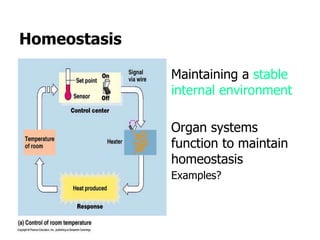
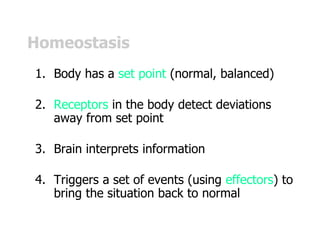
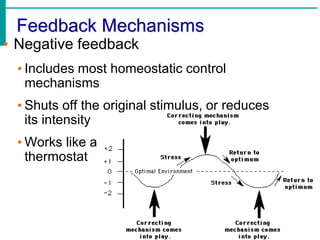
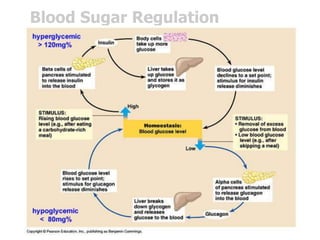
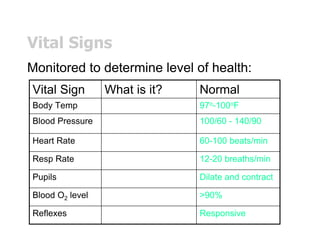
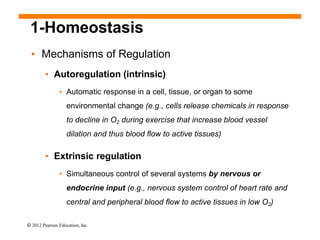
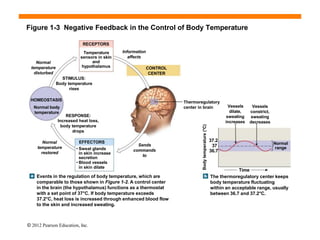
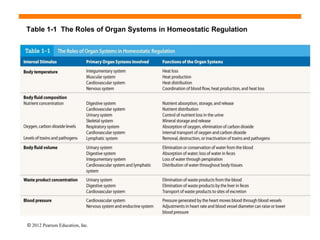
The document discusses homeostasis and how the body maintains internal balance. It defines homeostasis as the stable internal environment of the body. It describes how homeostasis is achieved through negative feedback loops. Negative feedback loops work to reduce any deviations from the normal set point. For example, if body temperature rises, the body engages mechanisms like sweating to cool down and return to the normal temperature. The document also mentions positive feedback loops help amplify necessary responses, like increased milk production when a baby suckles. Overall, the body uses feedback mechanisms and interactions between organ systems to constantly monitor and adjust internal conditions to maintain homeostasis.