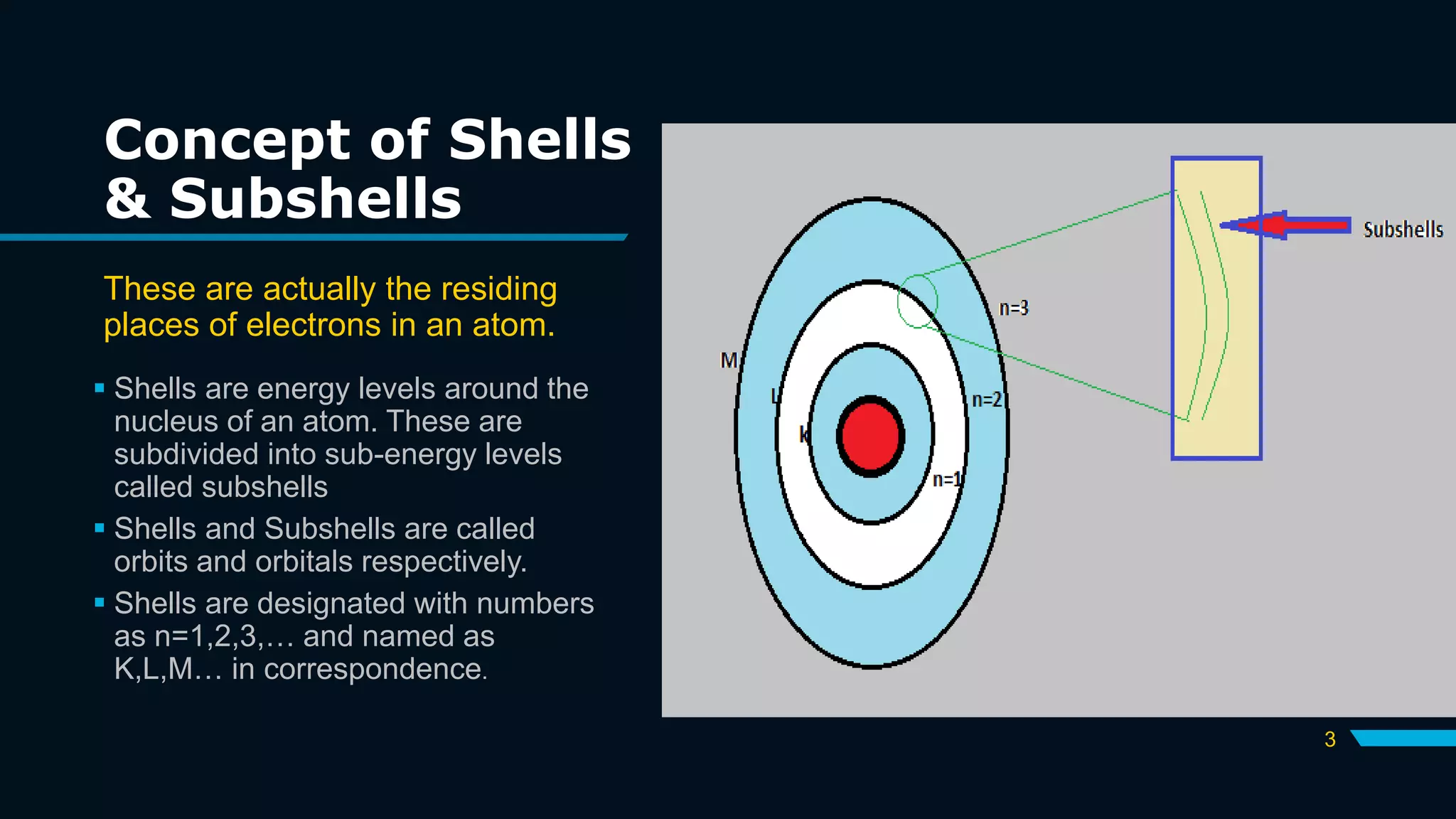
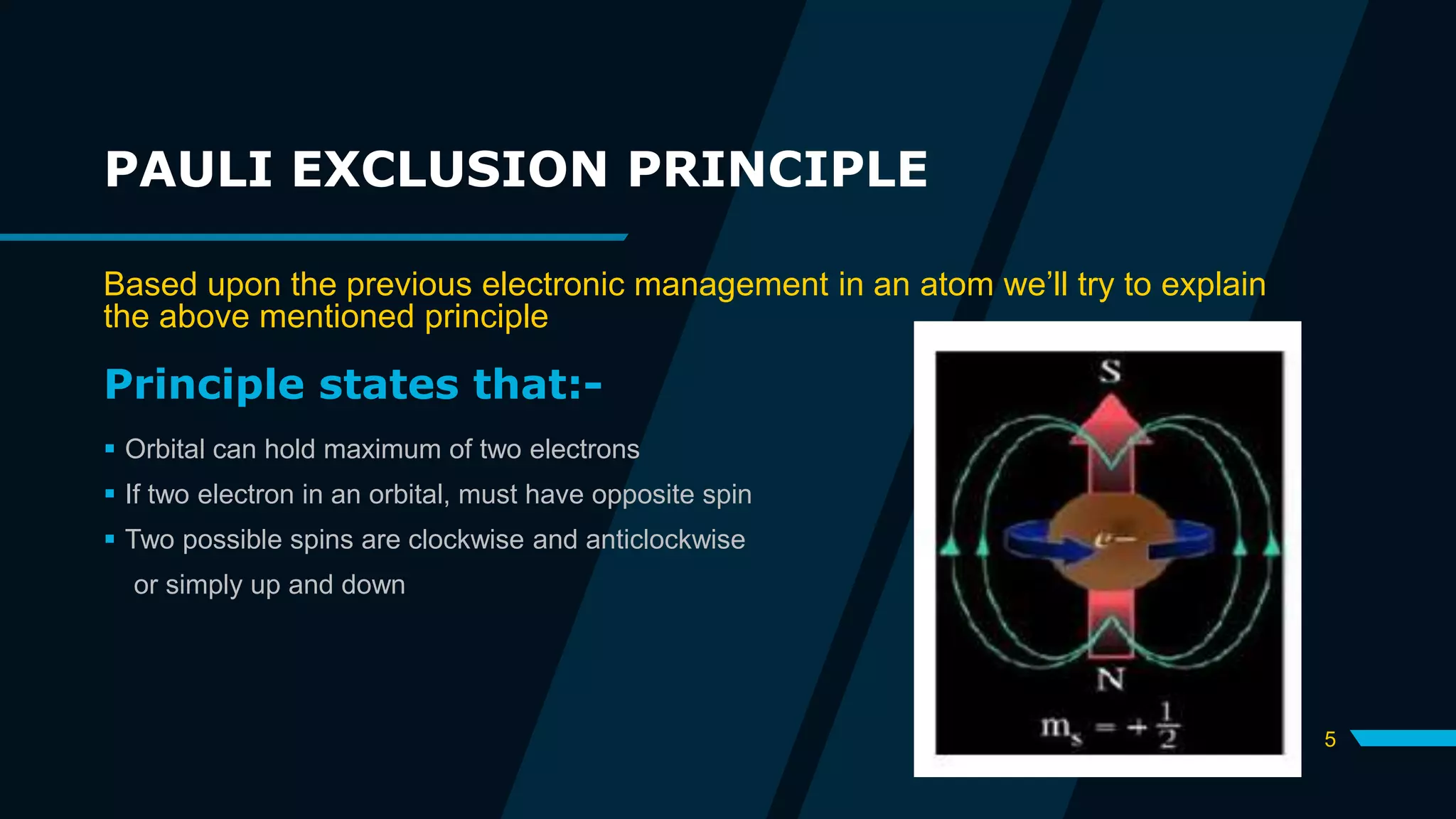
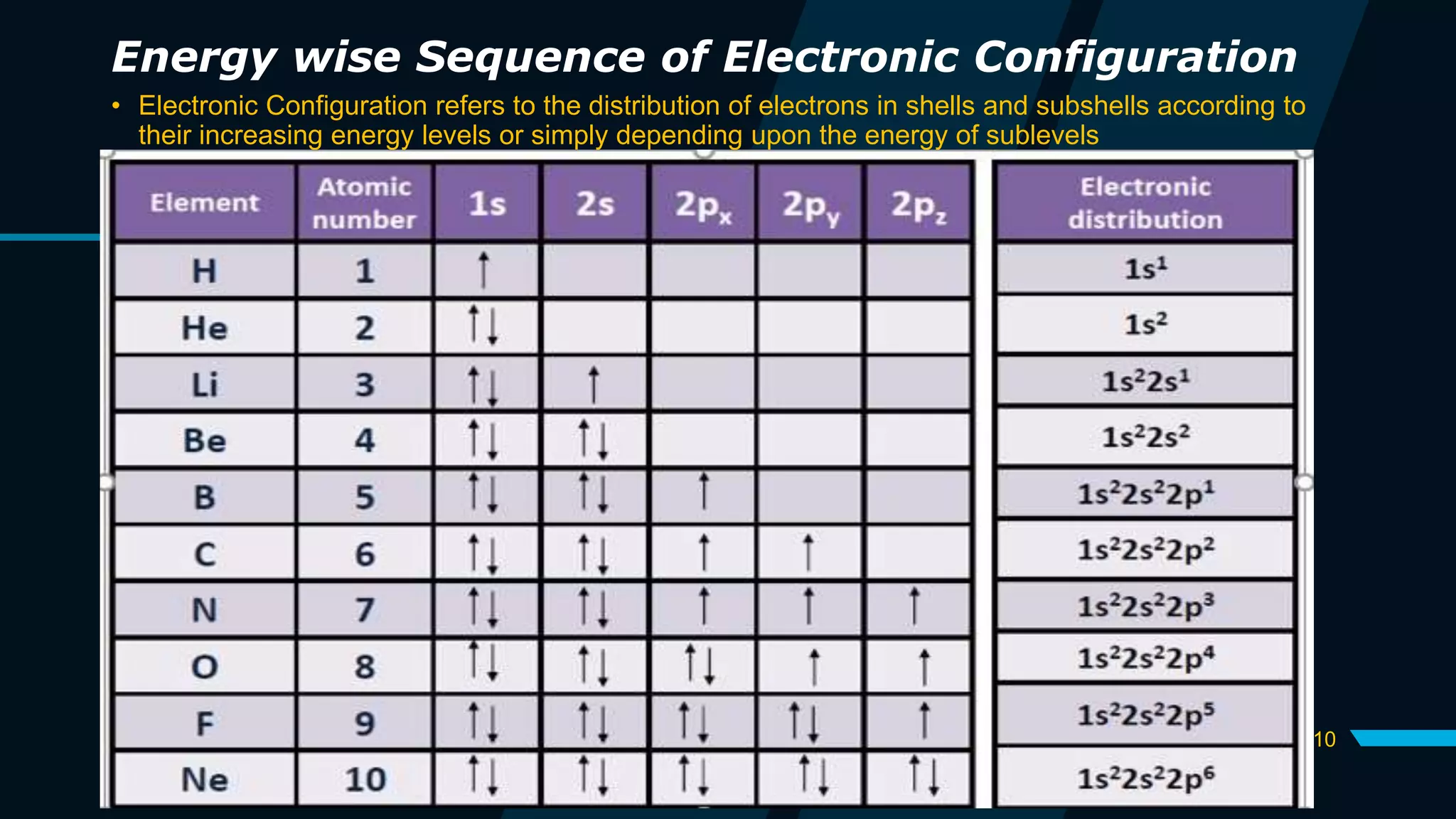
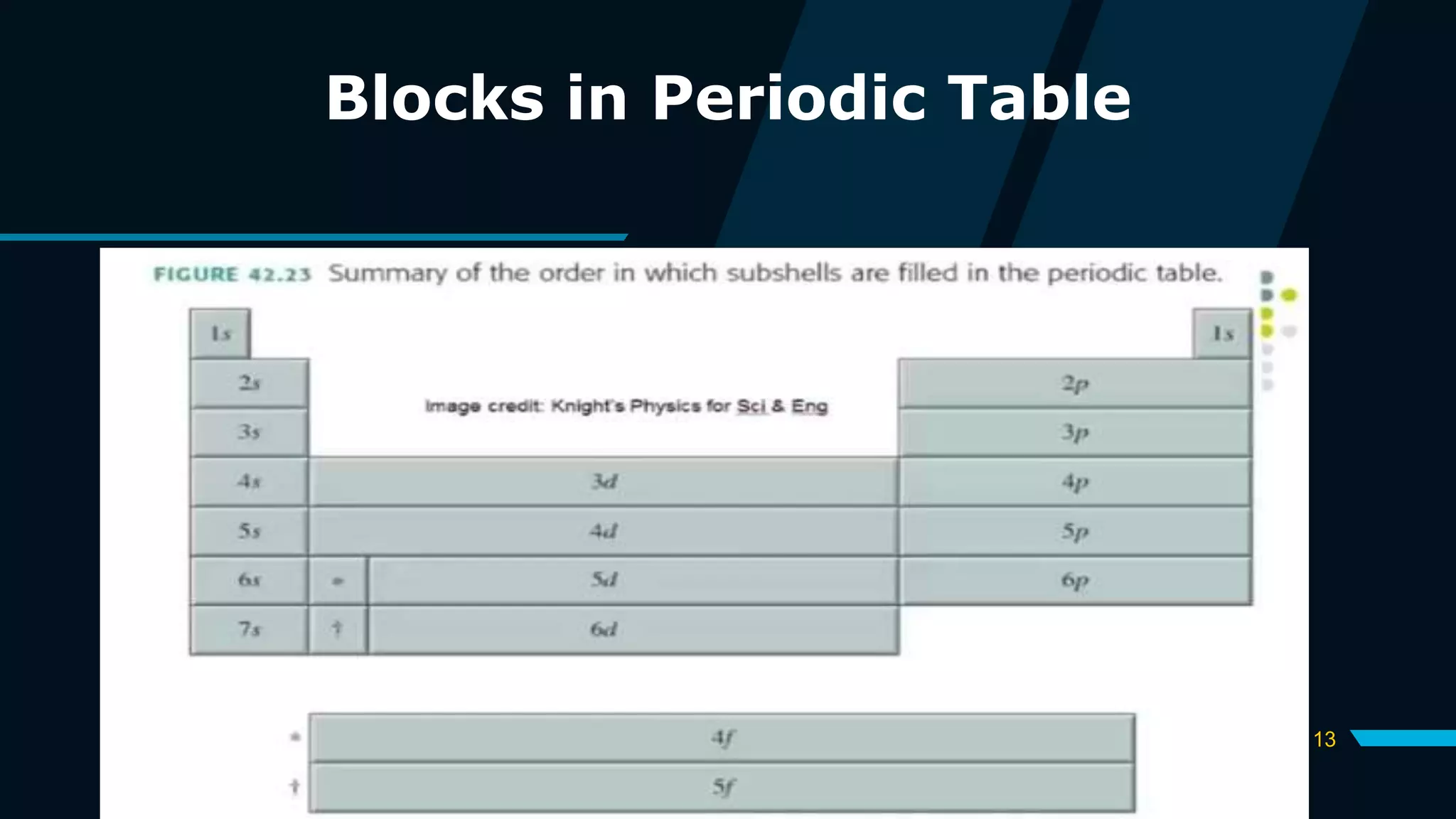
The document discusses the Pauli Exclusion Principle and its importance in the periodic table. It explains that the principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers, and electrons must have opposite spins when occupying the same orbital. This principle allows electrons to be arranged in shells and is crucial for determining an element's chemical properties and for constructing the periodic table by blocks.