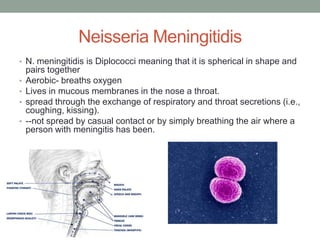
1) Meningococcal disease is caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis and can cause meningitis or sepsis. It is spread through respiratory and throat secretions.
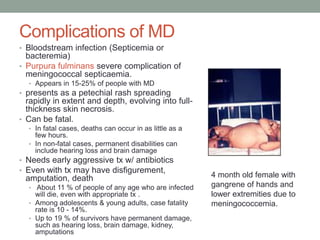
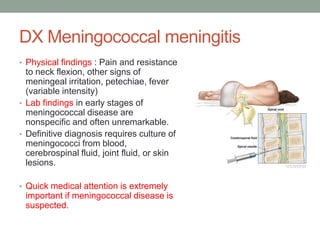
2) Symptoms include headache, fever, neck stiffness, and rash. Complications can include blood infections, skin necrosis, hearing loss, and limb amputations. Early treatment with antibiotics is important.
3) There are two vaccines that protect against some common strains of N. meningitidis. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of adolescents and those at increased risk. Preventive measures include vaccination and good hygiene.









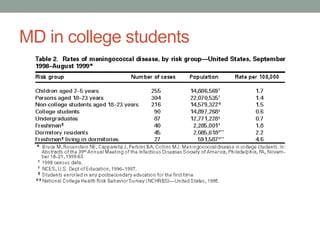




![MD vaccine and college students
• September 30, 1997, American College Health
Association (ACHA), which represents about half of
colleges that have student health services, released a
statement recommending that "college health services
[take] a more proactive role in alerting students and their
parents about the dangers of meningococcal disease,"
that "college students consider vaccination against
potentially fatal MD ," and that "colleges and universities
ensure all students have access to a vaccination program
for those who want to be vaccinated"
• Varies by state](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week9meningococcaldisease-131208023244-phpapp02/85/Meningococcal-disease-21-320.jpg)
