Hybridization
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
0 likes•1,730 views
Hybridization: Developed by Linus Pauling, the concept of hybrid orbitals was a theory created to explain the structures of molecules in space. The theory consists of combining atomic orbitals (ex: s,p,d,f) into new hybrid orbitals (ex: sp, sp2, sp3).
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Mot

It is about molecular orbital theory specially mo diagram of diatomic atoms,their bond orders,bond lengths and stability and experimental evidences of ionisation energy from PES.
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT)

A detailed presentation about what is MOT. Explaining its principles, sigma and pi bonds, bond order, and molecular stability. A good and knowledgeable presentation to understand these concepts.
Hybridization- sp, sp2 and sp3

Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals fuse to form newly hybridized orbitals, which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybridization is also an expansion of the valence bond theory.
Lattice energy

Concept of lattice energy and its significance along with the approaches to determine it.
Recommended
Mot

It is about molecular orbital theory specially mo diagram of diatomic atoms,their bond orders,bond lengths and stability and experimental evidences of ionisation energy from PES.
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT)

A detailed presentation about what is MOT. Explaining its principles, sigma and pi bonds, bond order, and molecular stability. A good and knowledgeable presentation to understand these concepts.
Hybridization- sp, sp2 and sp3

Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals fuse to form newly hybridized orbitals, which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybridization is also an expansion of the valence bond theory.
Lattice energy

Concept of lattice energy and its significance along with the approaches to determine it.
Vsepr theory

Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm
Hyperconjugation - organic chemistry

This presentation describes the concept of Hyperconjugation in simple words, gives definition of hyperconjugation, explains why it is called as 'No bond Resonance' and gives the effects of hyperconjugation on the chemical properties of compounds: alkyl cations and their relative stability, alkyl radicals and their relative stability, alkenes and their relative stability, bond length, anomeric effect and Baker - Nathan effect.
Unit 1.1(Molecular Orbital Theory)

Power point presentation according to AKTU syllabus of Engineering Chemistry
Aromaticity Antiaromaticity Non aromaticity

Aromaticity
Antiaromaticity
Non aromaticity
on slide share
Hybridization of orbitals, 11 (1)

A description of covalent bond formation in terms of atomic orbital overlap is called the valence-bond method
More Related Content
What's hot
Vsepr theory

Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm
Hyperconjugation - organic chemistry

This presentation describes the concept of Hyperconjugation in simple words, gives definition of hyperconjugation, explains why it is called as 'No bond Resonance' and gives the effects of hyperconjugation on the chemical properties of compounds: alkyl cations and their relative stability, alkyl radicals and their relative stability, alkenes and their relative stability, bond length, anomeric effect and Baker - Nathan effect.
Unit 1.1(Molecular Orbital Theory)

Power point presentation according to AKTU syllabus of Engineering Chemistry
Aromaticity Antiaromaticity Non aromaticity

Aromaticity
Antiaromaticity
Non aromaticity
on slide share
What's hot (20)
Similar to Hybridization
Hybridization of orbitals, 11 (1)

A description of covalent bond formation in terms of atomic orbital overlap is called the valence-bond method
In chemistry, hybridisation (or hybridization) is.pdf

In chemistry, hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic
orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for the qualitative description of atomic bonding
properties. Hybridised orbitals are very useful in the explanation of the shape of molecular
orbitals for molecules. It is an integral part of valence bond theory. Although sometimes taught
together with the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory, valence bond and
hybridization are in fact not related to the VSEPR model.[1] Contents [hide] 1 Historical
development 2 Types of hybridisation 2.1 sp3 hybrids 2.2 sp2 hybrids 2.3 sp hybrids 3
Hybridisation and molecule shape 3.1 Explanation of the shape of water 3.2 Controversy
regarding d-orbital participation 4 Hybridisation theory vs. MO theory 5 See also 6 External
links 7 References [edit]Historical development Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the
hybridisation theory in order to explain the structure of molecules such as methane (CH4).[2]
This concept was developed for such simple chemical systems, but the approach was later
applied more widely, and today it is considered an effective heuristic for rationalizing the
structures of organic compounds. For quantitative calculations of electronic structure and
molecular properties, hybridisation theory is not as practical as molecular orbital theory.
Problems with hybridisation are especially notable when the d orbitals are involved in bonding,
as in coordination chemistry and organometallic chemistry. Although hybridisation schemes in
transition metal chemistry can be used, they are not generally as accurate. Orbitals are a model
representation of the behaviour of electrons within molecules. In the case of simple
hybridisation, this approximation is based on atomic orbitals, similar to those obtained for the
hydrogen atom, the only atom for which an exact analytic solution to its Schrödinger equation is
known. In heavier atoms, like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, the atomic orbitals used are the 2s
and 2p orbitals, similar to excited state orbitals for hydrogen. Hybridised orbitals are assumed to
be mixtures of these atomic orbitals, superimposed on each other in various proportions. The
theory of hybridisation is most applicable under these assumptions. It gives a simple orbital
picture equivalent to Lewis structures. Hybridisation is not required to describe molecules, but
for molecules made up from carbon, nitrogen and oxygen (and to a lesser extent, sulfur and
phosphorus) the hybridisation theory/model makes the description much easier. The
hybridisation theory finds its use mainly in organic chemistry. Its explanation starts with the way
bonding is organized in methane. [edit]Types of hybridisation [edit]sp3 hybrids Hybridisation
describes the bonding atoms from an atom\'s point of view. That is, for a tetrahedrally
coordinated carbon (e.g., methane, CH4), the carbon should have 4 orbitals with the correct
symmetry to bond to the 4 hydrogen atoms. The .
Chapter 9 Lecture- Molecular Geometry

Chapter nine lecture for AP Chemistry on molecular geometries and bonding theories
Valence bond therory.pptx

Valence bond theory is one of the main basic theory of chemistry to know about the geometry of molecules and bonding
ATOICV1-1-3-Bent-Rule-and-Energetic-of-Hybridization.pptx

Bent's rule and energectic of hybridization helps us to understand the basic concept of geometry and hybridization
Similar to Hybridization (20)
In chemistry, hybridisation (or hybridization) is.pdf

In chemistry, hybridisation (or hybridization) is.pdf
Chapter-82-Advanced-Theories-of-Covalent-Bonding.ppt

Chapter-82-Advanced-Theories-of-Covalent-Bonding.ppt
ATOICV1-1-3-Bent-Rule-and-Energetic-of-Hybridization.pptx

ATOICV1-1-3-Bent-Rule-and-Energetic-of-Hybridization.pptx
More from Amjad Afridi
Hospital Infectious Materials Waste Management

Incineration is the method of choice for treating large volumes of infectious waste, animal carcasses, and contaminated bedding materials. Because incinerators usually are located some distance from the laboratory, additional precautions for handling and packaging of infectious waste are necessary.
Types of Biomedical Waste Disposal
Autoclaving. The process of autoclaving involves steam sterilization. ...
Incineration. The major benefits of incineration are that it is quick, easy, and simple. ...
Chemicals. When it comes to liquid waste, a common biomedical waste disposal method can be chemical disinfection. ...
Microwaving.
Introduction to the Management of Infectious MaterialsWaste.pptx

Infectious Medical Waste is defined as medical waste capable of producing an infectious disease.
Waste is considered Infectious when it is:
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 

Prokaryotes are always unicellular, while eukaryotes are often multi-celled organisms. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are more than 100 to 10,000 times larger than prokaryotic cells and are much more complex. The DNA in eukaryotes is stored within the nucleus, while DNA is stored in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes
Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.pptx

Eukaryotic cells have several other membrane-bound organelles not found in prokaryotic cells.
These include the mitochondria (convert food energy into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, to power biochemical reactions); rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum ,golgi complex and in the case of plant cells, chloroplasts
All of these organelles are located in the eukaryotic cell's cytoplasm.
Fungi

Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi.
The word 'myco' is derived from the Greek word mýkēs meaning “mushroom, fungus”.
Heinrich Anton de Bary is the father of Mycology.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include such as yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. These organisms are classified under kingdom fungi.
Fungi are diverse and widespread.
Fungal Metabolism.pptx

Fungi metabolism consists on a series of reactions (biochemical reactions) constantly occurring inside the cells to keep it alive and active and in the results biosynthesis of a huge number of compounds.
These compounds area usually divided into primary and secondary metabolites.
Primary metabolism is common to several species and usually produces compounds with the function of assuring fungi growth and development.
Primary metabolites are involved in the growth, development, and reproduction of organisms.
The primary metabolites consist of vitamins, amino acids, nucleosides and organic acids
Staphylococcus

Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that causes staphylococcal food poisoning, a form of gastroenteritis with rapid onset of symptoms. S. aureus is commonly found in the environment (soil, water and air) and is also found in the nose and on the skin of humans.
Communicable diseases.pptx

Communicable diseases are illnesses that spread from one person to another or from an animal to a person, or from a surface or a food. Diseases can be transmitted during air travel through: direct contact with a sick person. respiratory droplet spread from a sick person sneezing or coughing.
Host Parasite Relationship.pptx

Host-Parasite relationship is the extreme case of animal association, in which both partners influence each others life by affecting each others metabolism and behaviour using different adaptive mechanisms in order to ensure their survival.
Chemotherapy and Drug Resistance.pptx

Bacteria have their own enzymes for
1. Cell wall formation
2. Protein synthesis
3. DNA replication
4. RNA synthesis
5. Synthesis of essential metabolites
Zoonotic Infection.pptx

Infections spread from animals to human are called zoonotic infections.
The term zoonos is’ Derived from the Greek
ZOON (animals) and NOSES (diseases)
Pathogens shared with wild or domestic animals cause more than 60% of infectious diseases in man.
Ozone Layer.pptx

Ozone (O3) is a molecule made up of three atoms of oxygen (O), and very reactive gas.
Bluish gas that harmful to breathe.
Is mostly found in the stratosphere, where it protects us from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Although it represents only a tiny fraction of the atmosphere, ozone is essential for life on Earth.
Ozone in the stratosphere— a layer of the atmosphere between 15 and 50 kilometers (10 and 31 miles) above us—acts as a shield to protect Earth’s surface from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation.
HIV & AIDs.pptx

H: Infects only Human beings
I: Immunodeficiency Virus weakness the Immune system and increases the risk of infections
V: Virus that attacks the body and finally kills the body’s immune system
Tuberculosis.pptx

Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis , where the center of the granuloma is Caseous necrosis
It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the body
Airborne spread of droplet nuclei
Impact of Fungal Diseases.pptx

Economic Impact of Fungal Plant, Animal and Human Diseases and their Control
More from Amjad Afridi (20)
Introduction to the Management of Infectious MaterialsWaste.pptx

Introduction to the Management of Infectious MaterialsWaste.pptx
Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.pptx

Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.pptx
Recently uploaded
insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification

documents provide information about insect classification and taxonomy of insect
RNA INTERFERENCE: UNRAVELING GENETIC SILENCING

Introduction:
RNA interference (RNAi) or Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing (PTGS) is an important biological process for modulating eukaryotic gene expression.
It is highly conserved process of posttranscriptional gene silencing by which double stranded RNA (dsRNA) causes sequence-specific degradation of mRNA sequences.
dsRNA-induced gene silencing (RNAi) is reported in a wide range of eukaryotes ranging from worms, insects, mammals and plants.
This process mediates resistance to both endogenous parasitic and exogenous pathogenic nucleic acids, and regulates the expression of protein-coding genes.
What are small ncRNAs?
micro RNA (miRNA)
short interfering RNA (siRNA)
Properties of small non-coding RNA:
Involved in silencing mRNA transcripts.
Called “small” because they are usually only about 21-24 nucleotides long.
Synthesized by first cutting up longer precursor sequences (like the 61nt one that Lee discovered).
Silence an mRNA by base pairing with some sequence on the mRNA.
Discovery of siRNA?
The first small RNA:
In 1993 Rosalind Lee (Victor Ambros lab) was studying a non- coding gene in C. elegans, lin-4, that was involved in silencing of another gene, lin-14, at the appropriate time in the
development of the worm C. elegans.
Two small transcripts of lin-4 (22nt and 61nt) were found to be complementary to a sequence in the 3' UTR of lin-14.
Because lin-4 encoded no protein, she deduced that it must be these transcripts that are causing the silencing by RNA-RNA interactions.
Types of RNAi ( non coding RNA)
MiRNA
Length (23-25 nt)
Trans acting
Binds with target MRNA in mismatch
Translation inhibition
Si RNA
Length 21 nt.
Cis acting
Bind with target Mrna in perfect complementary sequence
Piwi-RNA
Length ; 25 to 36 nt.
Expressed in Germ Cells
Regulates trnasposomes activity
MECHANISM OF RNAI:
First the double-stranded RNA teams up with a protein complex named Dicer, which cuts the long RNA into short pieces.
Then another protein complex called RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex) discards one of the two RNA strands.
The RISC-docked, single-stranded RNA then pairs with the homologous mRNA and destroys it.
THE RISC COMPLEX:
RISC is large(>500kD) RNA multi- protein Binding complex which triggers MRNA degradation in response to MRNA
Unwinding of double stranded Si RNA by ATP independent Helicase
Active component of RISC is Ago proteins( ENDONUCLEASE) which cleave target MRNA.
DICER: endonuclease (RNase Family III)
Argonaute: Central Component of the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC)
One strand of the dsRNA produced by Dicer is retained in the RISC complex in association with Argonaute
ARGONAUTE PROTEIN :
1.PAZ(PIWI/Argonaute/ Zwille)- Recognition of target MRNA
2.PIWI (p-element induced wimpy Testis)- breaks Phosphodiester bond of mRNA.)RNAse H activity.
MiRNA:
The Double-stranded RNAs are naturally produced in eukaryotic cells during development, and they have a key role in regulating gene expression .
Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology

As consumer awareness of health and wellness rises, the nutraceutical market—which includes goods like functional meals, drinks, and dietary supplements that provide health advantages beyond basic nutrition—is growing significantly. As healthcare expenses rise, the population ages, and people want natural and preventative health solutions more and more, this industry is increasing quickly. Further driving market expansion are product formulation innovations and the use of cutting-edge technology for customized nutrition. With its worldwide reach, the nutraceutical industry is expected to keep growing and provide significant chances for research and investment in a number of categories, including vitamins, minerals, probiotics, and herbal supplements.
Deep Behavioral Phenotyping in Systems Neuroscience for Functional Atlasing a...

Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) provides means to characterize brain activations in response to behavior. However, cognitive neuroscience has been limited to group-level effects referring to the performance of specific tasks. To obtain the functional profile of elementary cognitive mechanisms, the combination of brain responses to many tasks is required. Yet, to date, both structural atlases and parcellation-based activations do not fully account for cognitive function and still present several limitations. Further, they do not adapt overall to individual characteristics. In this talk, I will give an account of deep-behavioral phenotyping strategies, namely data-driven methods in large task-fMRI datasets, to optimize functional brain-data collection and improve inference of effects-of-interest related to mental processes. Key to this approach is the employment of fast multi-functional paradigms rich on features that can be well parametrized and, consequently, facilitate the creation of psycho-physiological constructs to be modelled with imaging data. Particular emphasis will be given to music stimuli when studying high-order cognitive mechanisms, due to their ecological nature and quality to enable complex behavior compounded by discrete entities. I will also discuss how deep-behavioral phenotyping and individualized models applied to neuroimaging data can better account for the subject-specific organization of domain-general cognitive systems in the human brain. Finally, the accumulation of functional brain signatures brings the possibility to clarify relationships among tasks and create a univocal link between brain systems and mental functions through: (1) the development of ontologies proposing an organization of cognitive processes; and (2) brain-network taxonomies describing functional specialization. To this end, tools to improve commensurability in cognitive science are necessary, such as public repositories, ontology-based platforms and automated meta-analysis tools. I will thus discuss some brain-atlasing resources currently under development, and their applicability in cognitive as well as clinical neuroscience.
Nucleic Acid-its structural and functional complexity.

This presentation explores a brief idea about the structural and functional attributes of nucleotides, the structure and function of genetic materials along with the impact of UV rays and pH upon them.
extra-chromosomal-inheritance[1].pptx.pdfpdf![extra-chromosomal-inheritance[1].pptx.pdfpdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![extra-chromosomal-inheritance[1].pptx.pdfpdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Slide 1: Title Slide
Extrachromosomal Inheritance
Slide 2: Introduction to Extrachromosomal Inheritance
Definition: Extrachromosomal inheritance refers to the transmission of genetic material that is not found within the nucleus.
Key Components: Involves genes located in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and plasmids.
Slide 3: Mitochondrial Inheritance
Mitochondria: Organelles responsible for energy production.
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA): Circular DNA molecule found in mitochondria.
Inheritance Pattern: Maternally inherited, meaning it is passed from mothers to all their offspring.
Diseases: Examples include Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) and mitochondrial myopathy.
Slide 4: Chloroplast Inheritance
Chloroplasts: Organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plants.
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA): Circular DNA molecule found in chloroplasts.
Inheritance Pattern: Often maternally inherited in most plants, but can vary in some species.
Examples: Variegation in plants, where leaf color patterns are determined by chloroplast DNA.
Slide 5: Plasmid Inheritance
Plasmids: Small, circular DNA molecules found in bacteria and some eukaryotes.
Features: Can carry antibiotic resistance genes and can be transferred between cells through processes like conjugation.
Significance: Important in biotechnology for gene cloning and genetic engineering.
Slide 6: Mechanisms of Extrachromosomal Inheritance
Non-Mendelian Patterns: Do not follow Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
Cytoplasmic Segregation: During cell division, organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts are randomly distributed to daughter cells.
Heteroplasmy: Presence of more than one type of organellar genome within a cell, leading to variation in expression.
Slide 7: Examples of Extrachromosomal Inheritance
Four O’clock Plant (Mirabilis jalapa): Shows variegated leaves due to different cpDNA in leaf cells.
Petite Mutants in Yeast: Result from mutations in mitochondrial DNA affecting respiration.
Slide 8: Importance of Extrachromosomal Inheritance
Evolution: Provides insight into the evolution of eukaryotic cells.
Medicine: Understanding mitochondrial inheritance helps in diagnosing and treating mitochondrial diseases.
Agriculture: Chloroplast inheritance can be used in plant breeding and genetic modification.
Slide 9: Recent Research and Advances
Gene Editing: Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 are being used to edit mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA.
Therapies: Development of mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT) for preventing mitochondrial diseases.
Slide 10: Conclusion
Summary: Extrachromosomal inheritance involves the transmission of genetic material outside the nucleus and plays a crucial role in genetics, medicine, and biotechnology.
Future Directions: Continued research and technological advancements hold promise for new treatments and applications.
Slide 11: Questions and Discussion
Invite Audience: Open the floor for any questions or further discussion on the topic.
Comparing Evolved Extractive Text Summary Scores of Bidirectional Encoder Rep...

Comparing Evolved Extractive Text Summary Scores of Bidirectional Encoder Rep...University of Maribor
Slides from:
11th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (IcETRAN), Niš, 3-6 June 2024
Track: Artificial Intelligence
https://www.etran.rs/2024/en/home-english/Richard's aventures in two entangled wonderlands

Since the loophole-free Bell experiments of 2020 and the Nobel prizes in physics of 2022, critics of Bell's work have retreated to the fortress of super-determinism. Now, super-determinism is a derogatory word - it just means "determinism". Palmer, Hance and Hossenfelder argue that quantum mechanics and determinism are not incompatible, using a sophisticated mathematical construction based on a subtle thinning of allowed states and measurements in quantum mechanics, such that what is left appears to make Bell's argument fail, without altering the empirical predictions of quantum mechanics. I think however that it is a smoke screen, and the slogan "lost in math" comes to my mind. I will discuss some other recent disproofs of Bell's theorem using the language of causality based on causal graphs. Causal thinking is also central to law and justice. I will mention surprising connections to my work on serial killer nurse cases, in particular the Dutch case of Lucia de Berk and the current UK case of Lucy Letby.
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Article written for leader telegram
Comparative structure of adrenal gland in vertebrates

Adrenal gland comparative structures in vertebrates
filosofia boliviana introducción jsjdjd.pptx

La filosofía boliviana y la búsqueda por construir pensamientos propios
Richard's entangled aventures in wonderland

Since the loophole-free Bell experiments of 2020 and the Nobel prizes in physics of 2022, critics of Bell's work have retreated to the fortress of super-determinism. Now, super-determinism is a derogatory word - it just means "determinism". Palmer, Hance and Hossenfelder argue that quantum mechanics and determinism are not incompatible, using a sophisticated mathematical construction based on a subtle thinning of allowed states and measurements in quantum mechanics, such that what is left appears to make Bell's argument fail, without altering the empirical predictions of quantum mechanics. I think however that it is a smoke screen, and the slogan "lost in math" comes to my mind. I will discuss some other recent disproofs of Bell's theorem using the language of causality based on causal graphs. Causal thinking is also central to law and justice. I will mention surprising connections to my work on serial killer nurse cases, in particular the Dutch case of Lucia de Berk and the current UK case of Lucy Letby.
Recently uploaded (20)
insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification

insect taxonomy importance systematics and classification
Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions

Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions
Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology

Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology
Deep Behavioral Phenotyping in Systems Neuroscience for Functional Atlasing a...

Deep Behavioral Phenotyping in Systems Neuroscience for Functional Atlasing a...
Nucleic Acid-its structural and functional complexity.

Nucleic Acid-its structural and functional complexity.
Comparing Evolved Extractive Text Summary Scores of Bidirectional Encoder Rep...

Comparing Evolved Extractive Text Summary Scores of Bidirectional Encoder Rep...
In silico drugs analogue design: novobiocin analogues.pptx

In silico drugs analogue design: novobiocin analogues.pptx
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...
Comparative structure of adrenal gland in vertebrates

Comparative structure of adrenal gland in vertebrates
Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx

Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx
Hybridization
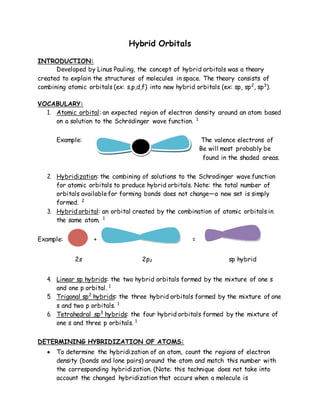
- 1. INTRODUCTION: Hybrid Orbitals Developed by Linus Pauling, the concept of hybrid orbitals was a theory created to explain the structures of molecules in space. The theory consists of combining atomic orbitals (ex: s,p,d,f) into new hybrid orbitals (ex: sp, sp2 , sp3 ). VOCABULARY: 1. Atomic orbital: an expected region of electron density around an atom based on a solution to the Schrödinger wave function. 1 Example: The valence electrons of Be will most probably be found in the shaded areas. 2. Hybridization: the combining of solutions to the Schrodinger wave function for atomic orbitals to produce hybrid orbitals. Note: the total number of orbitals availablefor forming bonds does not change—a new set is simply formed. 2 3. Hybrid orbital: an orbital created by the combination of atomic orbitals in the same atom. 1 Example: + = 2s 2pz sp hybrid 4. Linear sp hybrids: the two hybrid orbitals formed by the mixture of one s and one p orbital. 1 5. Trigonal sp2 hybrids: the three hybrid orbitals formed by the mixture of one s and two p orbitals. 1 6. Tetrahedral sp3 hybrids: the four hybrid orbitals formed by the mixture of one s and three p orbitals. 1 DETERMINING HYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMS: To determine the hybridization of an atom, count the regions of electron density (bonds and lone pairs) around the atom and match this number with the corresponding hybridization. (Note: this technique does not take into account the changed hybridization that occurs when a molecule is
- 2. conjugated—this will be discussed under “Note on Conjugation and Hybridization,” because it must always be taken into account to identify the more accurate hybridization) o An sp hybridized atom has two regions of electron density - Consider the carbon atom of HCN: H C N: It is important to note that a double or triple bond only counts as ONE region of electron density; the carbon of the HCN therefore has two regions of electron density. o An sp2 hybridized atom has three regions of electron density: Consider the sulfur of SO2 o An sp3 hybridized atom has four regions of electron density: Consider the oxygen atom of water o This same pattern applies for the hybrid orbitals containing d orbitals (dsp3 , d2 sp3 ), but organic chemistry focuses on carbon, which is limited to four bonds/regions of electron density. DETERMINING GEOMETRY: Geometry determines hybridization; the geometry of a molecule will be the most energetically favorable arrangement, and this geometry will cause hybridization to accommodate the correct shape.
- 3. sp hybrids: Linear Structures: o sp hybrids share characteristics evenly between s and p orbitals. The other unhybridized p orbitals remain the same. The front lobes of the sp orbitals point in opposite directions (at 180°). The back lobes also point in opposite directions. A linear structure is created. o In general: The overlap of the lobes of atoms creates bonds; large front lobes overlap more completely, resulting in a relatively stronger bond. sp2 hybrids: Trigonal Structures: o The small amount of energy needed to promote an electron from the 2s to one of the 2p levels is compensated by bond formation. The three filled atomic orbitals mix to form three sp2 orbitals—each is of 33% s character and 67% p character. The last p orbital stays the same. The front lobes (and their corresponding back lobes) face in opposite directions (at 120° from each other). Electron repulsion therefore creates a trigonal planar geometry. sp3 hybrids: Tetrahedral structures: o The 2s orbital is mixed with all three of the 2p orbitals, creating four hybridized sp3 orbitals. Each of these has 25% s and 75% p character; electron repulsion favors a tetrahedral shape, so the orbitals are 109.5° apart from each other. 2pz o Hybrid orbitals can overlap with any atomic orbital of a different atom to form a bond; this is seen with the substitution of a chlorine atom in place
- 4. : : . . of a hydrogen atom on methane. They may also contain lone pairs—this explains the geometry of water, which is sp3 hybridized due to the lone pair, which occupies one of the four hybrid orbitals. Again, the bond angle is slightly distorted due to the electron repulsion of this lone pair. o Bond angles are distorted because of these changes; typical bond angles of certain hybridization are often increased or decreased due to the relative electronegativities of atoms on a molecule. Note on Conjugation and Hybridization: To accommodate resonance, the hybridization of an atom may change. This change will occur due to the movement of a lone pair into a p orbital, and must be taken into consideration when determining the hybridization of atoms in a molecule. Hybridization will change if: o The atom is surrounded by two or more adjacent p orbitals. o The atom has a lone pair to move into a p orbital. Amide molecule—nitrogen looks sp3 hybridized but it is sp2 because of conjugation (lone pair goes into a p orbital to have three adjacent, parallel p orbitals).
