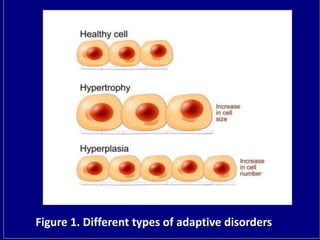
1. Adaptive disorders are changes cells undergo in response to physiological needs or pathological injury, including atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, and dysplasia.
2. Atrophy is a decrease in cell size and number, hypertrophy is an increase in cell size without a change in number, and hyperplasia is an increase in cell number.
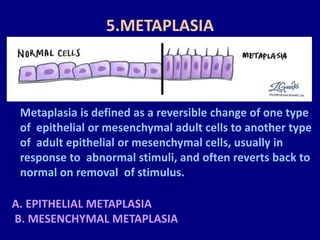
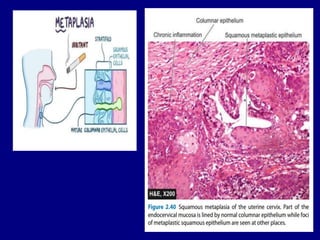
3. Metaplasia and dysplasia involve changes in cell type and abnormal cell development, respectively. Metaplasia is a reversible change from one adult cell type to another, while dysplasia shows disordered cell development and arrangement.