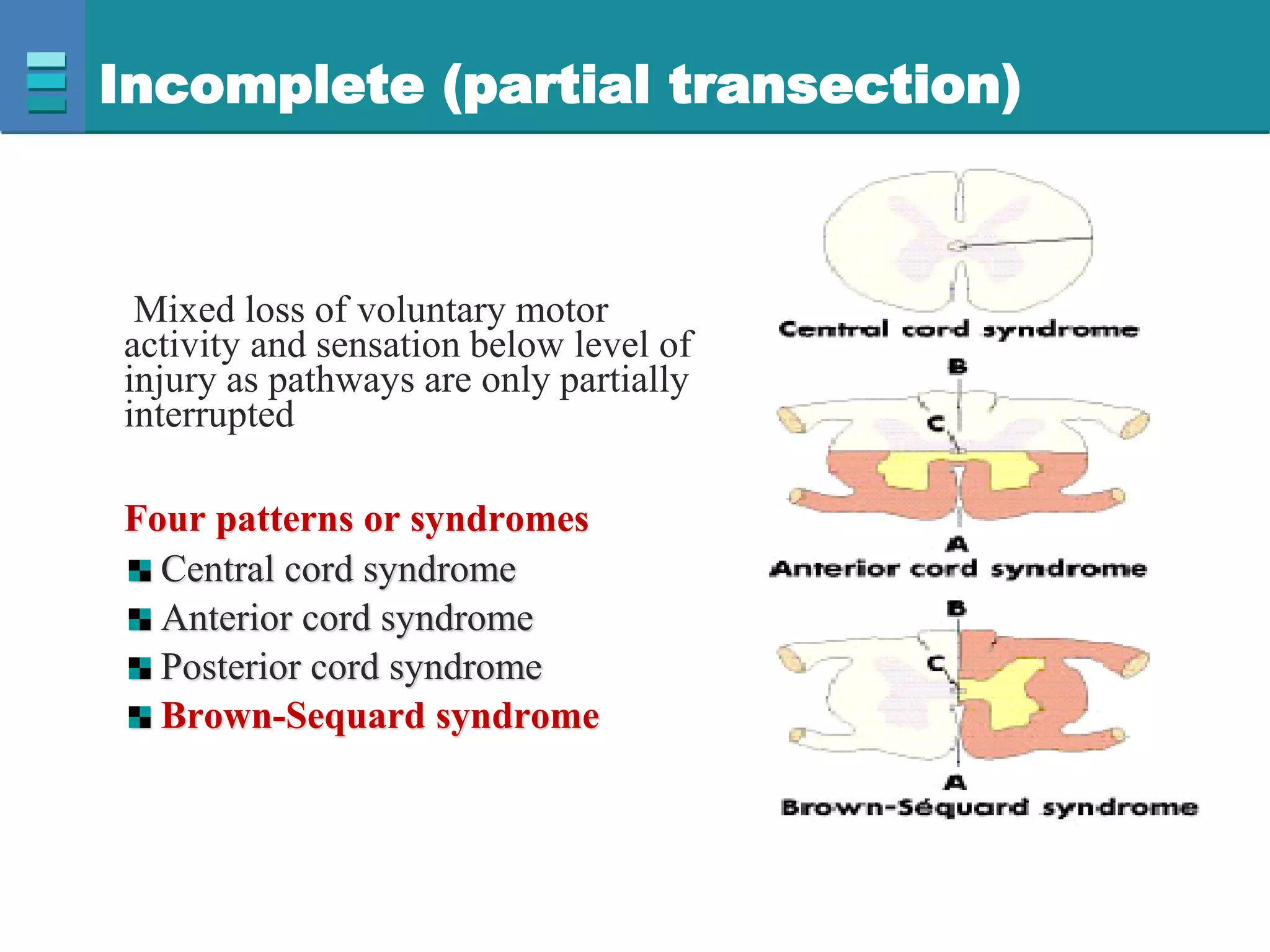
This document discusses spinal cord injuries, their classification and effects. It describes the following types of spinal cord injury: concussion, contusion, compression, laceration, hemorrhage and transection. Complete transection results in loss of all sensations and motor functions below the level of injury, causing tetraplegia or paraplegia. Incomplete injuries can cause central cord syndrome, anterior cord syndrome, posterior cord syndrome or Brown-Sequard syndrome. Brown-Sequard syndrome is caused by incomplete transection on one side and results in ipsilateral sensory and motor loss and contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation.