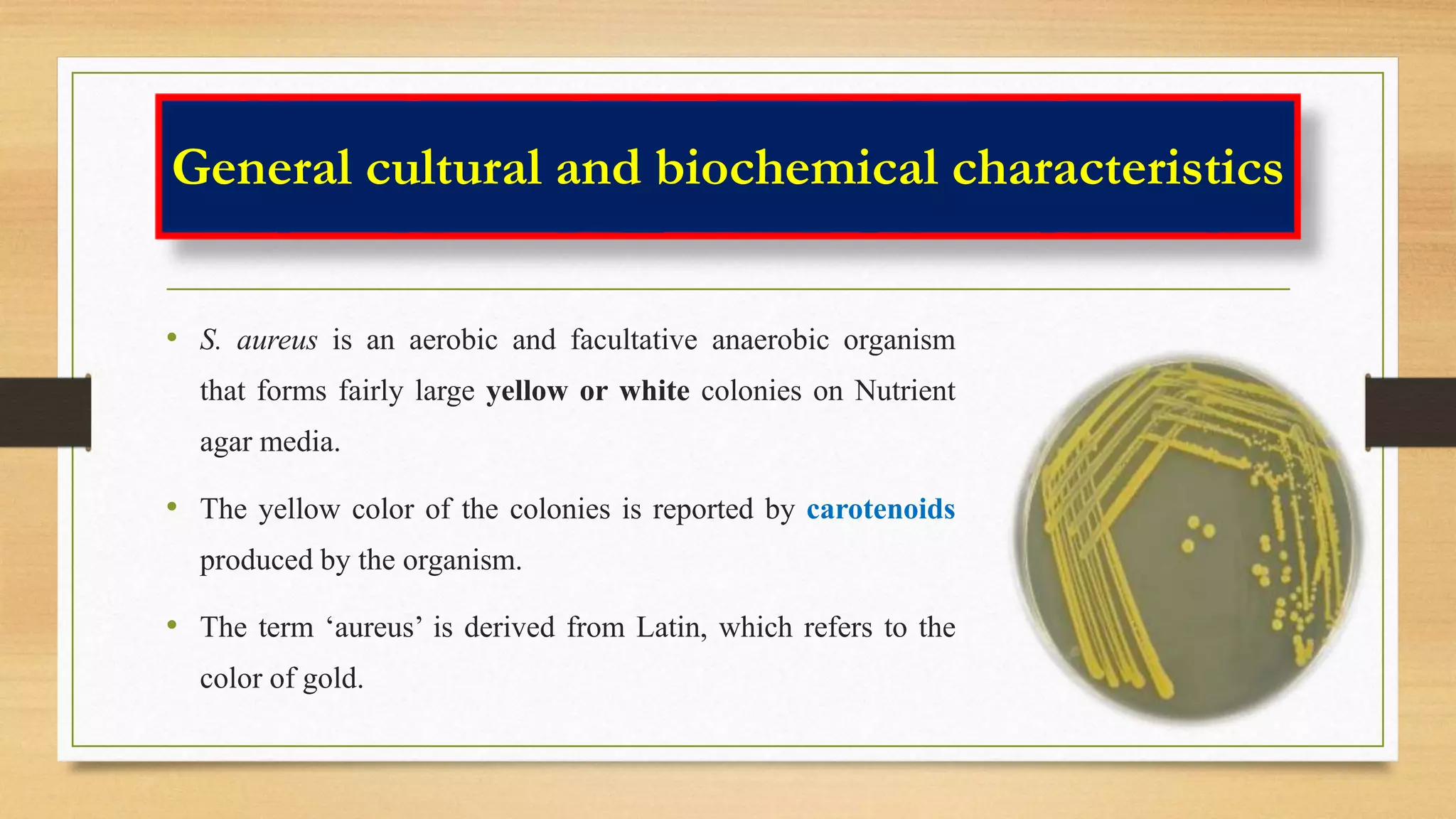
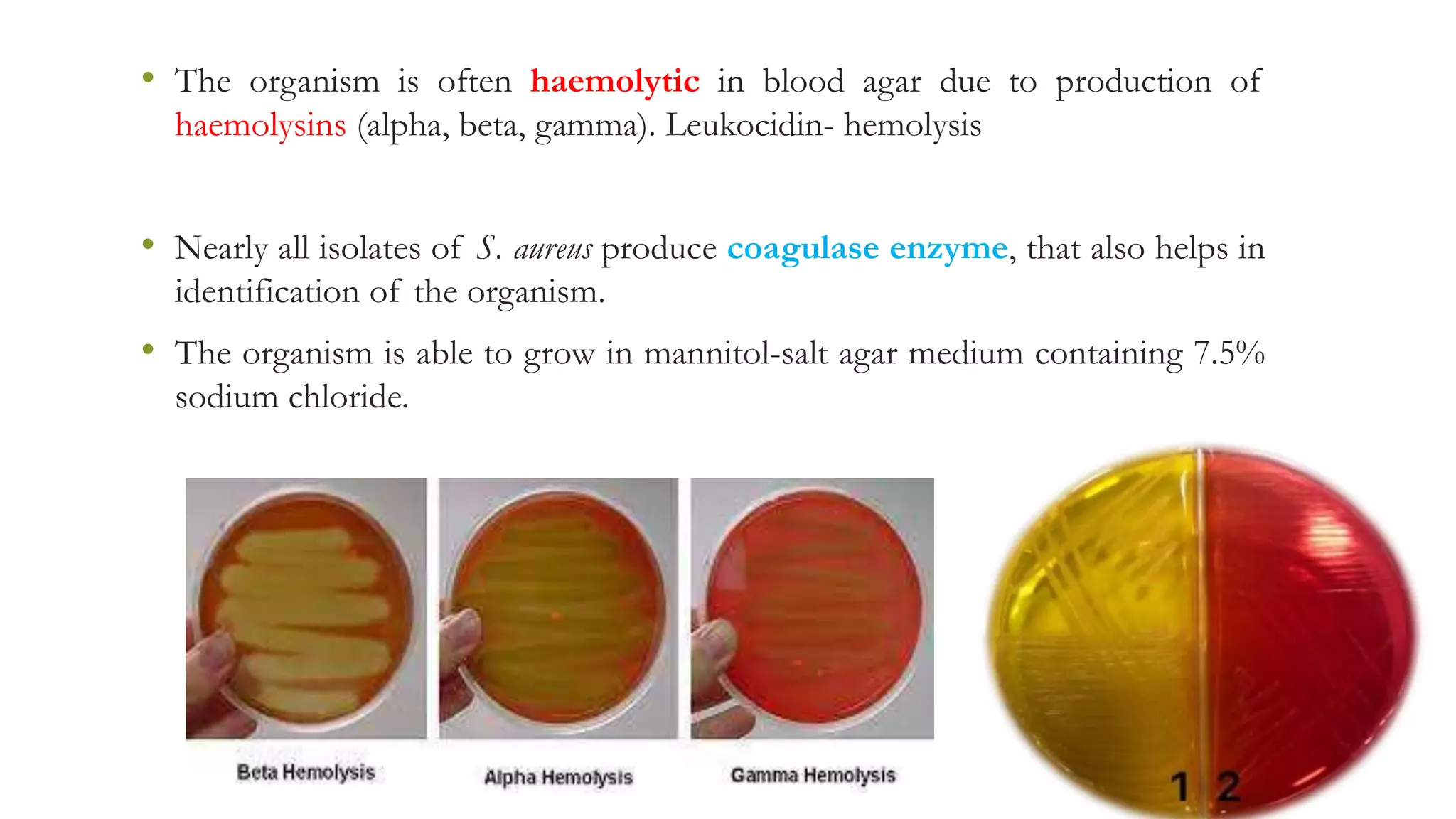
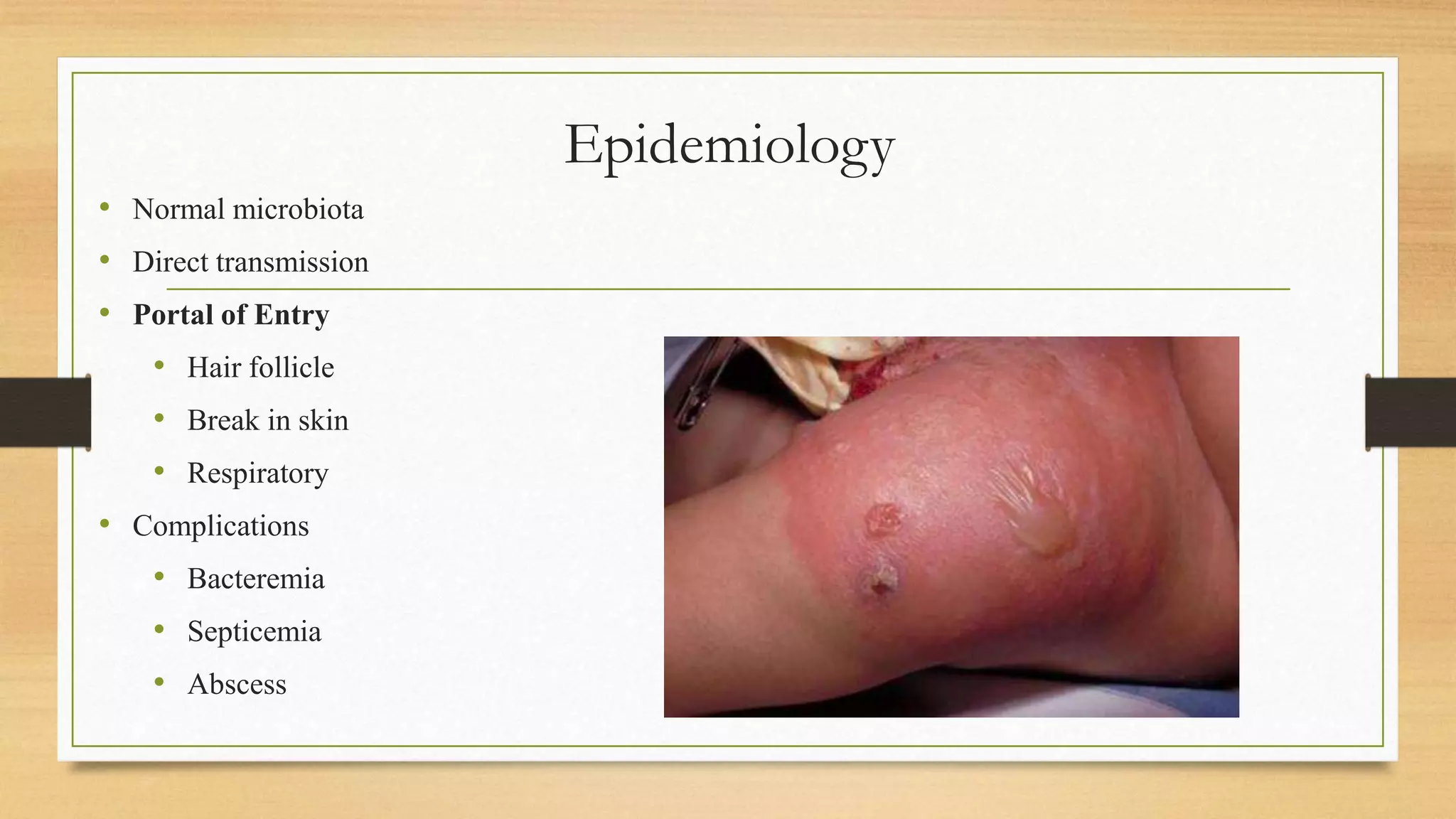
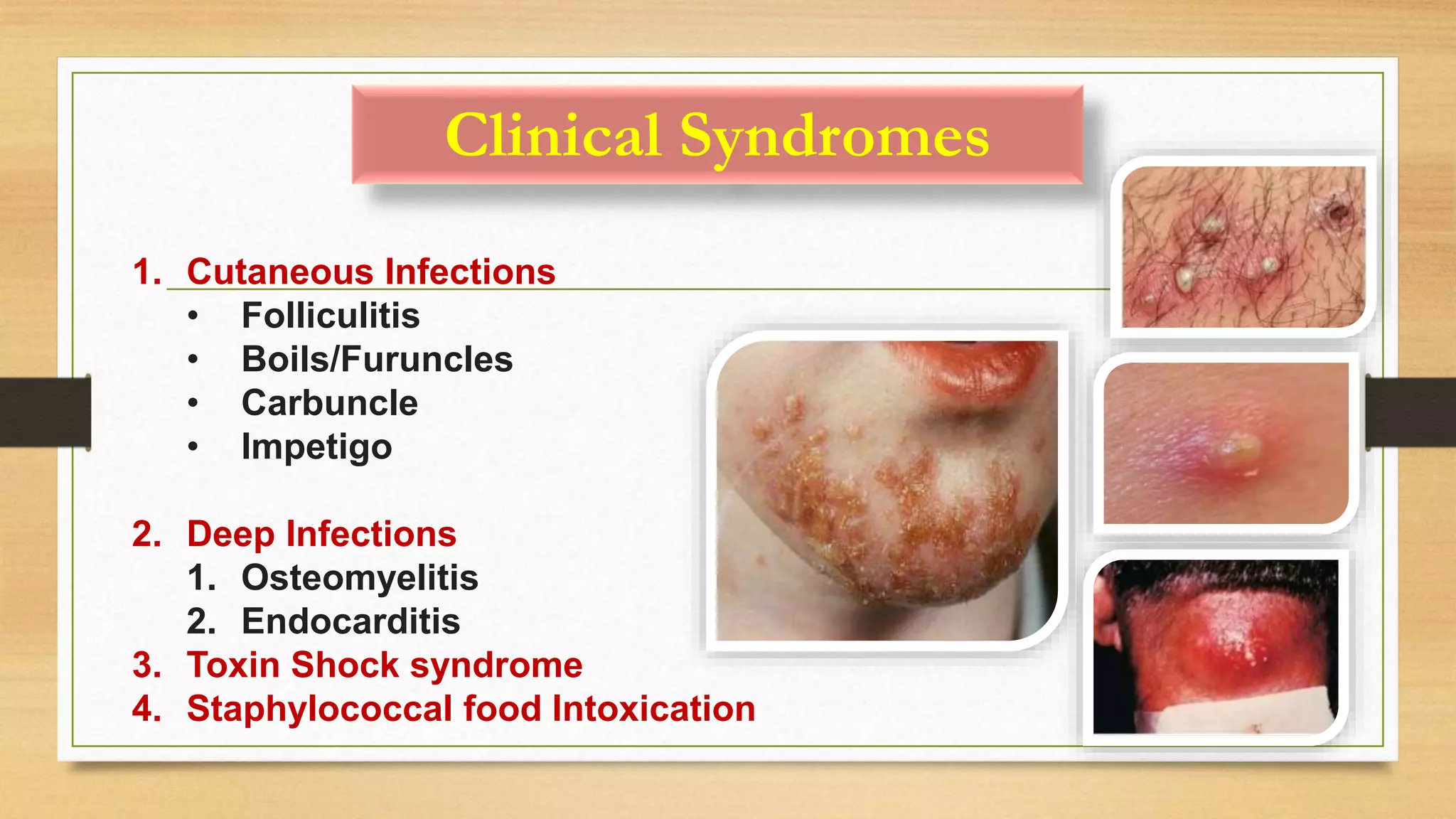
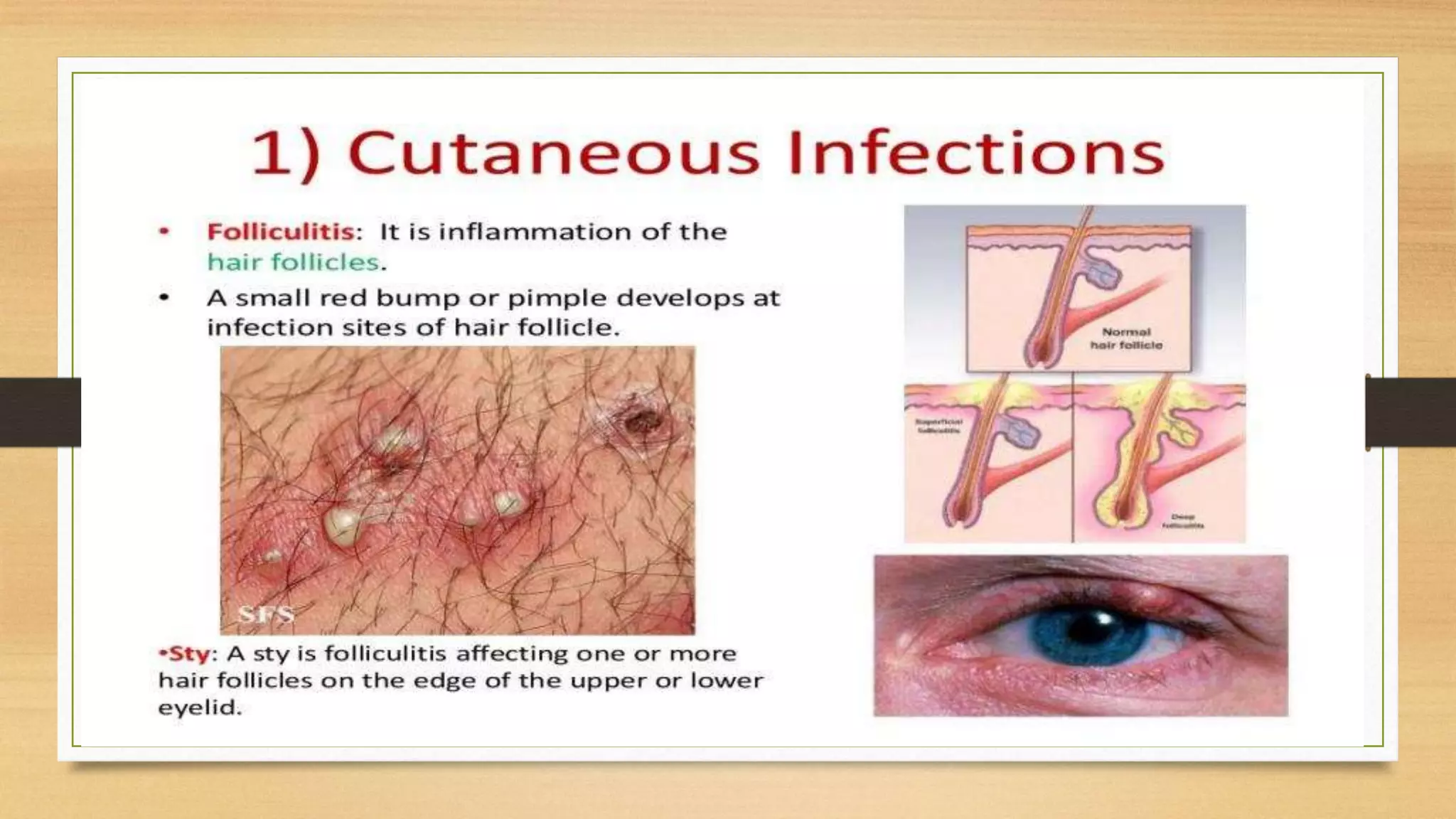
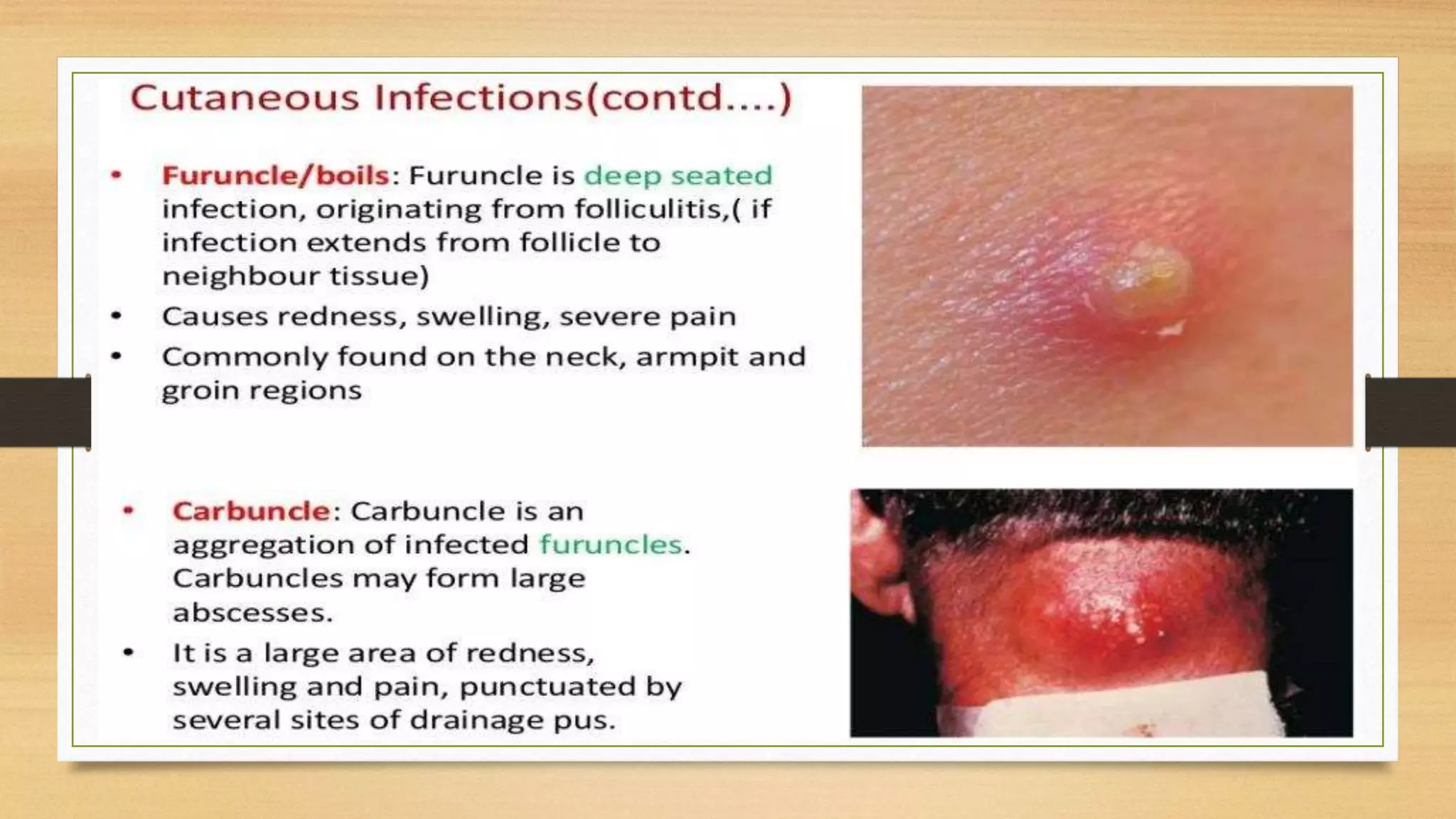
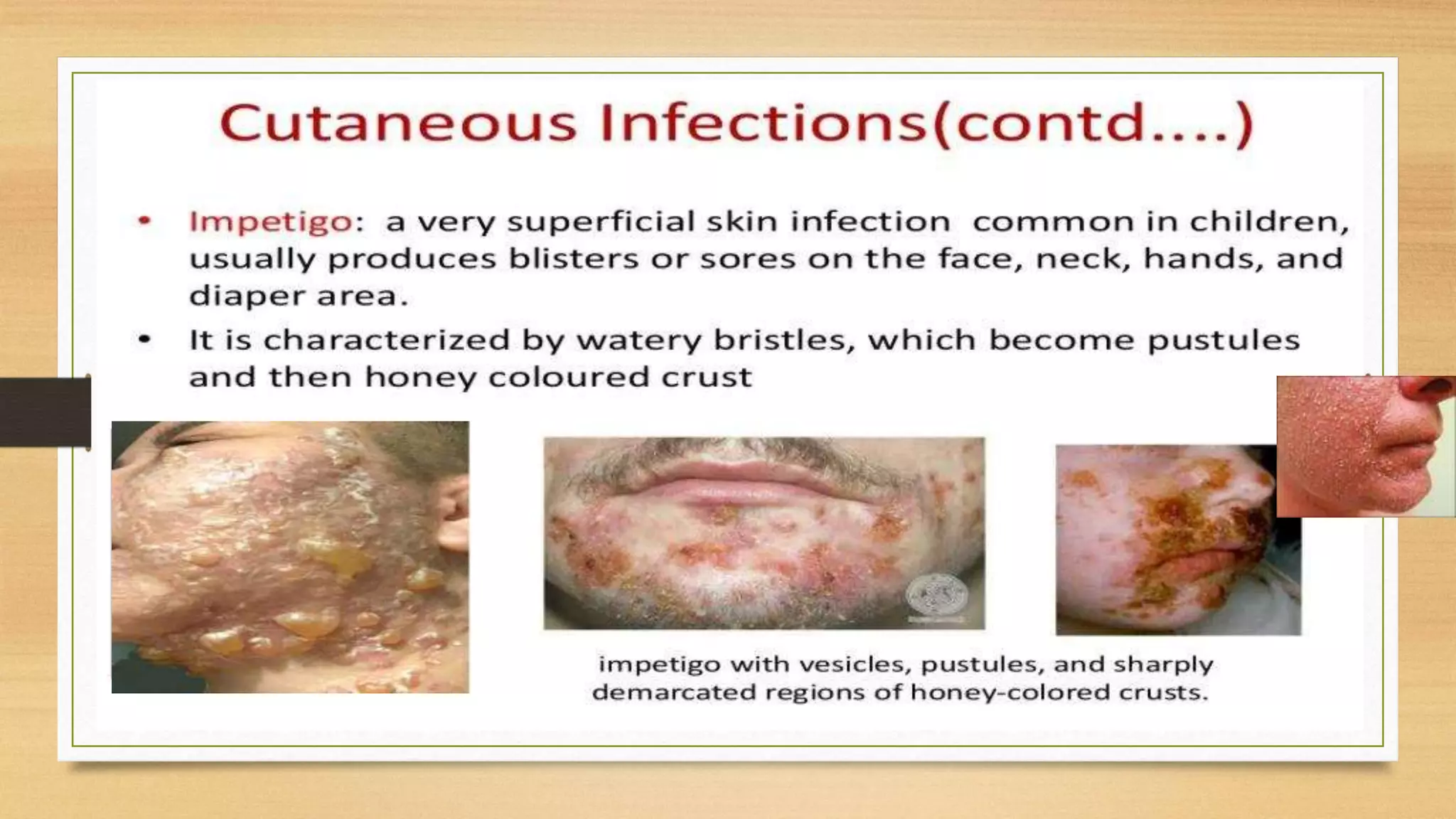
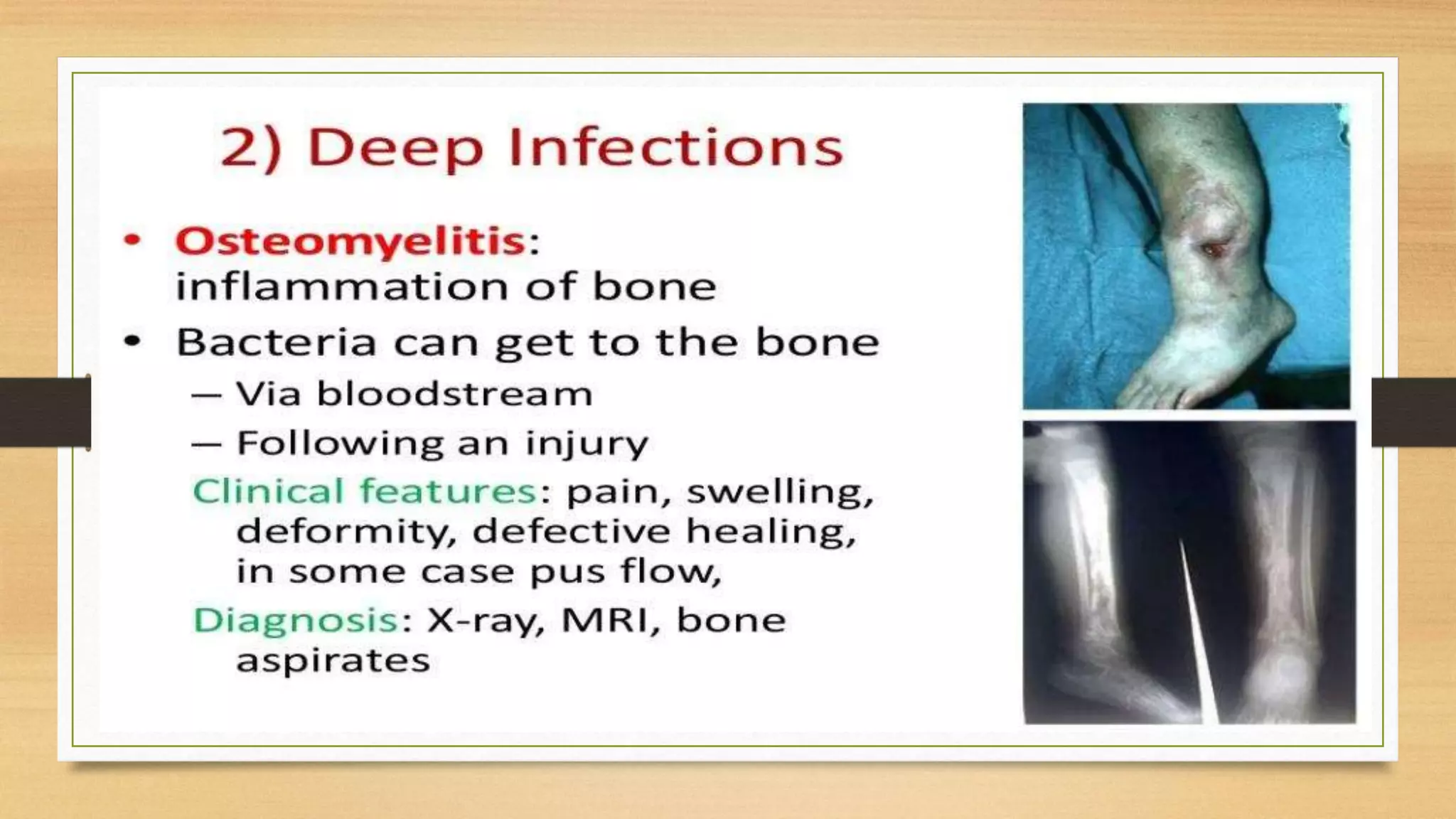
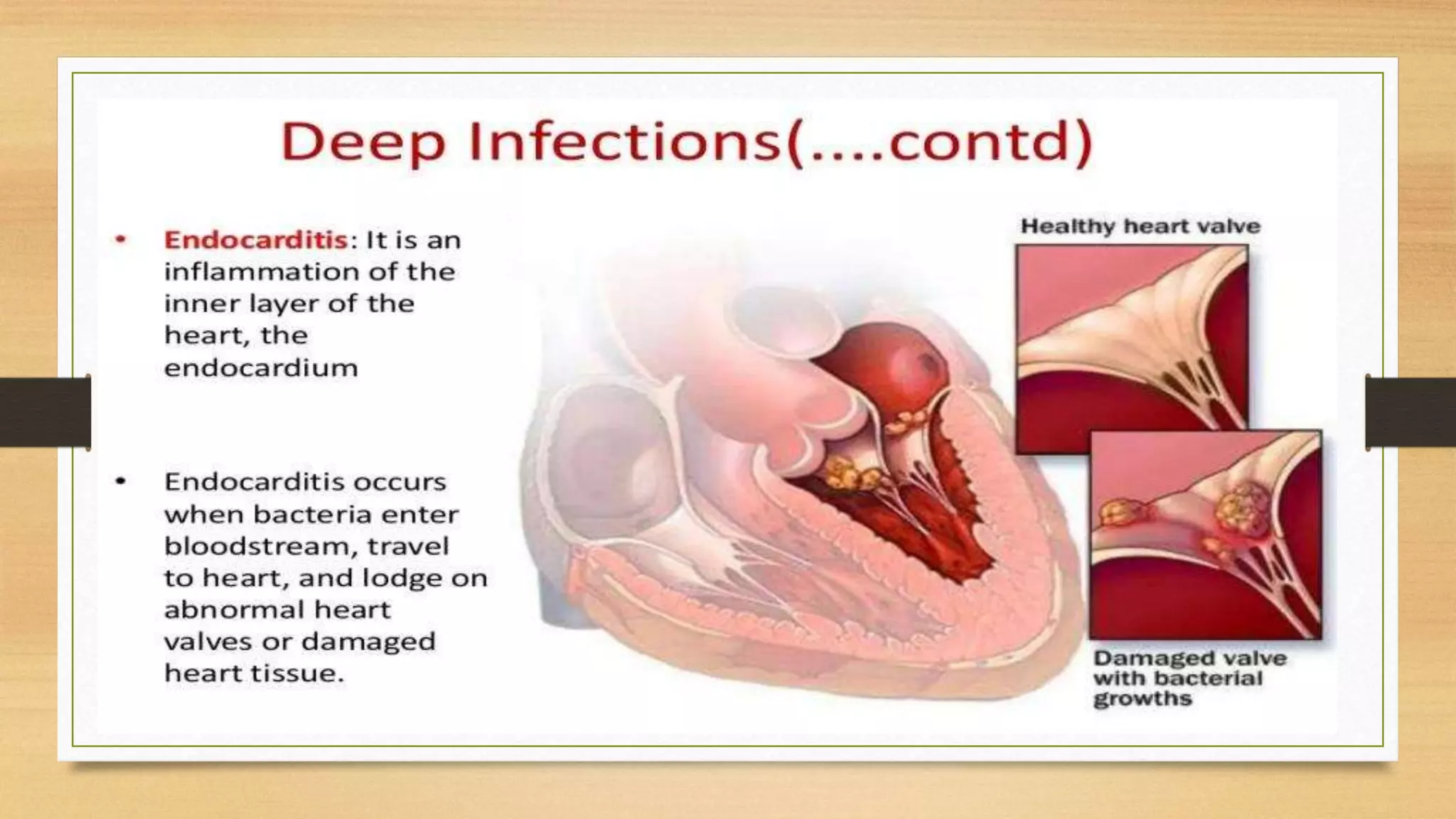
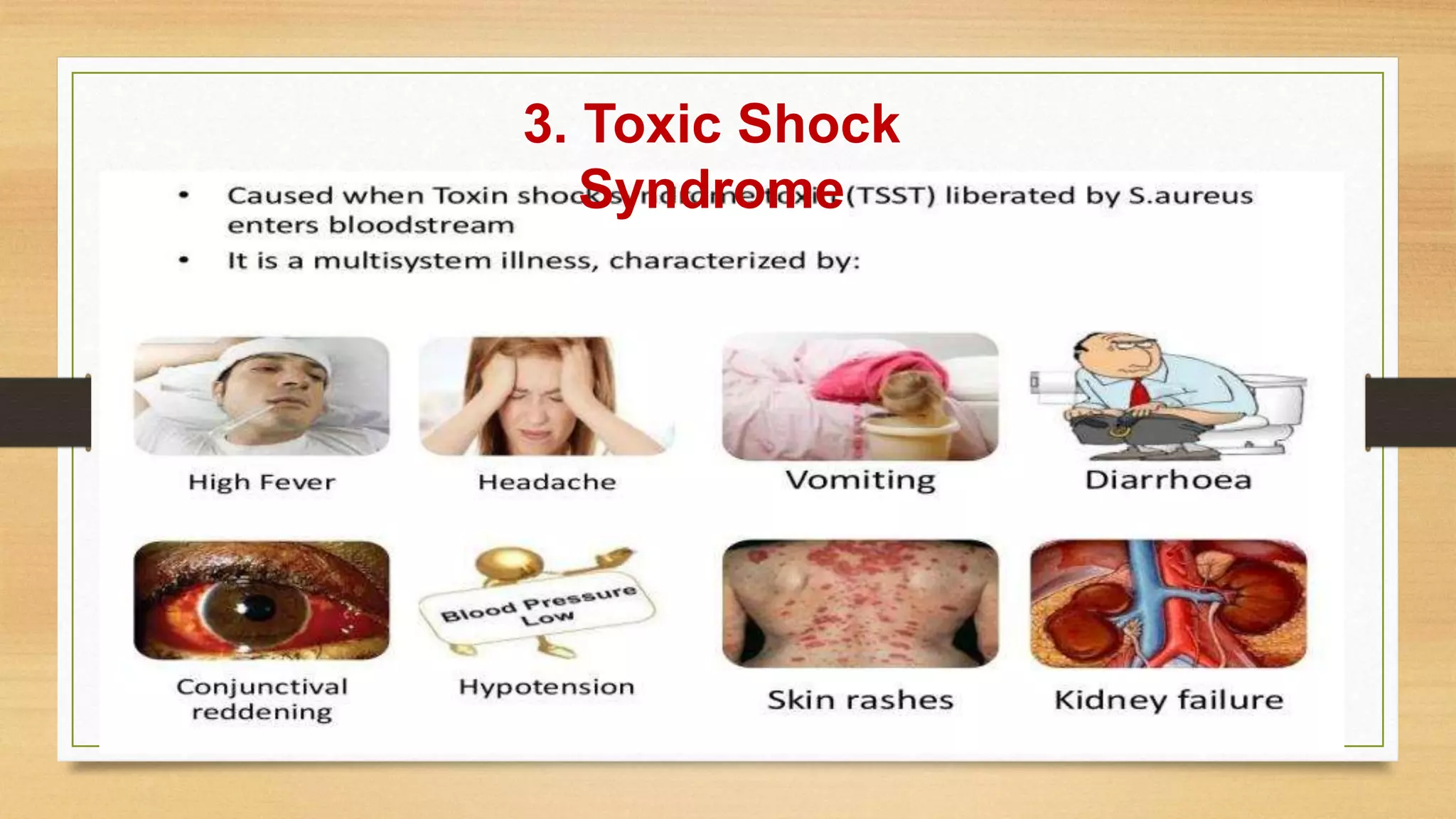
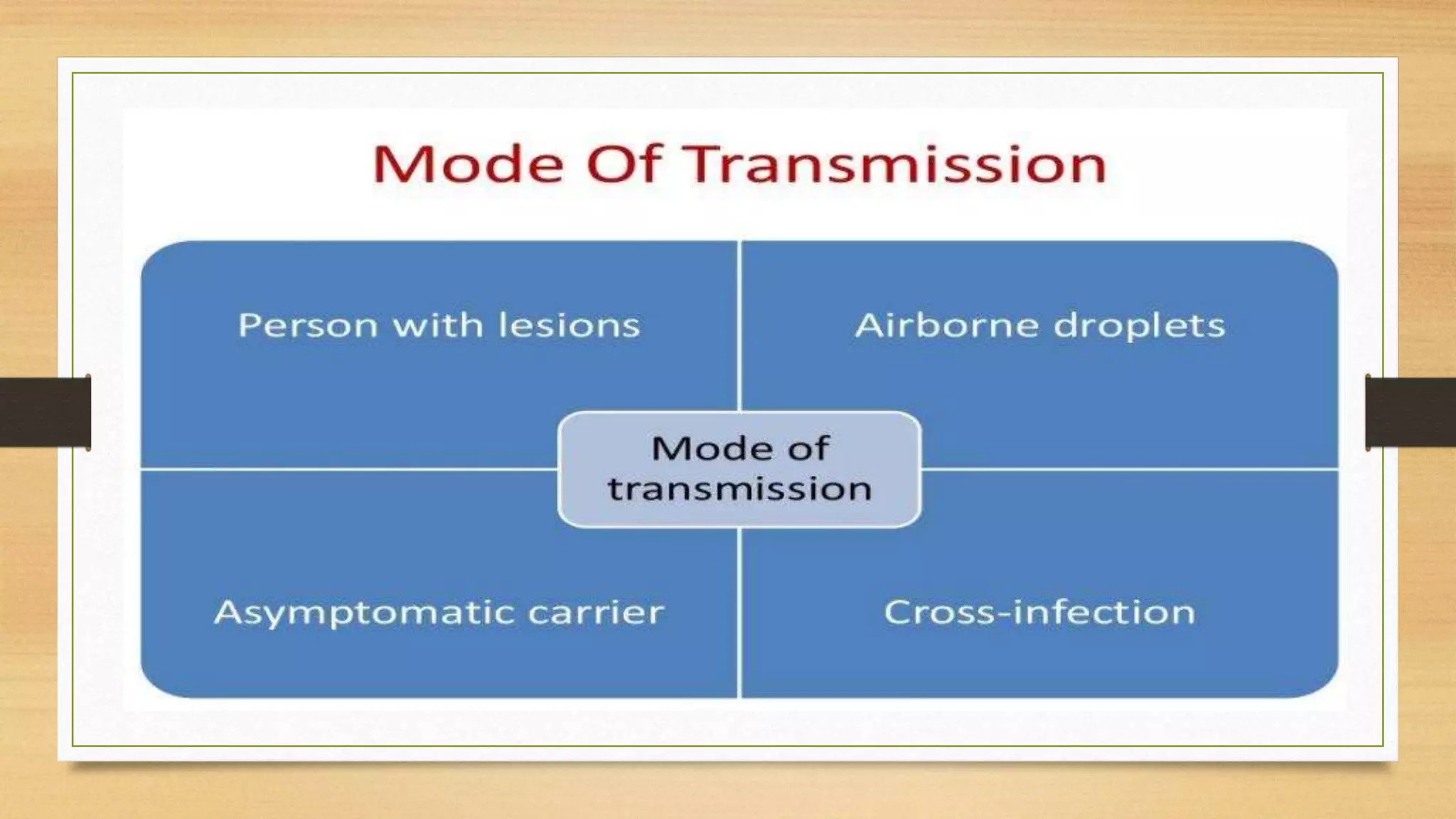
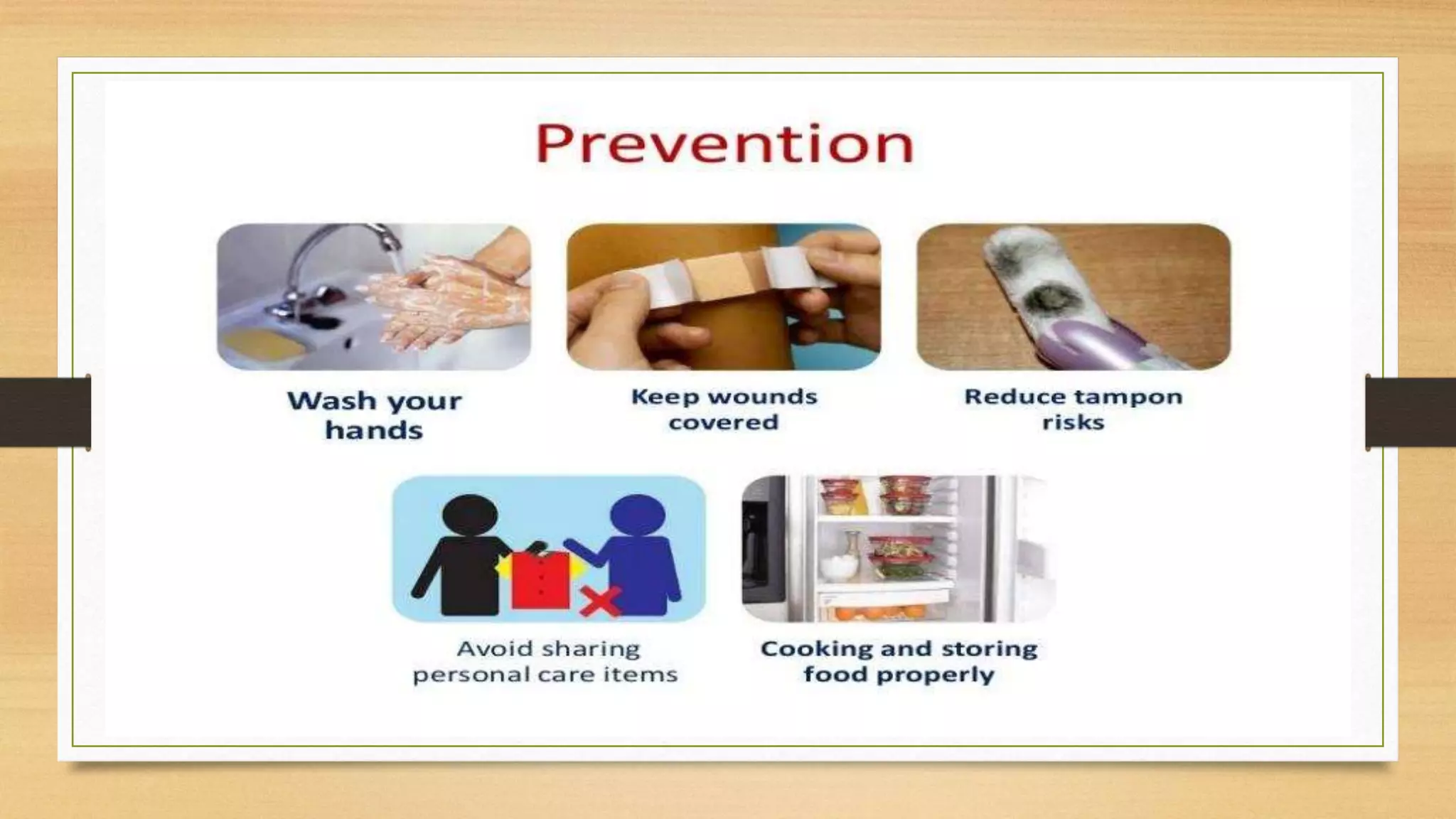
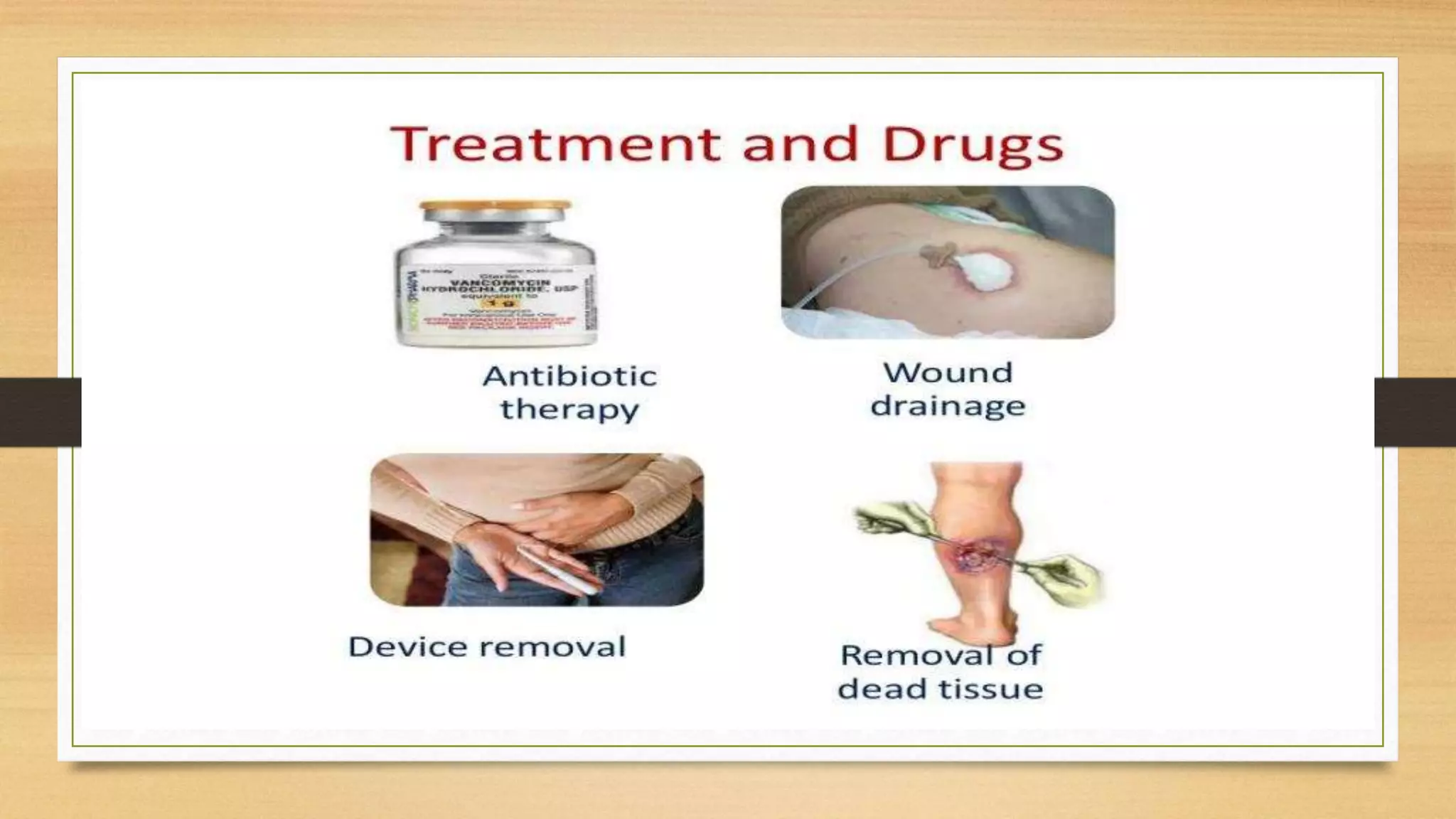
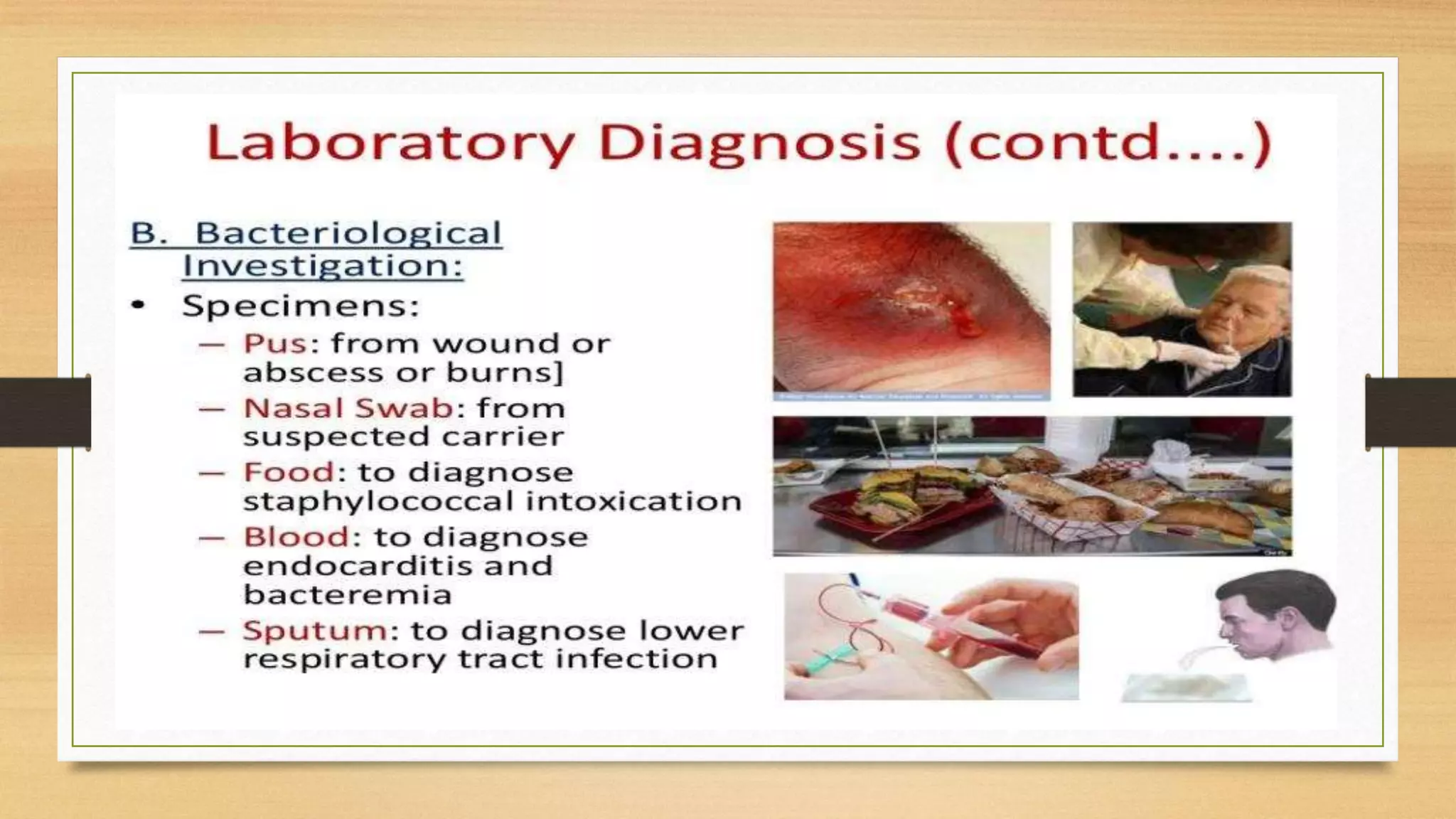
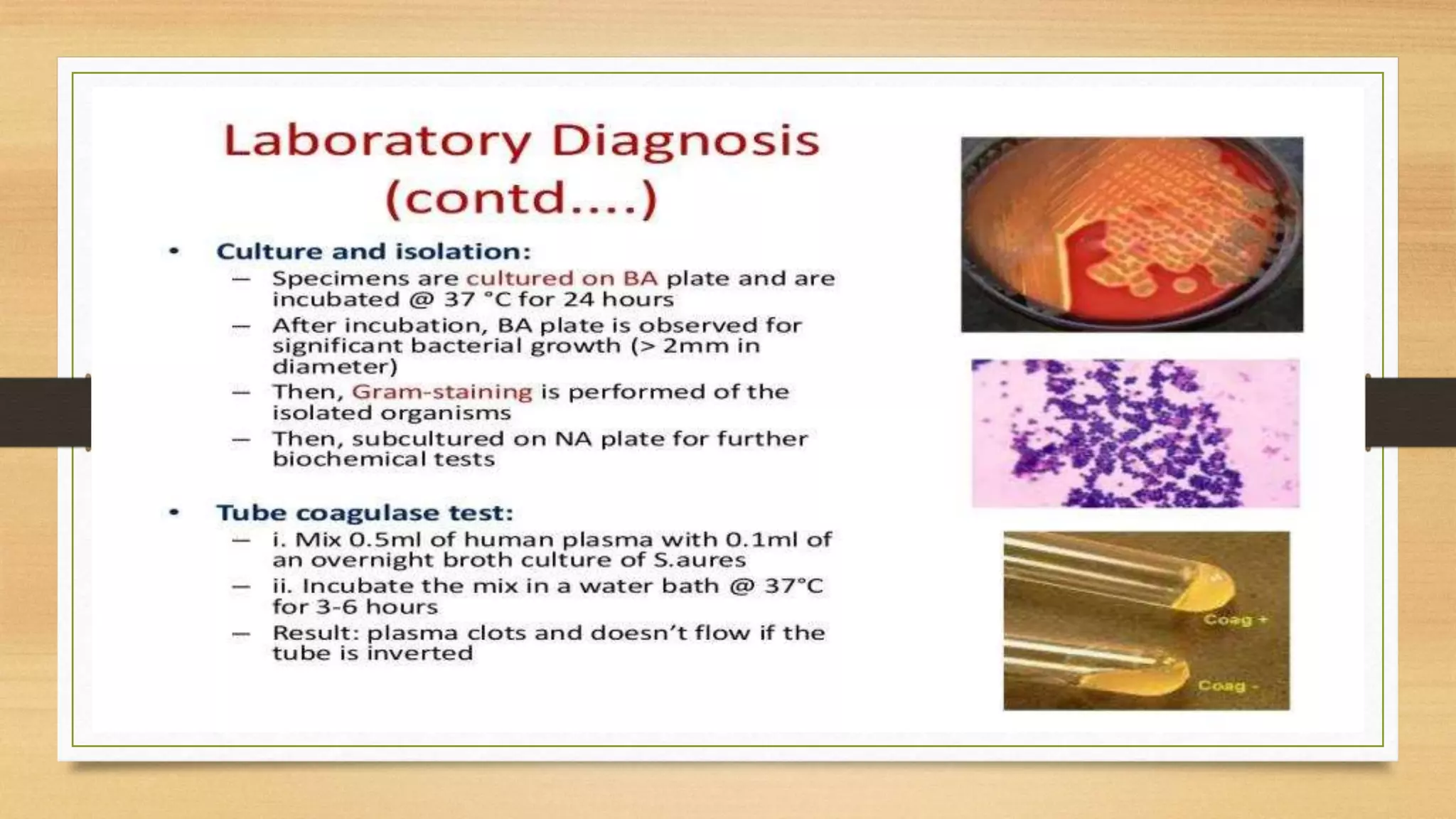
This document discusses Staphylococcus aureus, a gram-positive bacterium commonly found on human skin and in the environment. S. aureus can cause a variety of infections through adherence to skin or mucosa and releasing toxins. It is identified by being catalase-positive, coagulase-positive, and able to grow in 7.5% sodium chloride. S. aureus infections include skin infections like boils and impetigo, deep infections like osteomyelitis and endocarditis, and toxin-mediated diseases like toxic shock syndrome and food poisoning.