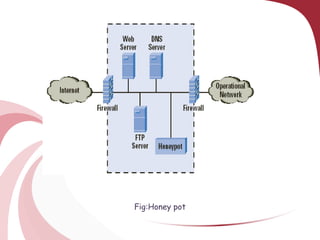
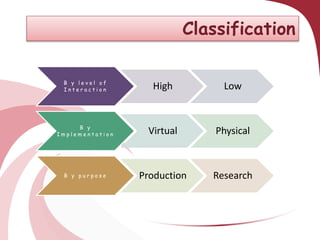
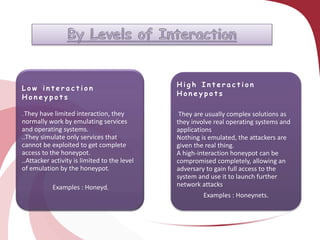
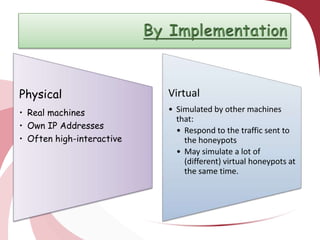
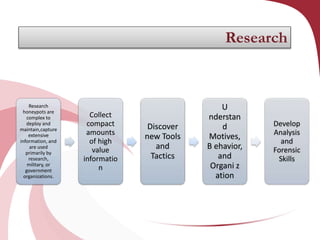
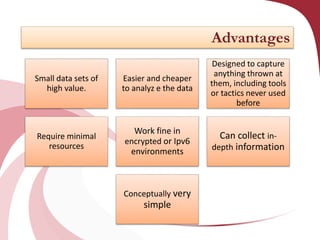
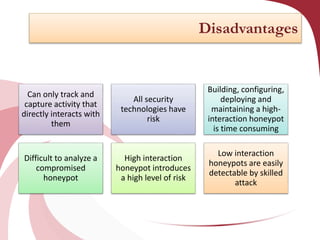
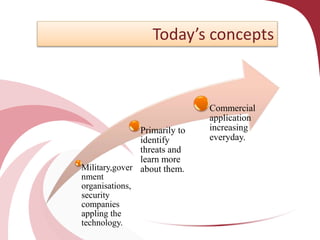
A honeypot is a security tool designed to detect and counteract unauthorized use of information systems, functioning through emulation of real systems to study hacker movements. They are classified into low and high interaction types, with low interaction honeypots simulating services and high interaction ones involving actual operating systems, providing different levels of risk and data capture. While effective for research and operational purposes, honeypots require significant maintenance and can only track interactions that occur directly with them.