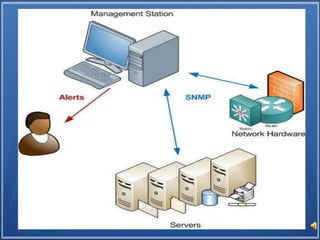
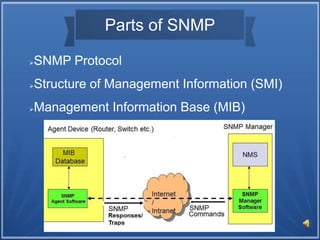
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a standardized protocol used to monitor network devices and services. It comprises an agent on each device that collects data, and a manager that can read or write the agent's data. SNMP allows centralized monitoring of things like bandwidth usage, server resources, errors, and configuration. It is widely supported, extendable, portable, and lightweight. The three versions are V1 (basic), V2c (most common with enhancements), and V3 (adds security features). Key parts of SNMP include the protocol, SMI structure, and MIB management information base.