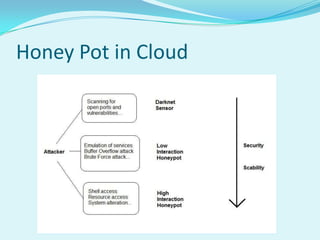
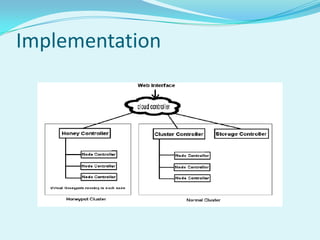
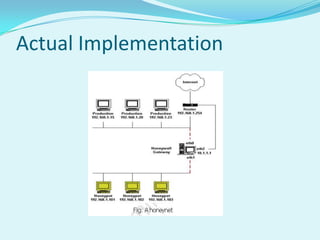
Honey pots can be implemented in cloud computing to improve security. There are several components, including a cloud controller, cluster controller, honey controller, and log storage system. Low interaction honey pots like Honeyd emulate services to detect attacks, while high interaction honey pots like Honeynets allow more flexibility for attackers but carefully control outbound traffic. Honey pots can be offered as a service for cloud customers, providing logs and statistics to help secure resources against future attacks.