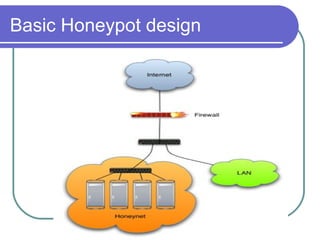
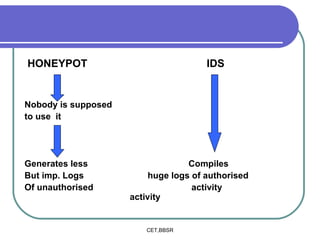
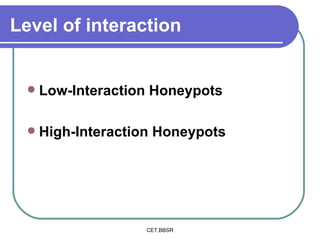
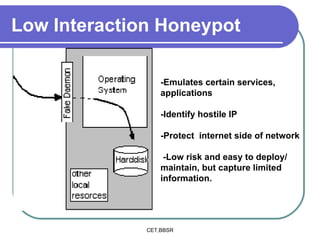
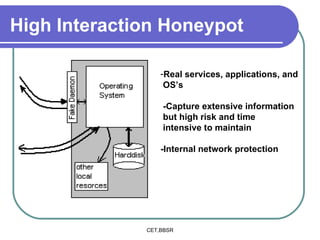
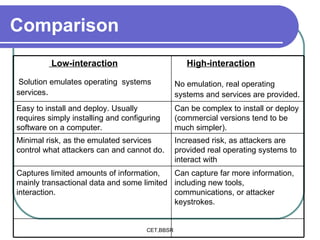
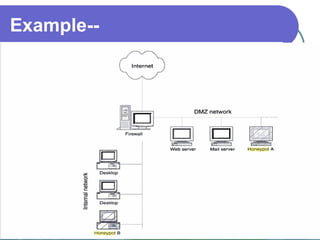
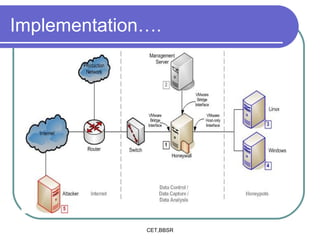
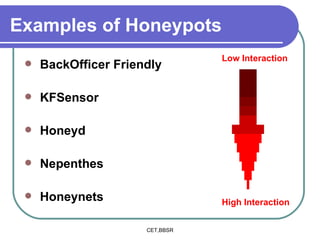
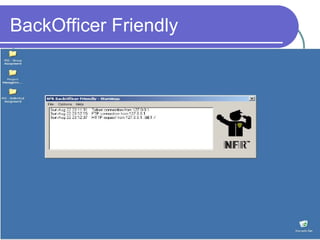
Honeypots are information systems designed to detect cyber threats. They emulate vulnerabilities to lure attackers and observe their behavior without authorization. There are two main types: low-interaction honeypots, which emulate services and capture limited data, and high-interaction honeypots, which use real systems and services to gather extensive information but pose higher risks. Honeypots help identify weaknesses, catch attackers, and design more secure networks by compiling logs of unauthorized activity without affecting authorized usage.