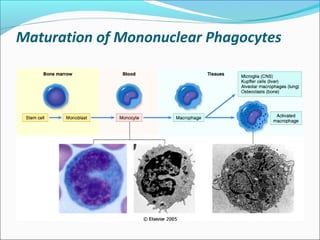
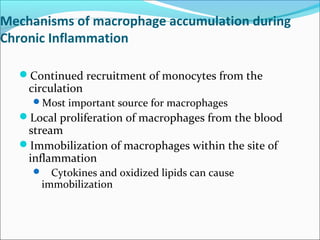
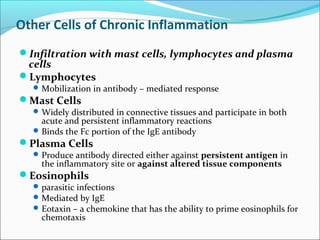
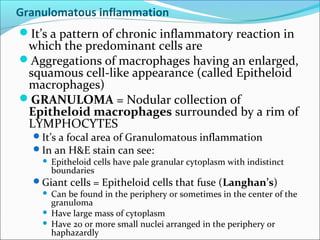
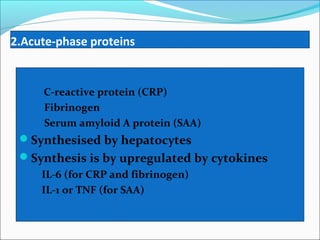
Chronic inflammation is inflammation of prolonged duration that involves ongoing active inflammation, tissue injury, and simultaneous healing. It can be caused by persistent infections, prolonged exposure to toxic agents, or autoimmunity. Morphologically, it is characterized by infiltration of mononuclear cells like macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells, as well as ongoing tissue destruction and attempts at repair through angiogenesis and fibrosis. Chronic inflammation involves recruitment and accumulation of macrophages from the blood and their activation, leading to effects like increased cytokine production. Other cells like mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils may also be present. Granulomatous inflammation features collections of macrophages that form granulomas. Chronic inflammation can also cause systemic effects through the acute