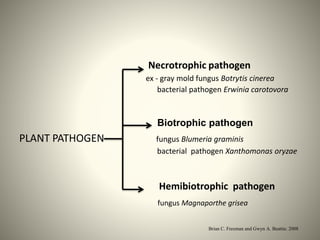
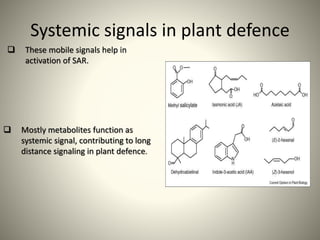
The document discusses the interaction between plants and pathogens, detailing the mechanisms of plant defense, including both constitutive and inducible responses. It explains the roles of systemic acquired resistance (SAR), pathogenesis-related proteins, and secondary metabolites in providing protection against various pathogens. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding these mechanisms for developing biotic stress-tolerant crop varieties.