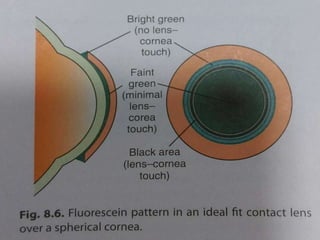
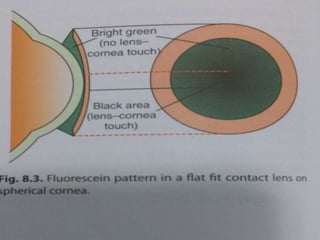
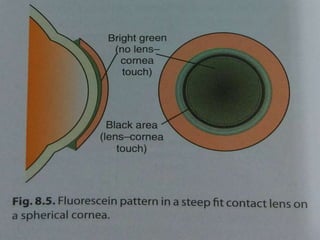
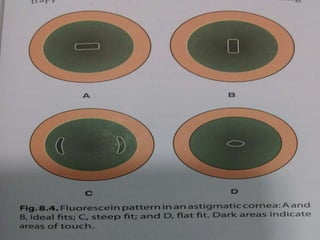
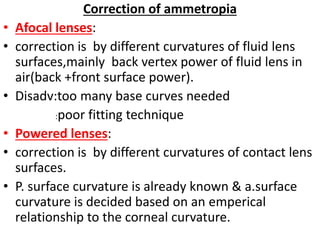
This document provides information on contact lenses, including their indications, contraindications, types, fitting procedures, parameters, complications, and special considerations. It discusses rigid gas permeable, soft, therapeutic, extended wear, disposable, and cosmetic contact lenses. Key details include the materials used to manufacture different contact lens types, advantages and disadvantages, fitting considerations like base curve and power, and potential post-fitting complications.






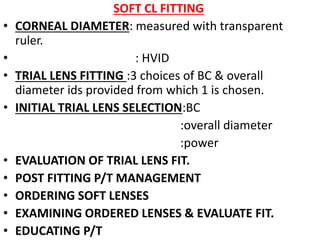
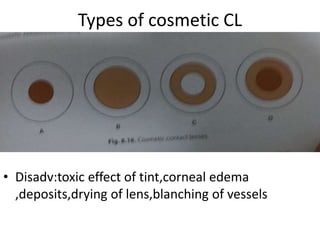
![SOFT CL
• Made of hydrogel[co-polymerisation products of
hydrophilic monomers with ethylene glycol
dimethyl acrylate].
• Hydrogel lens materials :HEMA
:HEMA VP
:MMA-PVD
:Glycidyl methacrylate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contactlens-170621160806/85/Contact-lens-7-320.jpg)


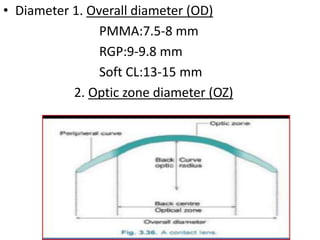





![• Diameter : 9mm in a p/t with avg corneal diameter &
palpebral aperture.
• BC usually flatter k reading.
• Astigmatism: BC is steeper than flatter k.
• 0.5-1 D BC 0.25 D steeper than flatter k.
• 1.0-2.0 D BC 0.5 D steeper than flatter k.
• >2D 1/3RD toricity shud b added to k 4 BC.
K1=44 K2=47, BC= 44 + [ 47-44]
3
• Power of trial lens=spectacle power in minus cylinder form
corrected 4 zero vertex distance.
Specs power : -9.25/+0.50x90⁰
Minus power form : -8.75/-0.50x 180⁰
Vertex distance : 15 mm
CL power : -7.75/ -0.50X180⁰](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contactlens-170621160806/85/Contact-lens-19-320.jpg)