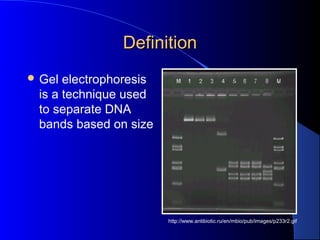
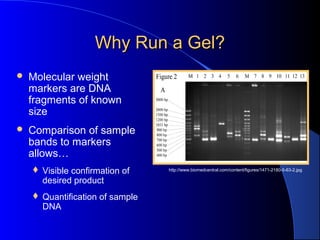
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments by size. DNA has a negative charge and will migrate toward the positive electrode in an agarose gel, with smaller fragments traveling farther than larger ones. Samples are run alongside a molecular weight marker to determine the size of fragments in the sample. After electrophoresis, DNA bands can be visualized under UV light by staining with ethidium bromide. Gel electrophoresis is used to analyze DNA, RNA, PCR products, and other biomolecules.