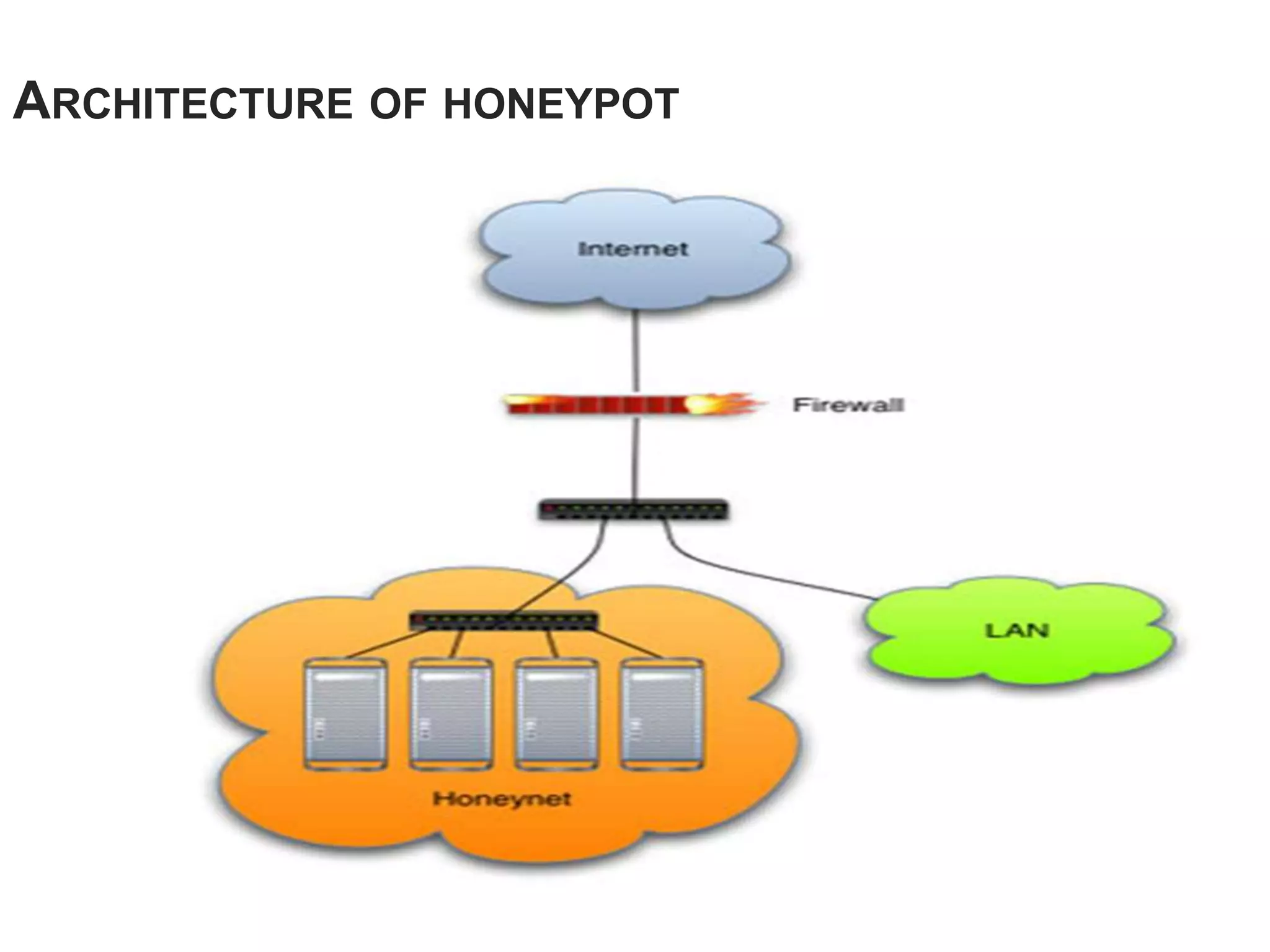
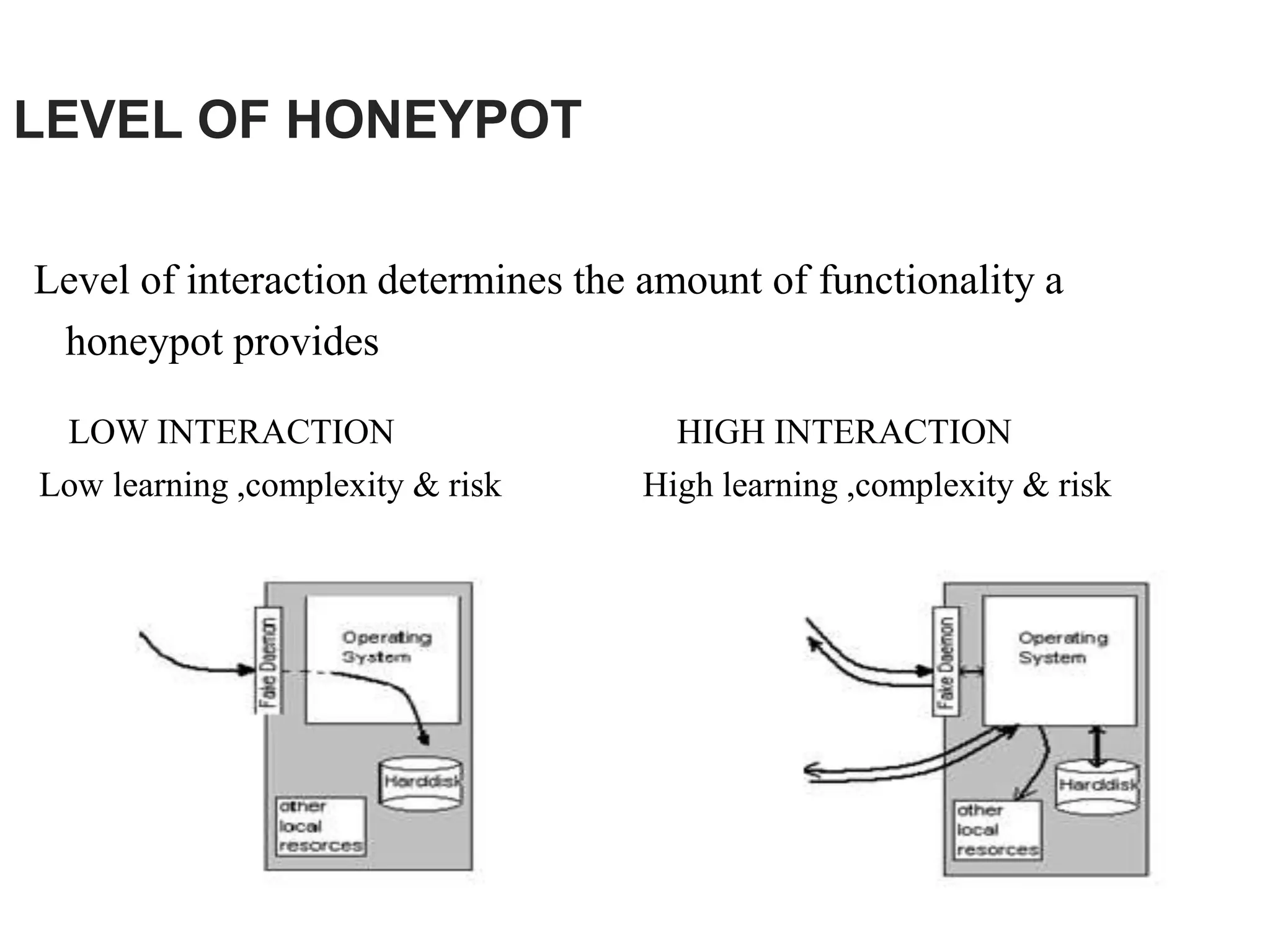
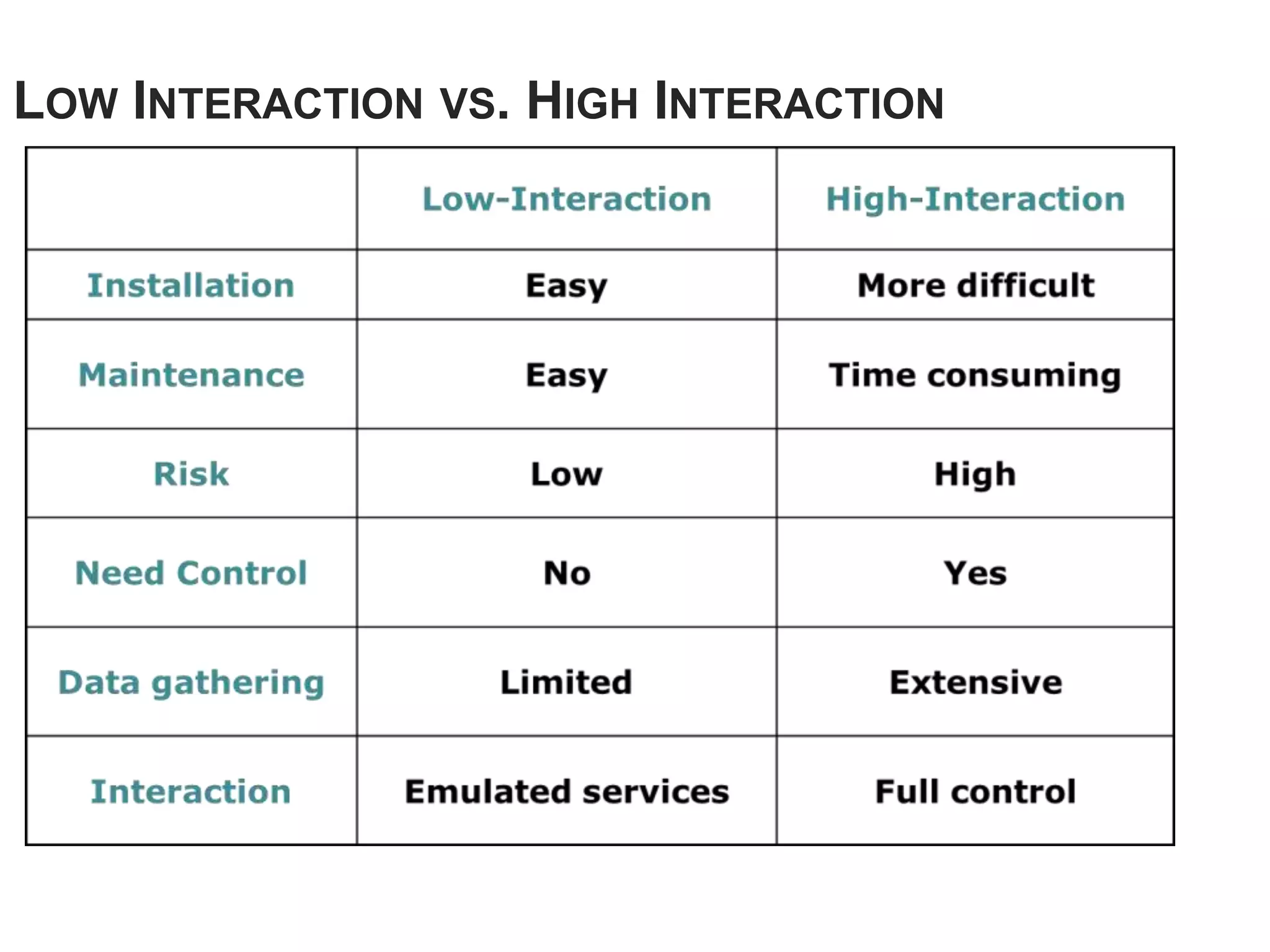
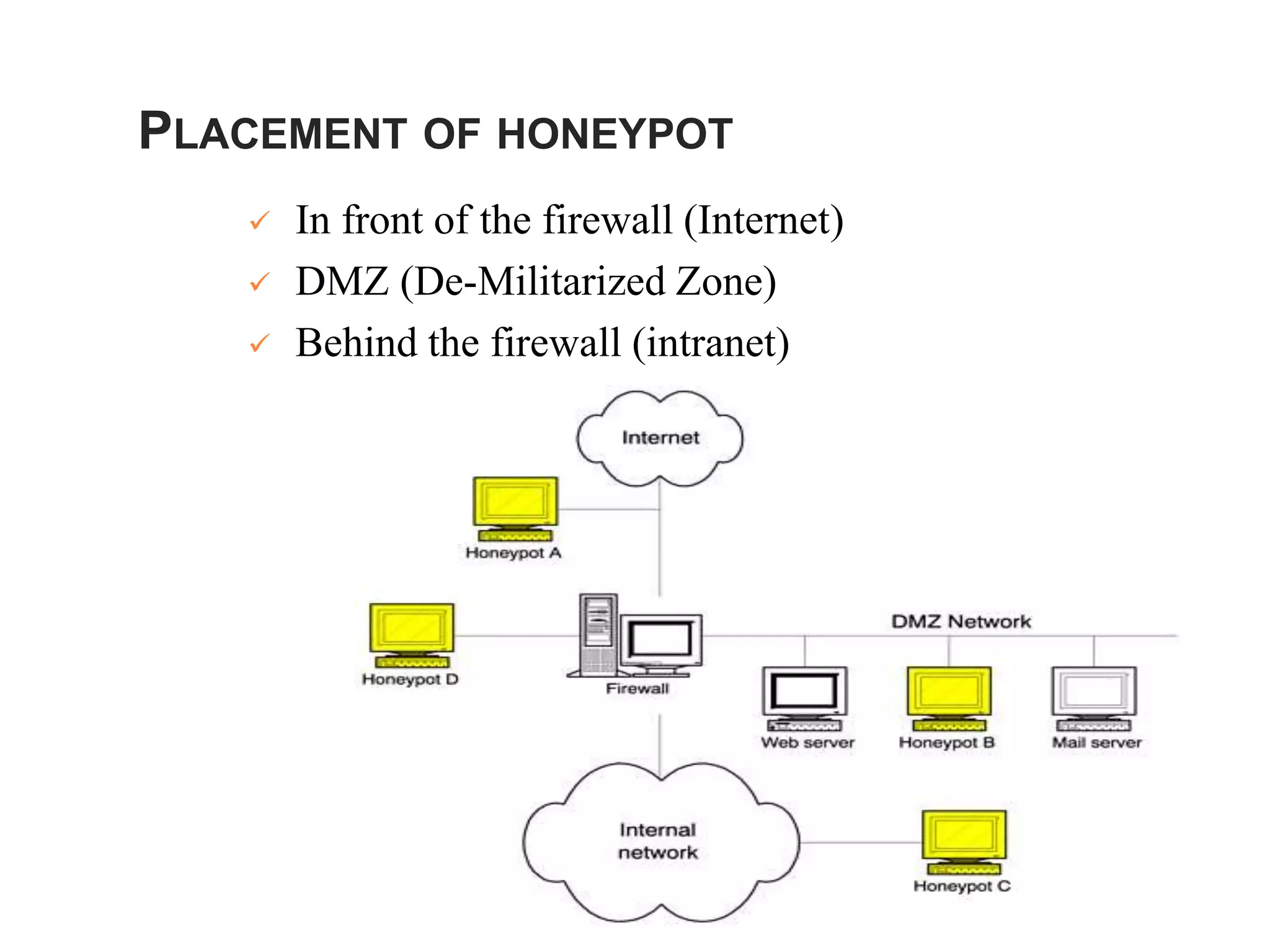
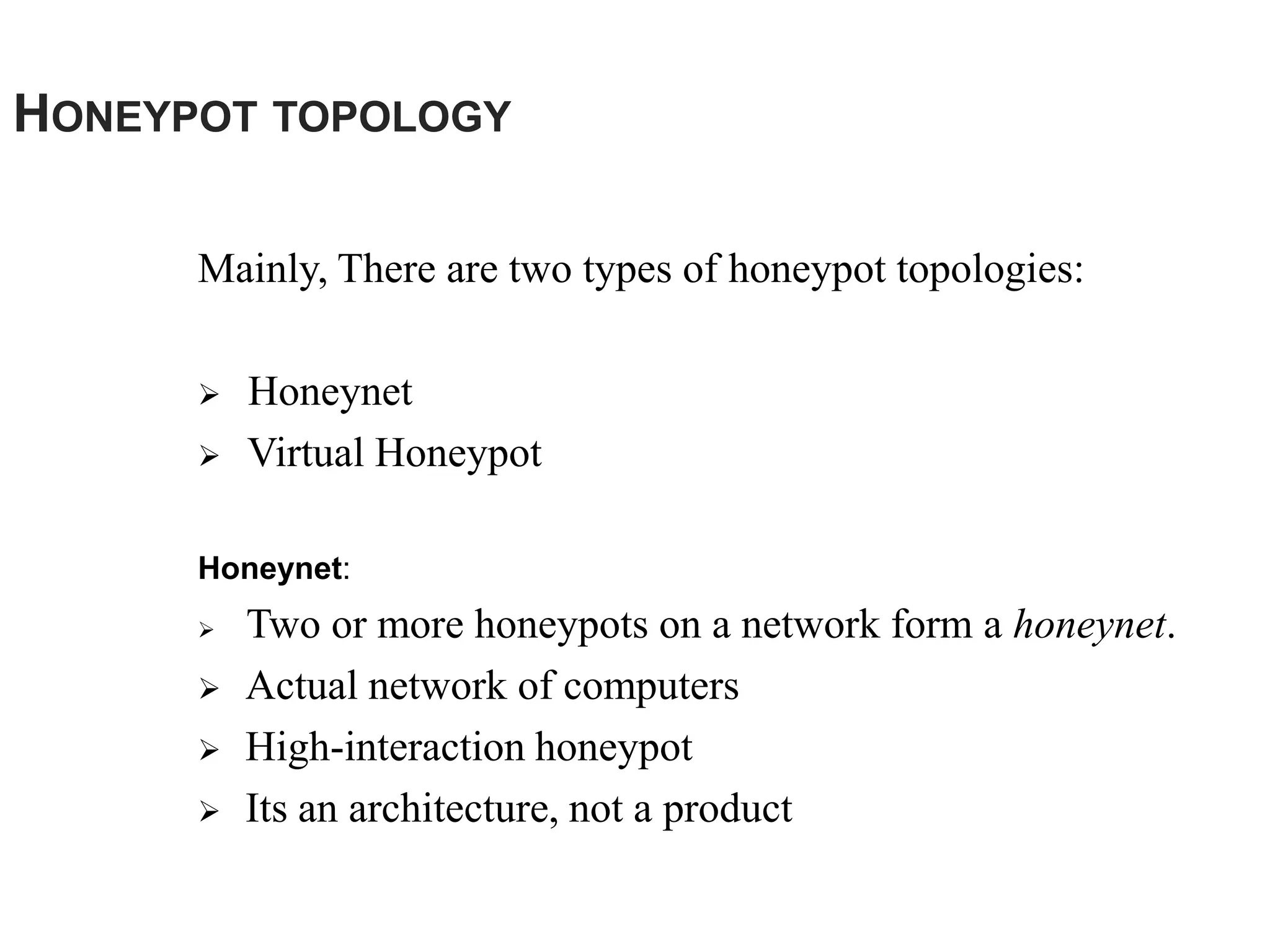
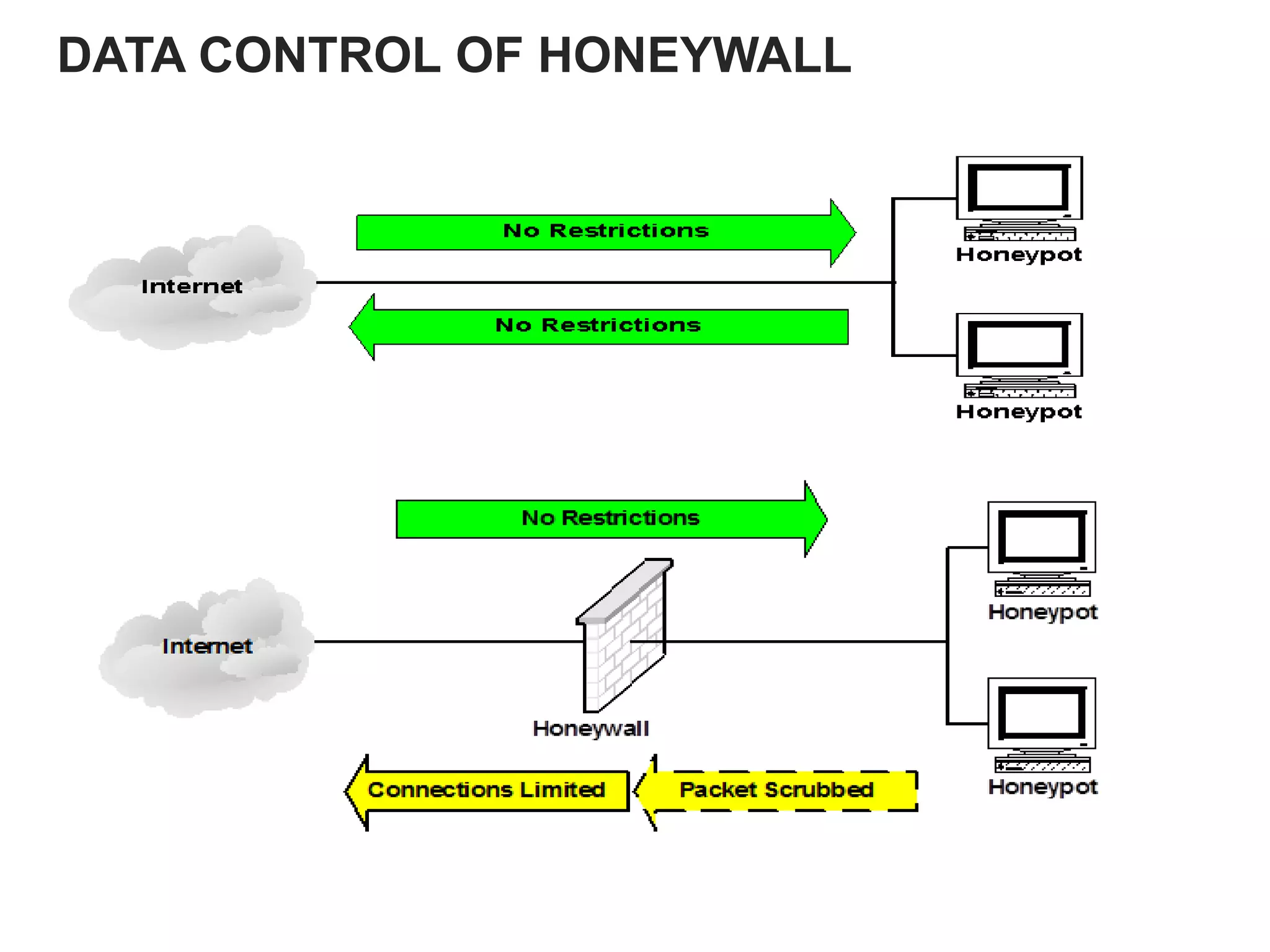
Honeypots are systems designed to be probed, attacked, or compromised by cyber attackers. They serve several purposes including detecting attacks, learning how attackers operate, and providing network security. There are two main types - research honeypots which capture extensive information but are complex to deploy, and production honeypots which are easier to use but capture limited data. Honeypots can be low or high interaction, with high interaction honeypots providing more realistic and detailed insights but posing greater risks if compromised.