1. Localized bonds involve electron density concentrated between two nuclei, while delocalized bonds involve electron density spread across multiple nuclei.
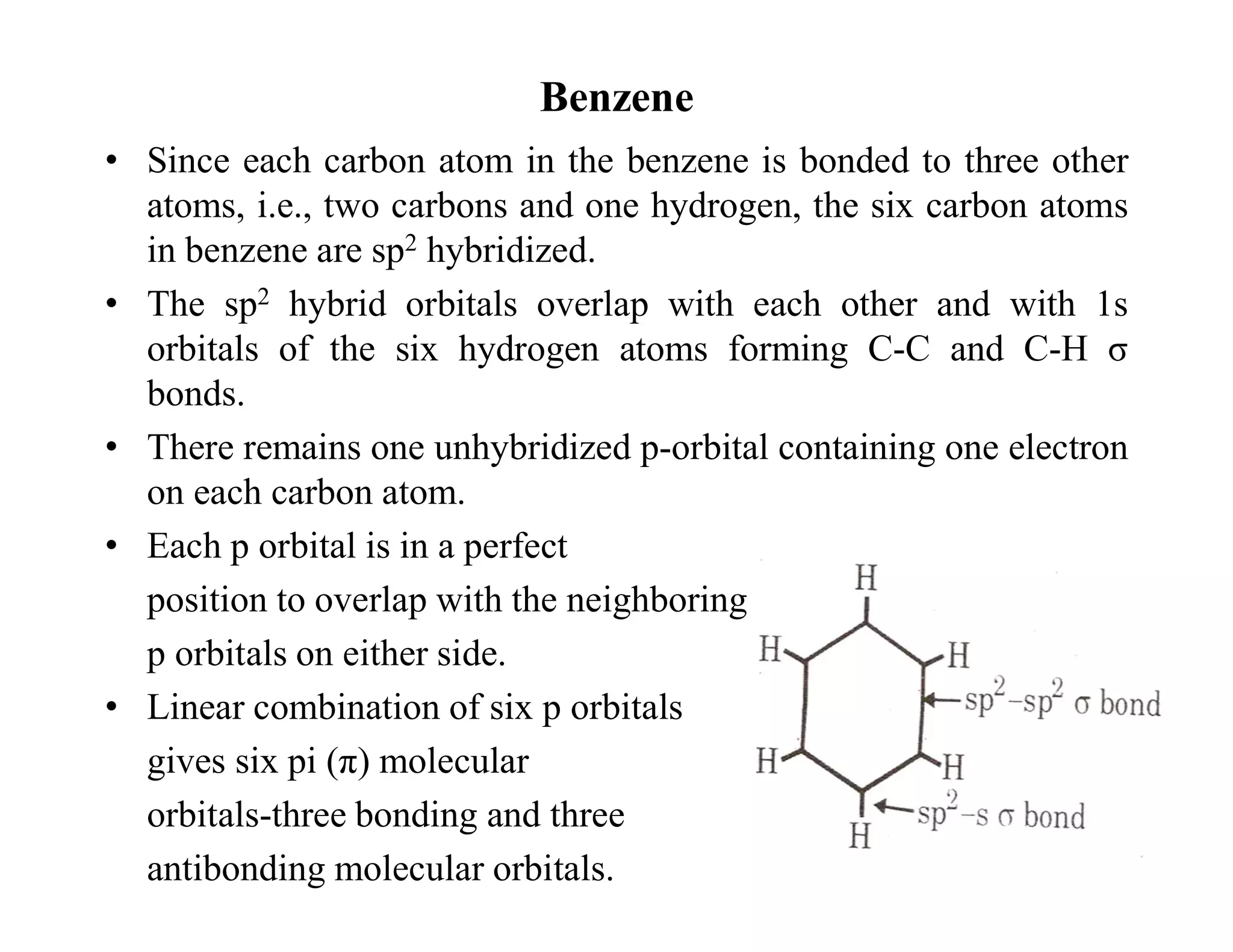
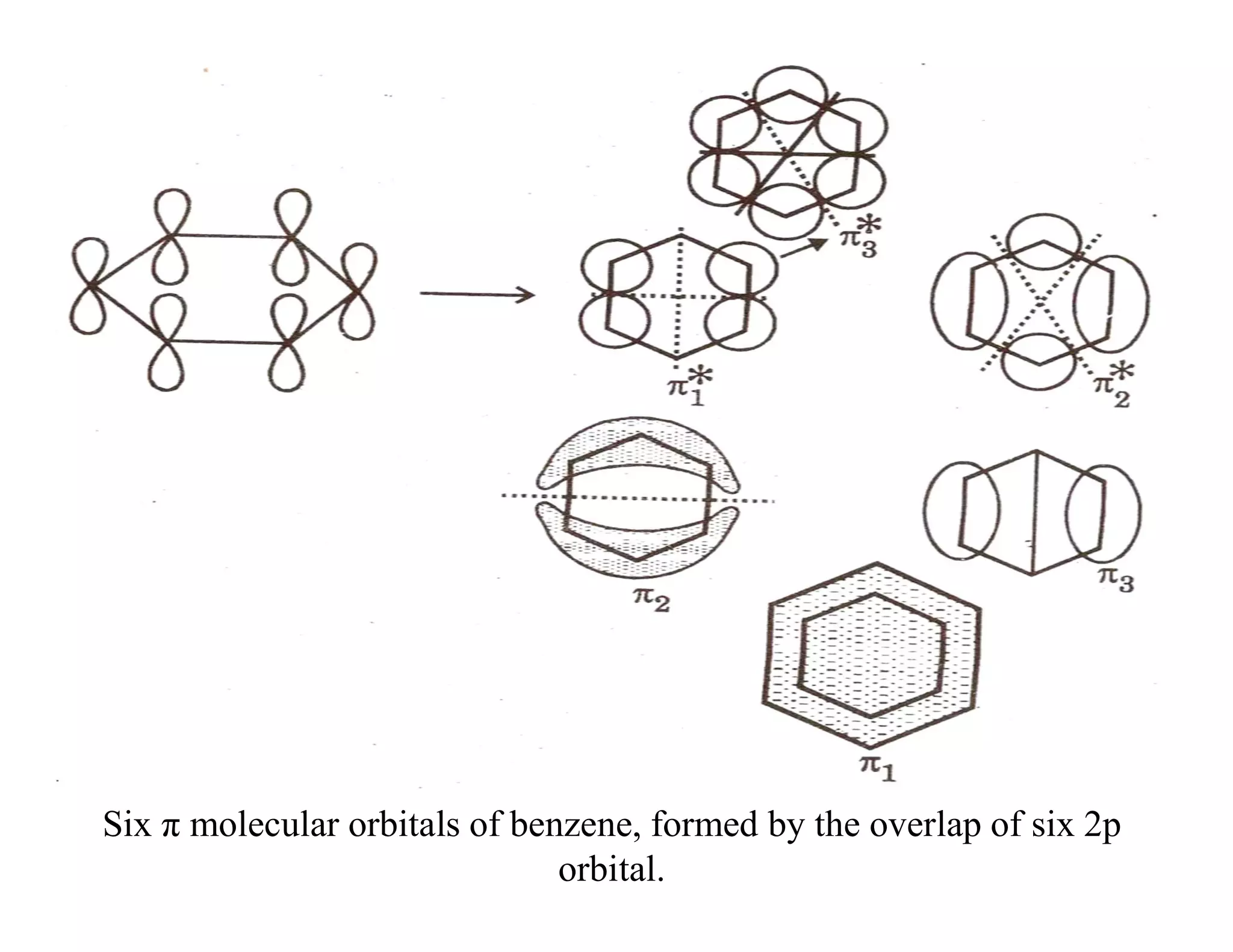
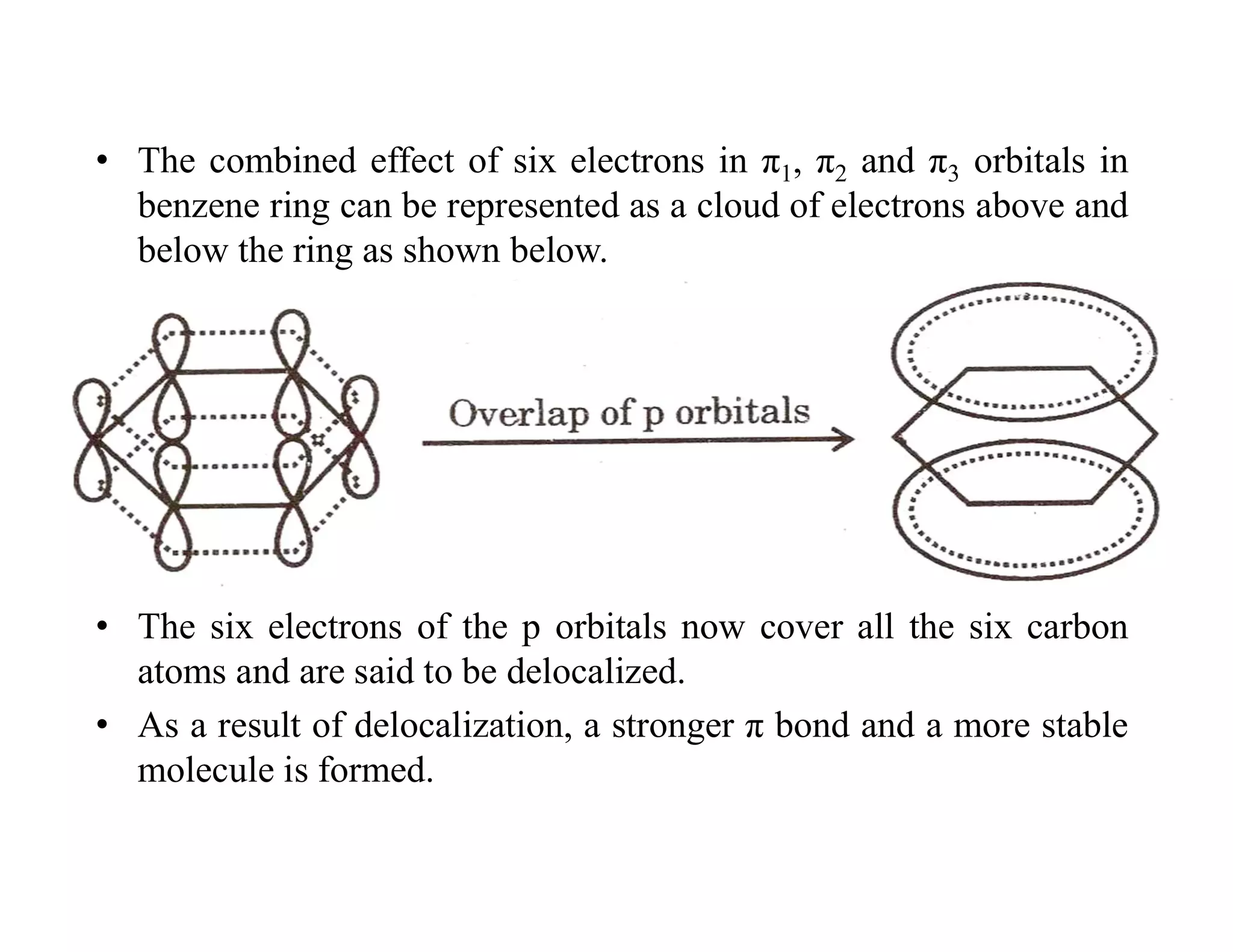
2. Conjugated systems have alternating single and multiple bonds, allowing p-orbitals to overlap and form delocalized molecular orbitals spread across multiple atoms. This delocalization increases stability.
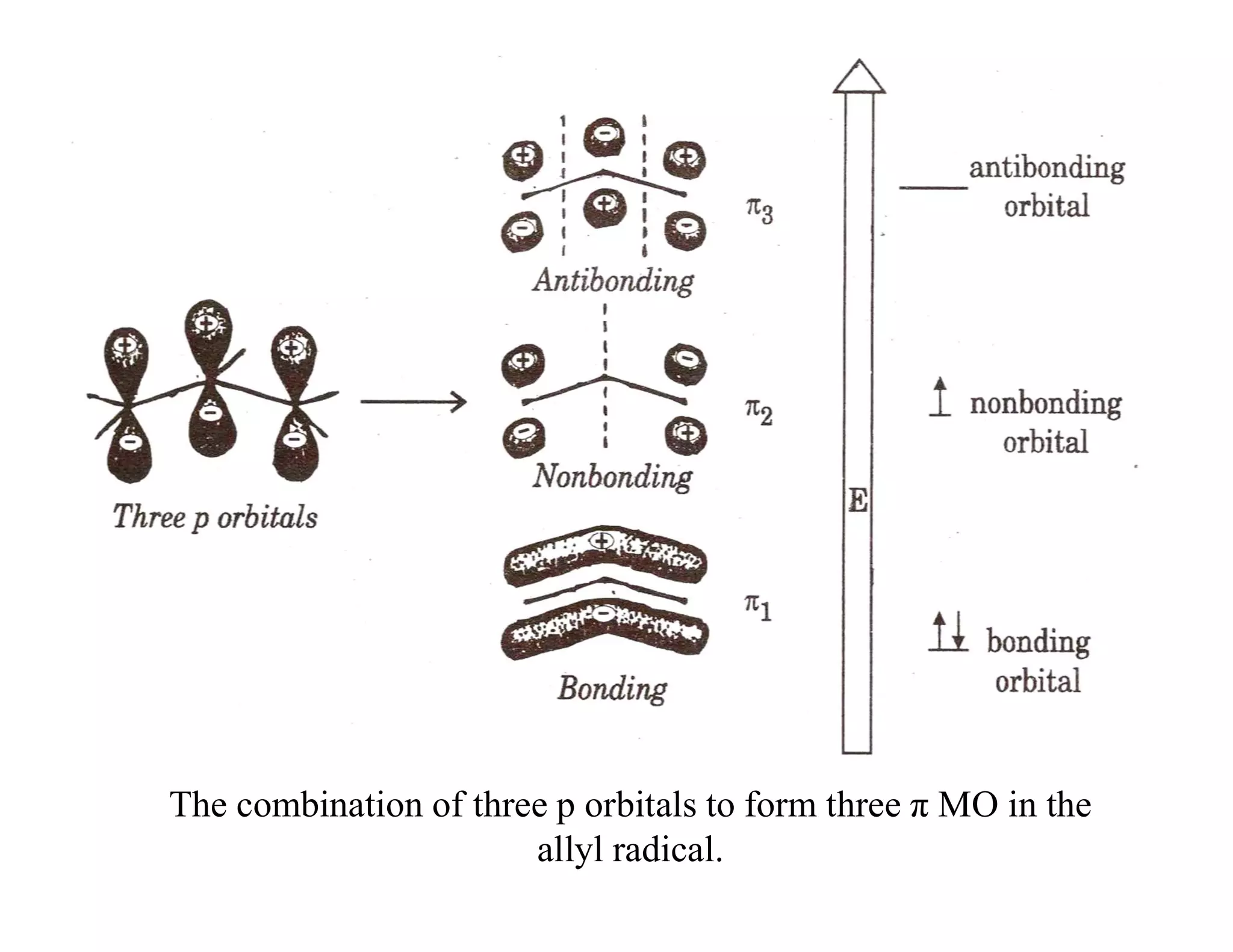
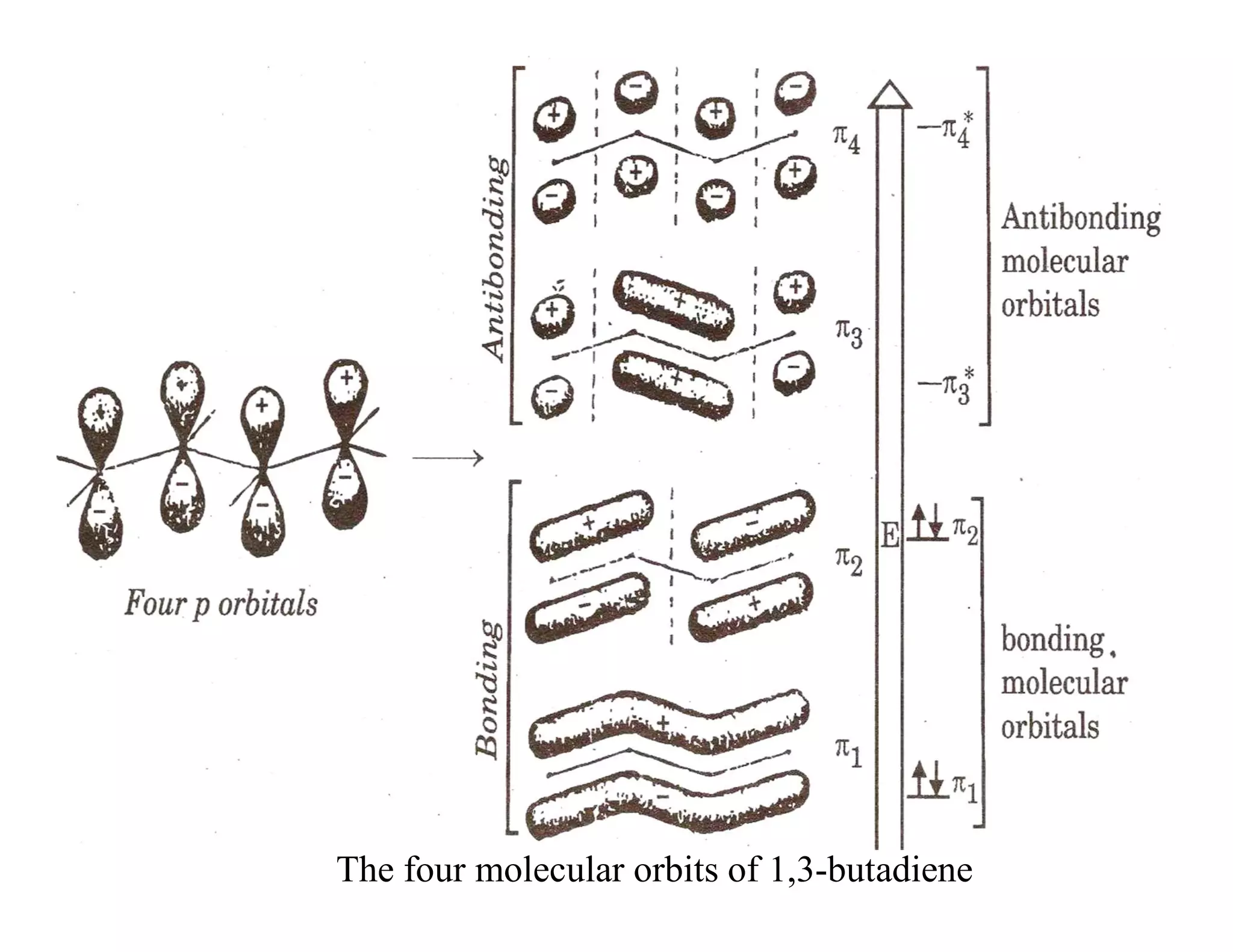
3. Examples given include the allyl radical and cation, which have three p-orbitals overlapping to form bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals delocalized across all three carbons. 1,3-Butadiene also has four overlapping p-orbitals forming delocalized molecular orbitals.