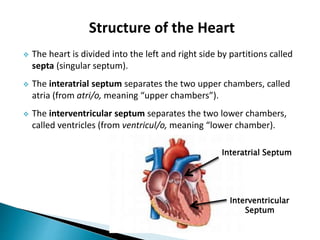
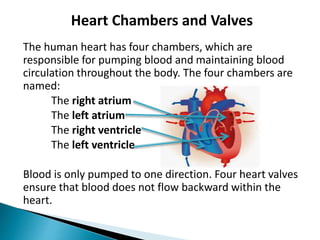
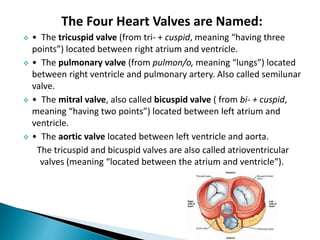
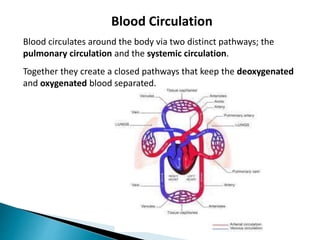
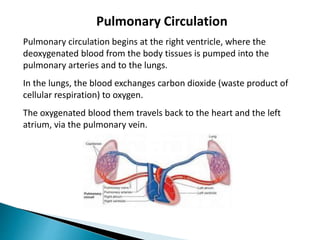
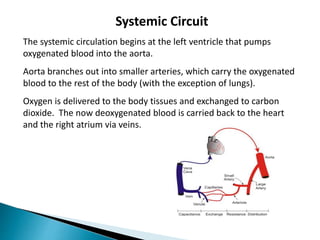
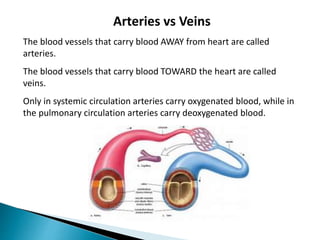
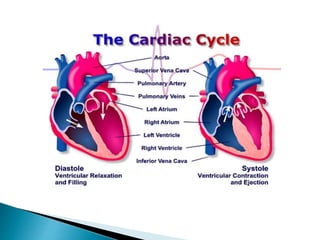
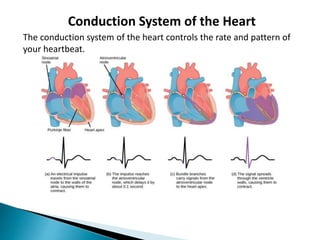
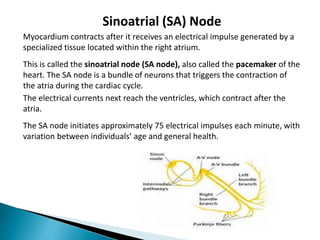
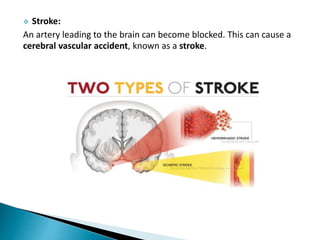
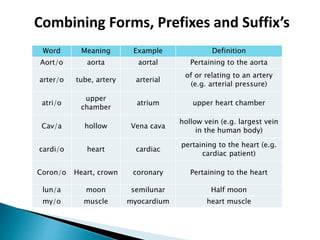
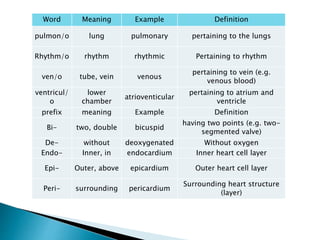
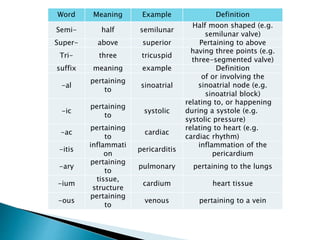
The document provides an overview of heart anatomy and physiology. It describes the four chambers of the heart, including the atria and ventricles, separated by septa. Blood flows through the heart in two circuits - pulmonary circulation from the heart to the lungs and systemic circulation from the heart to the body. The heart's conduction system controls heart rate and rhythm through the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and Purkinje fibers. An electrocardiogram traces the electrical activity of the heart as P, QRS, and T waves. High or low blood pressure can impact heart health.