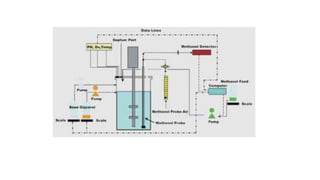
This document summarizes the application of computers in fermentation. It discusses the initial use of computers in the 1960s for modeling fermentation processes. Computers are now used for logging process data, analyzing the data, and controlling fermentation processes. Sensors are used to monitor important factors like temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and mineral/nutrient levels to provide data inputs for computer control and modeling of fermentation.



![USAGE OF FERMENTER
• Fermenter are used in the large scale production in the most
industries.
• Dairy production
[milk,cheese,beer]
• Antibiotic production
[penicillin,streptomycin]
• Enzyme production
[amylase,protease]
• Organic Acid production
[citric acid.glutamic acid]
• Vitamins production
[vitamin B and A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofcomputerinfermentation-171230164300/85/Application-of-computer-in-fermentation-5-320.jpg)



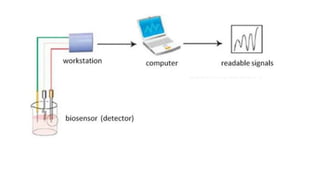

![DATA ANALYSIS
[Reduction of logging data]
• Data reduction is performed by the data analysis system ,which is a
computer program based on a series of selected mathematical
equation.
• The analysed information may then be put on a print out, fed into a
data bank or utilized for process control.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofcomputerinfermentation-171230164300/85/Application-of-computer-in-fermentation-12-320.jpg)