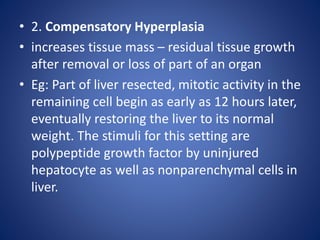
Hyperplasia is the enlargement of an organ due to an increased number of cells. There are two types of hyperplasia: physiological/compensatory and pathological. Physiological hyperplasia occurs as a normal response to hormonal or tissue loss stimuli, such as breast growth during pregnancy or liver regrowth after partial resection. Pathological hyperplasia results from excessive hormonal or growth factor stimulation and can lead to conditions like endometrial hyperplasia. Hyperplasia is caused by increased local growth factors, more growth factor receptors on cells, or activated cell signaling pathways, leading to increased cell proliferation.