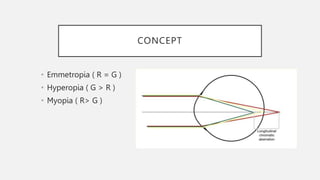
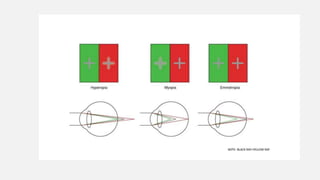
The document discusses the duochrome or bichrome test, which is used to refine the spherical endpoint during monocular refraction. It uses chromatic aberration and different wavelengths of light to determine if a patient is emmetropic, hyperopic, or myopic. The test involves showing the patient red and green filters and adding plus or minus lenses until the clarity is the same between the colors. It can detect refractive errors as small as 0.25 diopters and is reliable for patients with visual acuity of 6/9 or better. The document provides details on interpreting test results and final refractive corrections.