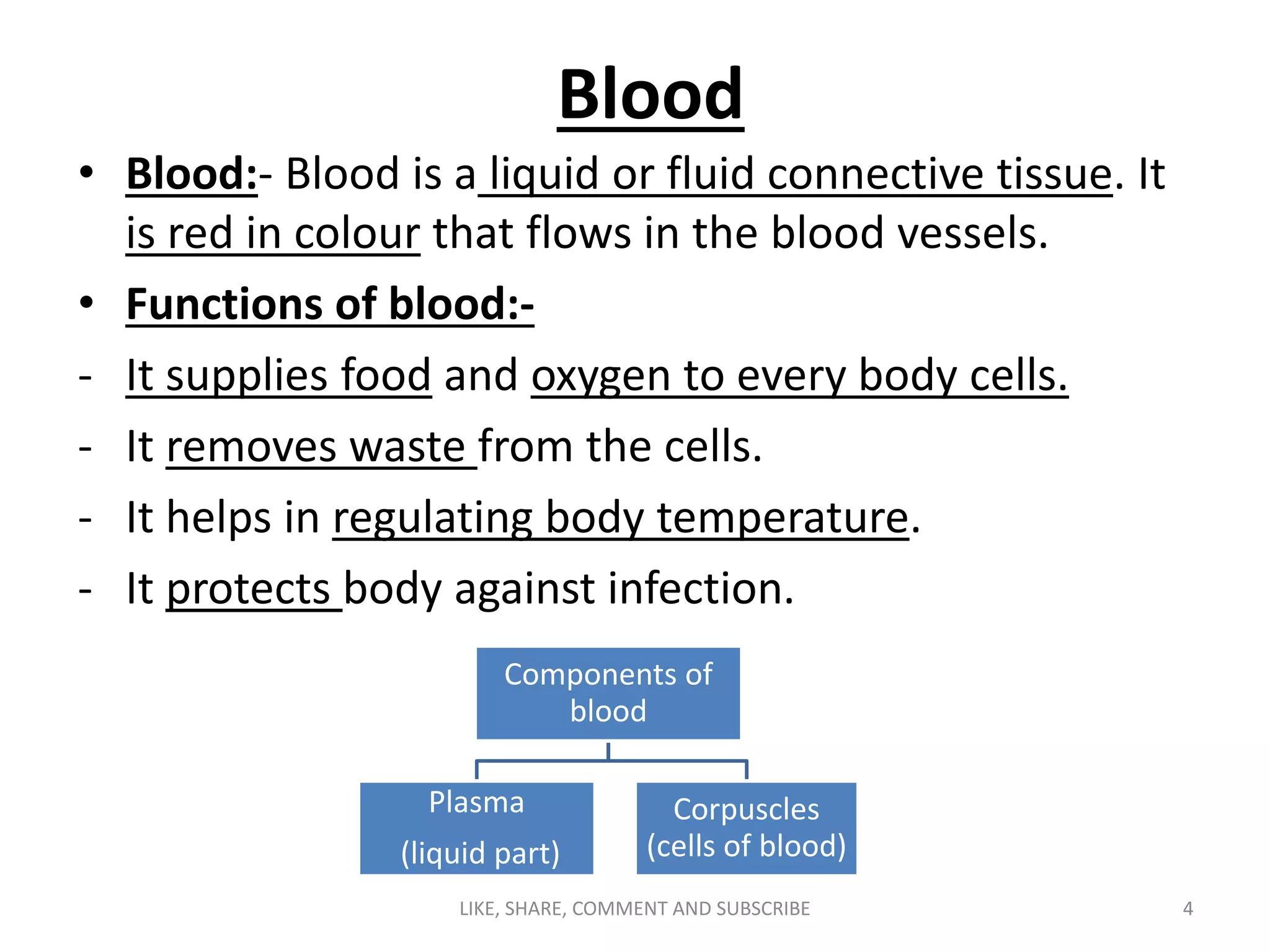
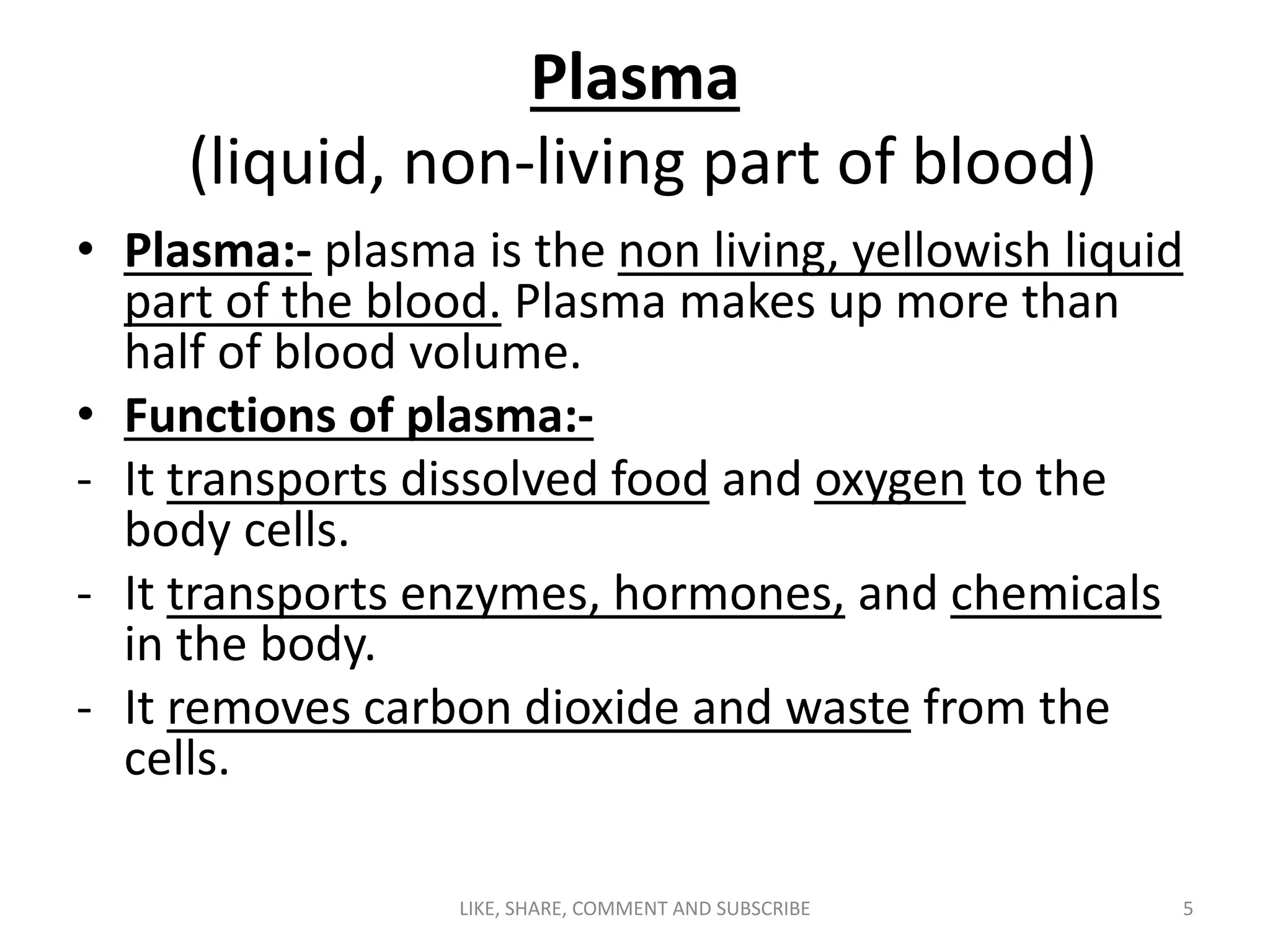
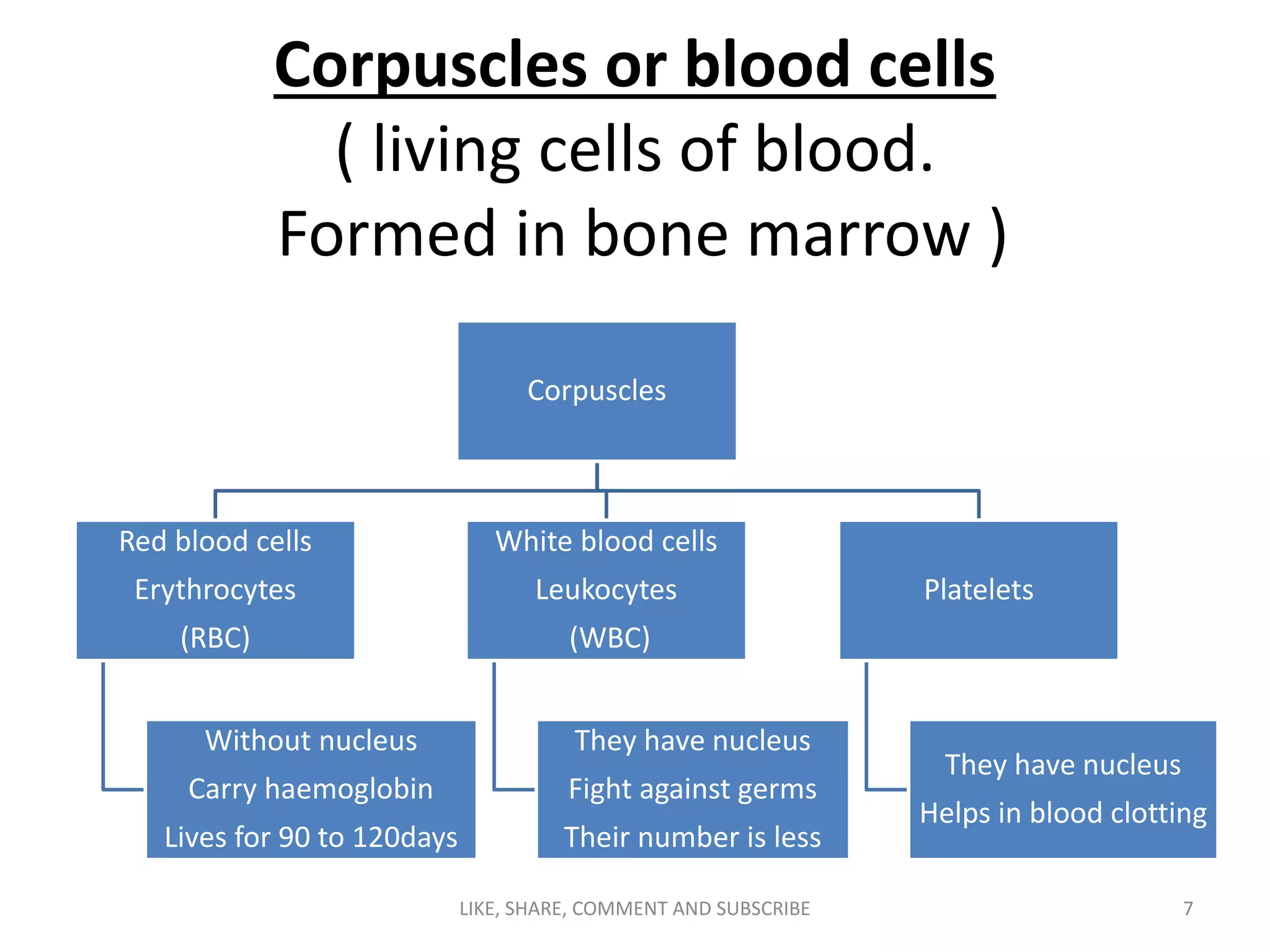
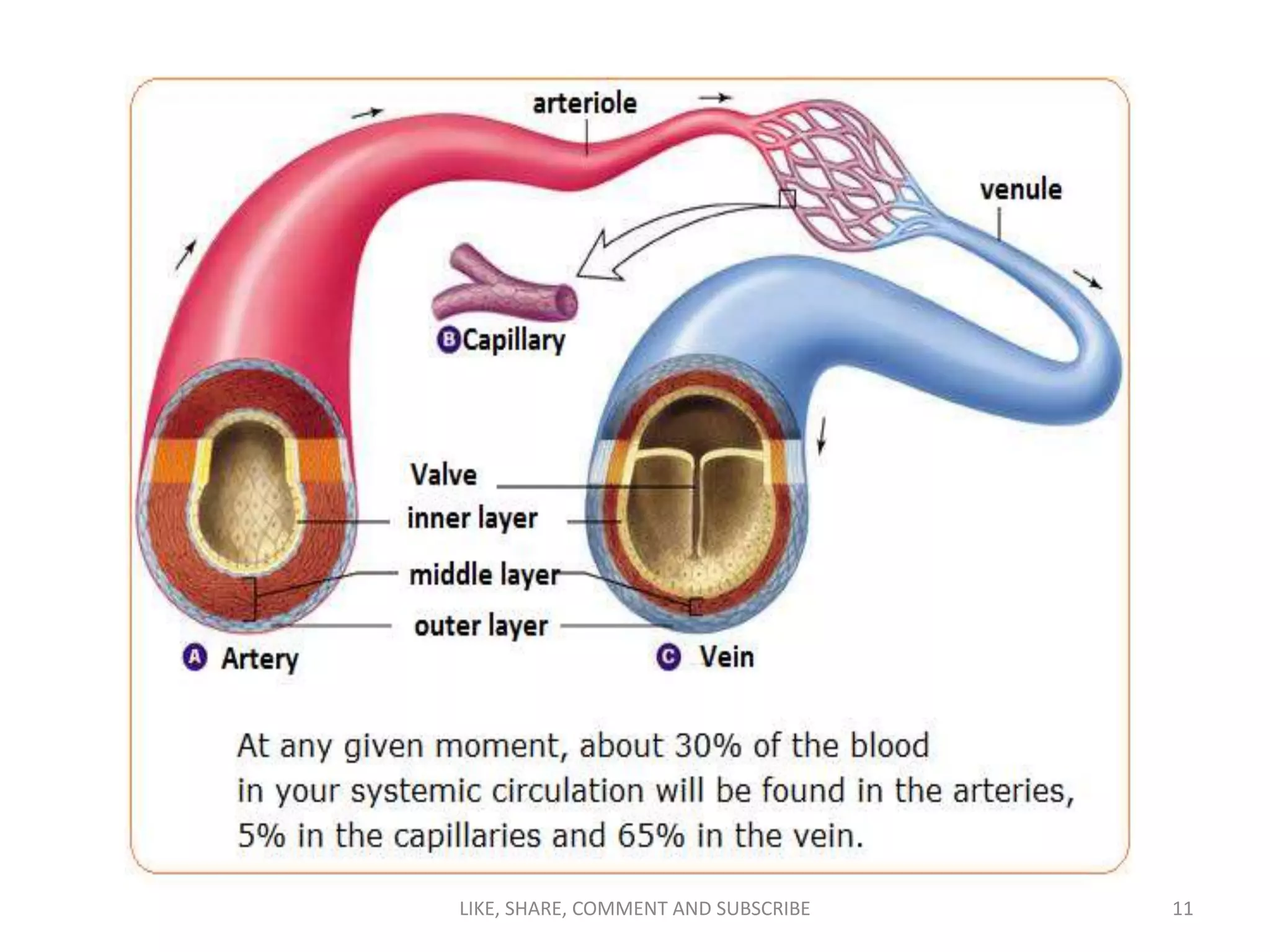
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body via blood vessels. It supplies oxygen and nutrients to cells, removes waste, and transports immune cells to sites of infection. The main components are the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), blood, and blood cells. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to it. Capillaries connect the two, allowing for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, waste and immune cells between blood and body tissues.