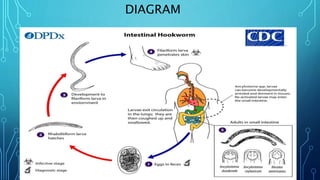
Hookworm is an intestinal parasite that infects people through skin contact with contaminated soil. It causes an itchy rash and can lead to iron deficiency anemia from blood loss. Over 151 million people were infected worldwide in 1997, especially in areas with poor sanitation. The parasites are transmitted when larvae in soil penetrate the skin of bare feet. People are infected by walking barefoot or using contaminated soil as fertilizer. Diagnosis involves examining stool samples for eggs. Treatment involves antiparasitic drugs like albendazole or mebendazole. Prevention relies on improved sanitation, hygiene, footwear, and health education.