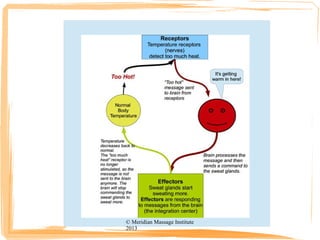
Homeostasis is the body's ability to maintain optimal physiological ranges, such as temperature, blood pressure, and glucose levels, through automatic adjustments by the nervous and endocrine systems. The process involves receptors detecting changes, the brain processing these signals, and effectors (like glands) executing responses to restore balance. Health is characterized by being within these homeostatic ranges, while disease symptoms arise when the body deviates from this balance.