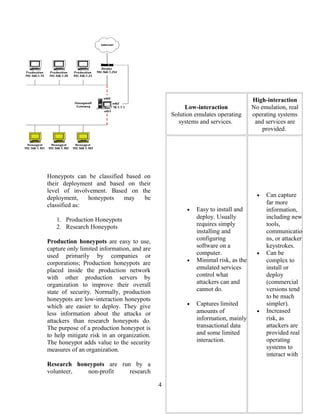
The document discusses honeypots, which are decoy computer systems used to detect cyber attacks. It describes two main types of honeypots: low-interaction honeypots, which emulate services and operating systems, and high-interaction honeypots, which use real systems and software. Low-interaction honeypots are easier to deploy but provide limited information, while high-interaction honeypots provide more complete data but also higher risks if not isolated properly. Specific honeypot examples discussed include Honeyd, a low-interaction honeypot, and Honeynets, which use entire decoy networks of high-interaction systems.






![unless the attacker or threat
interacts with the honeypots also.
• Risk: All security technologies
have risk. Firewalls have risk of
being penetrated, encryption has
the risk of being broken, IDS
sensors have the risk of failing to
detect attacks. Honeypots are no
different, they have risk also.
Specifically, honeypots have the
risk of being taken over by the
bad guy and being used to harm
other systems. Depending on the
type of honeypot, it can have no
more risk than an IDS sensor,
while some honeypots have a
great deal of risk.
Conclusion
Honeypots can be used for research,
gathering information on threats so we
can better understand and defend against
them. The modern rapid advancements
in computer networking, communication
and mobility increased the need of
reliable ways to verify the loopholes
within the system. Honeypots pave a
significant way towards production
purposes by preventing, detecting, or
responding to attacks.
References
[1] The Honeynet project,
http://www.honeynet.org
[2] Honeypots, by Lance Spitzner,
http://www.spitzner.net/honeypots.html
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/honeypots-130831120058-phpapp02/85/Honeypots-8-320.jpg)