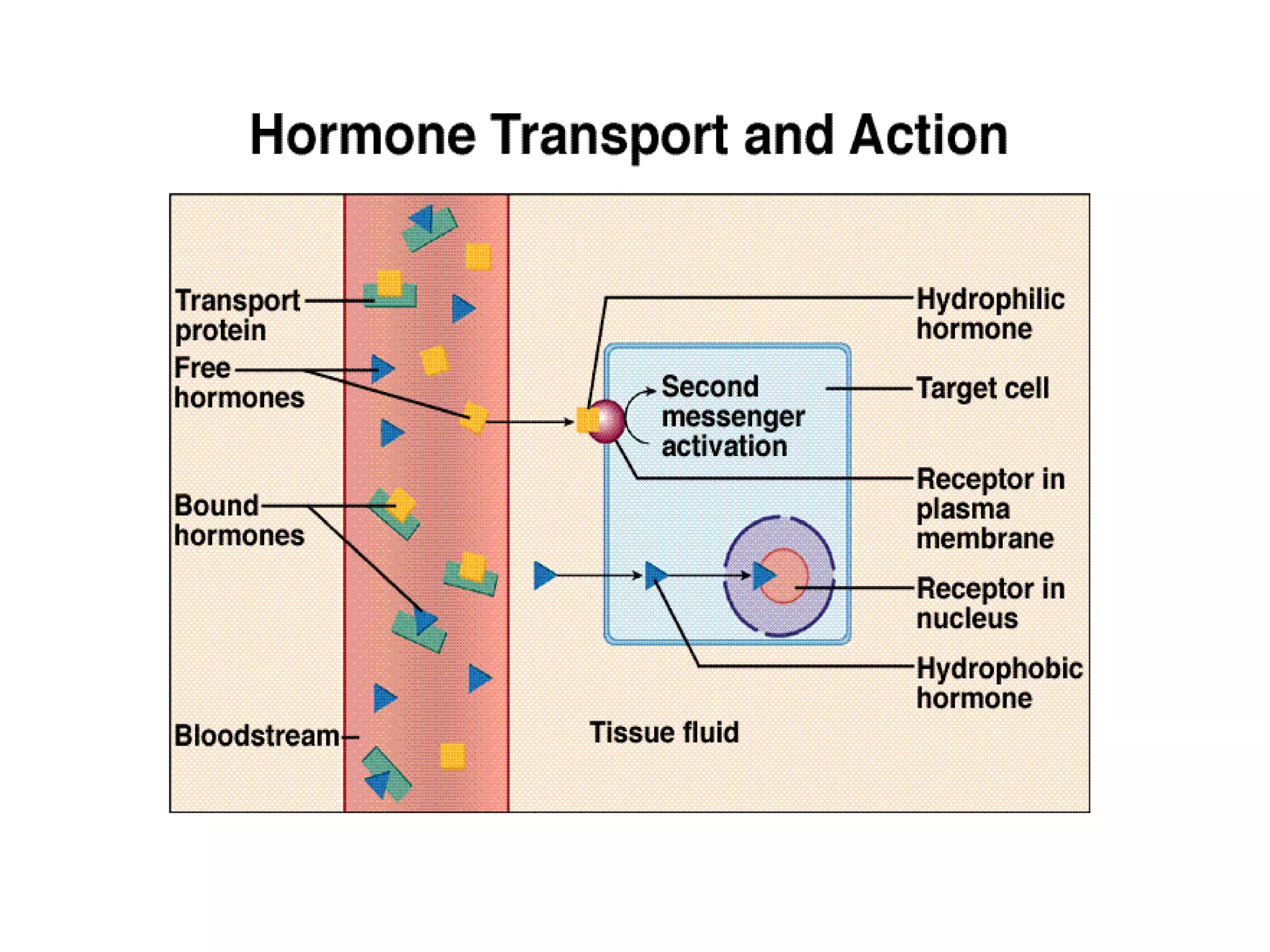
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs and tissues. There are three main types of hormones: steroid hormones like estrogen and testosterone which are lipid-soluble and pass through cell membranes to activate nuclear receptors; peptide hormones like insulin which are water-soluble and bind to cell surface receptors; and amine hormones like epinephrine which also bind to cell surface receptors. Hormones work through concentration-dependent effects and can have synergistic, permissive, or antagonistic interactions with each other to regulate various physiological processes in the body.