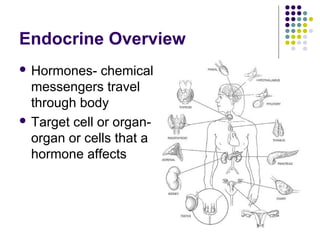
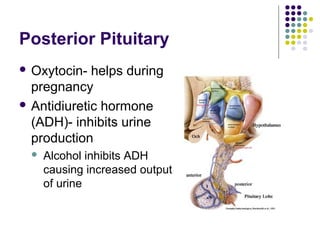
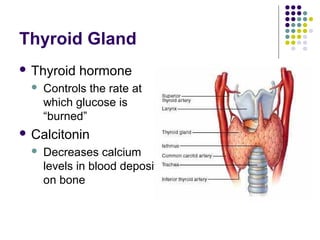
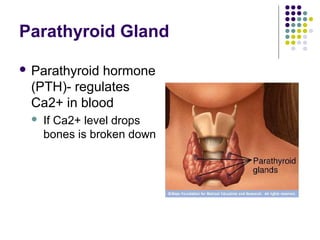
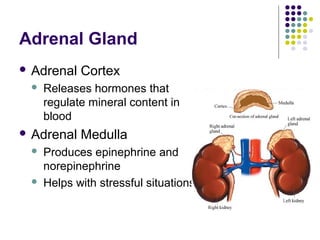
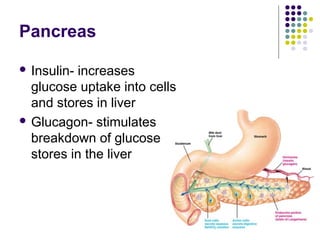
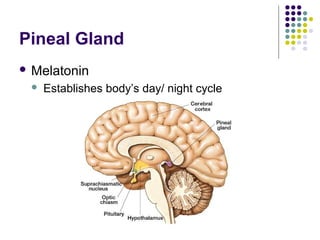
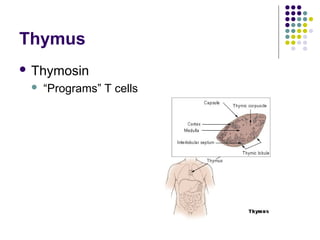
The endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones to regulate bodily functions. Hormones travel through the bloodstream to target organs and cells. Hormone release is controlled through negative feedback mechanisms where rising hormone levels inhibit further release. The pituitary gland regulates growth and milk production and stimulates other glands. The thyroid and parathyroid glands control calcium and metabolic rates while the adrenals produce stress hormones and regulate minerals. The pancreas regulates blood sugar through insulin and glucagon and the pineal establishes circadian rhythms.