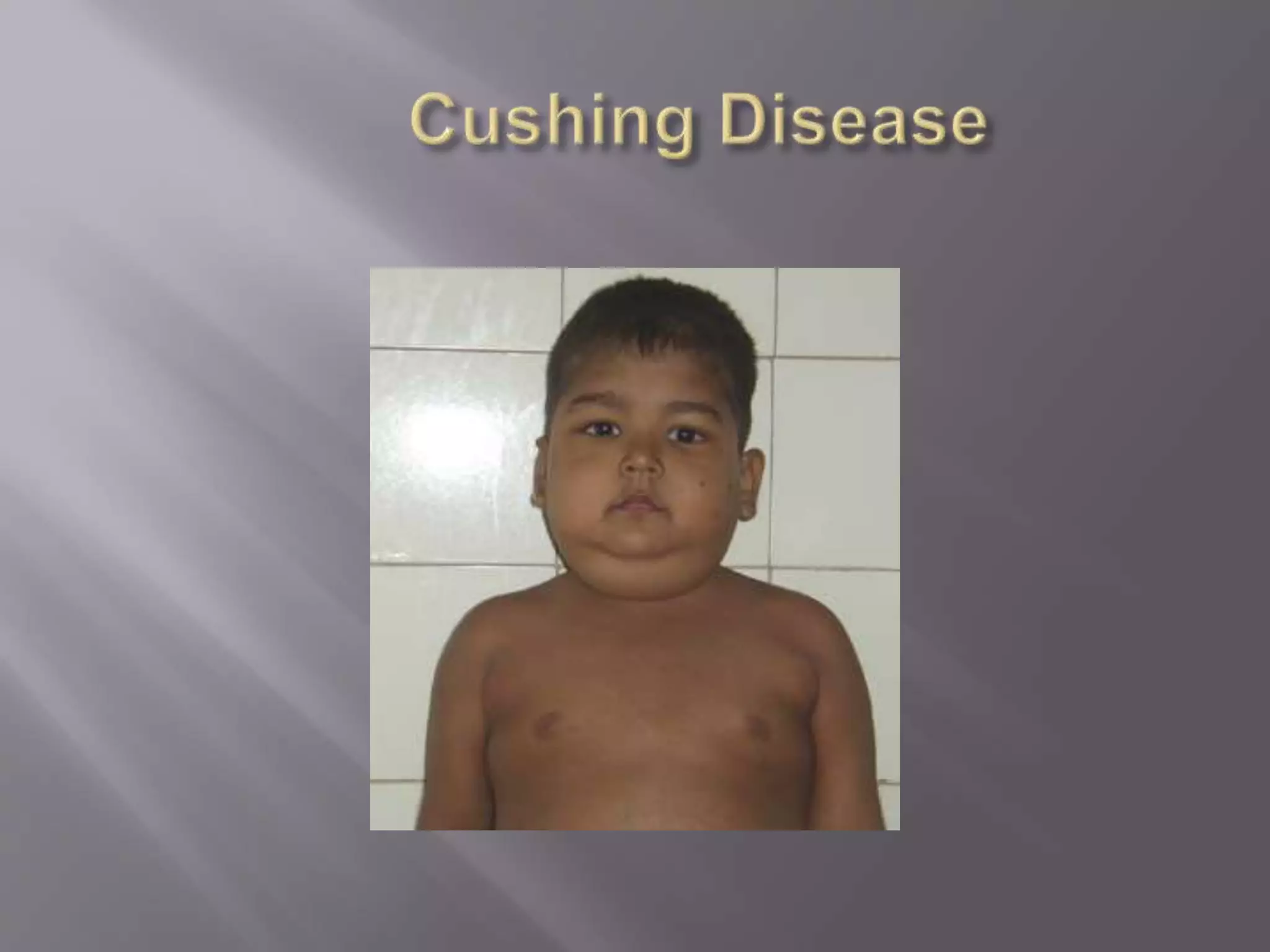
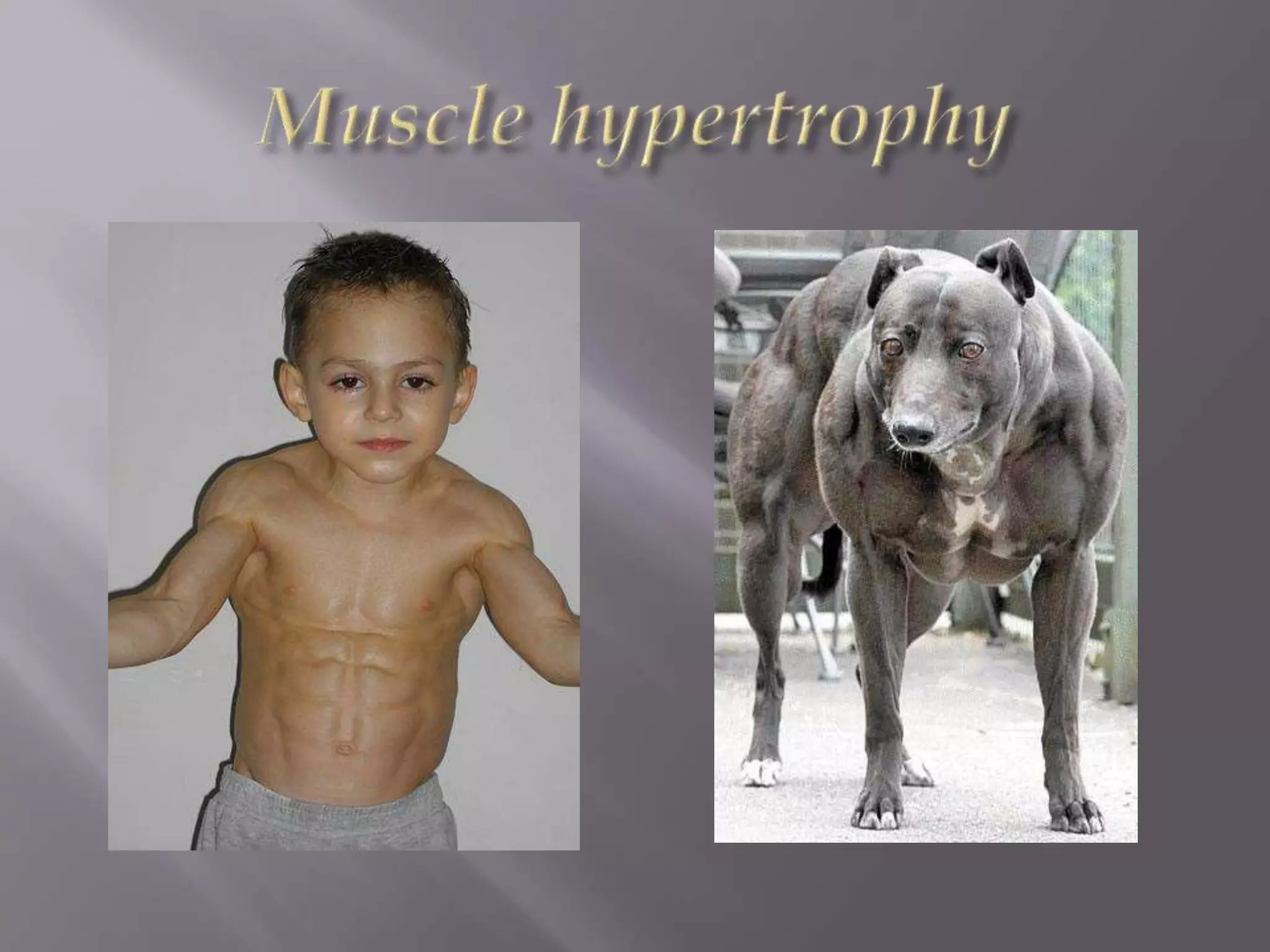
This document discusses hypertrophy and hyperplasia. Hypertrophy is an increase in the size of cells, while hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells. Some examples of hypertrophy and hyperplasia provided include muscle hypertrophy, cardiac hypertrophy, prostate hyperplasia, and endometrial hyperplasia. Causes, physiological vs pathological types, and treatments are described for selected conditions.