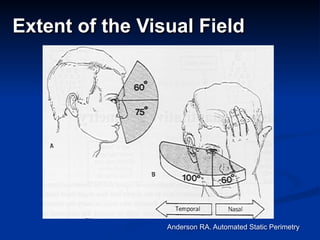
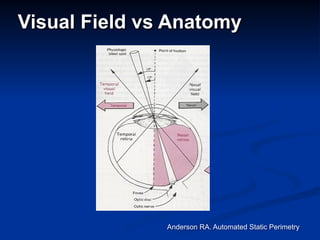
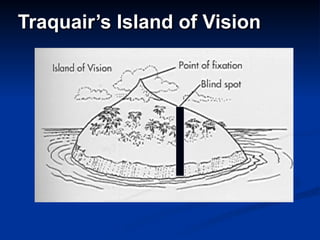
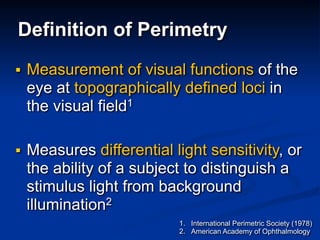
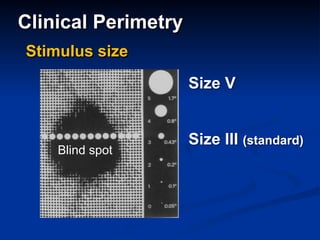
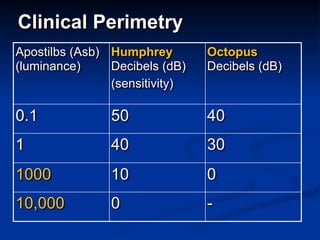
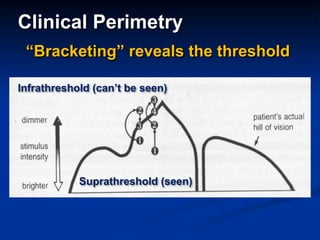
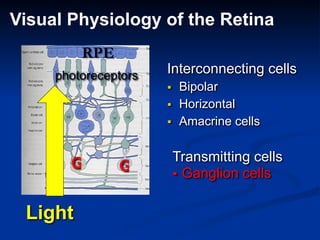
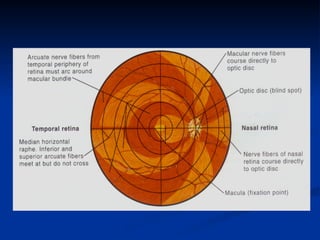
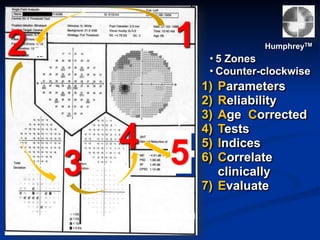
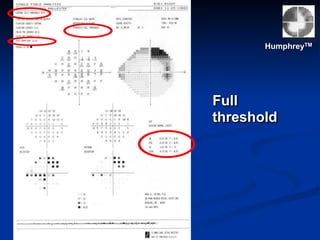
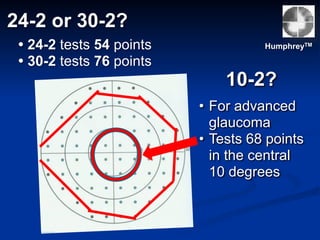
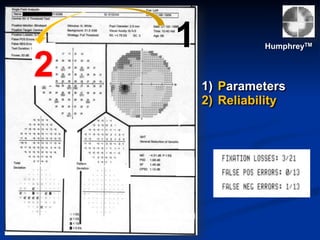
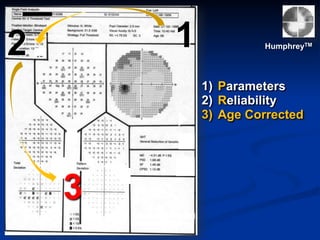
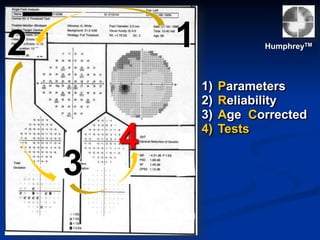
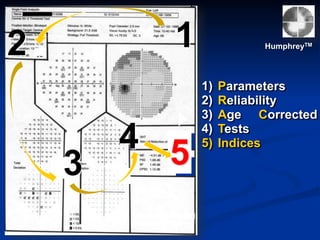
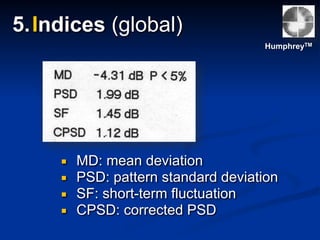
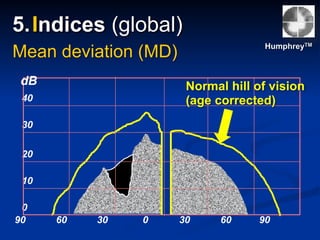
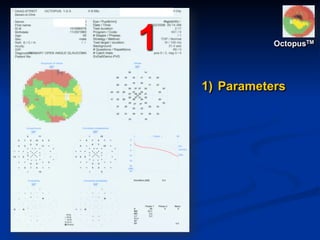
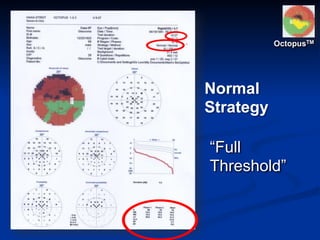
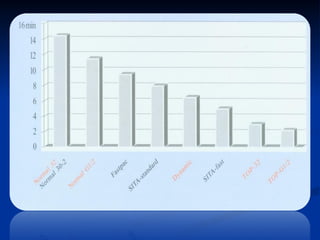
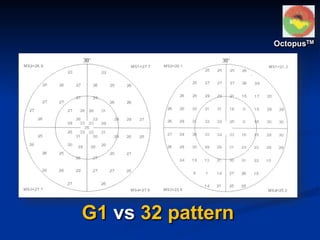
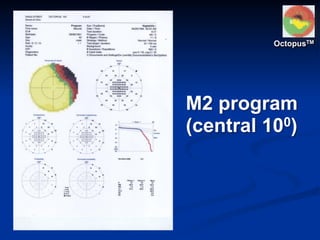
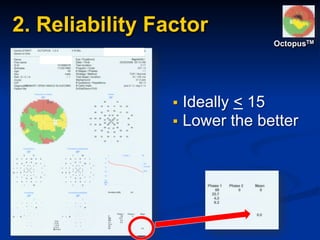
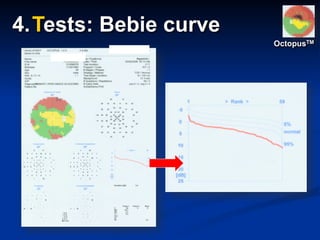
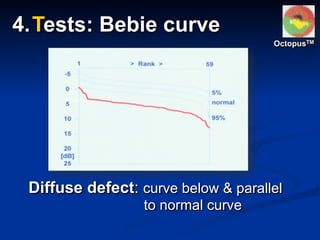
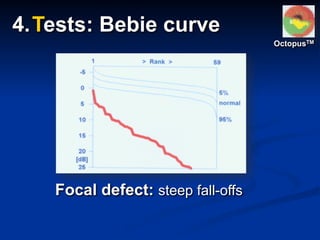
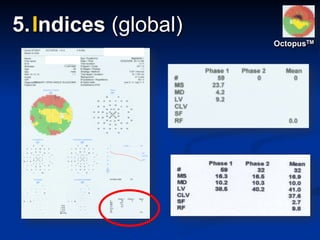
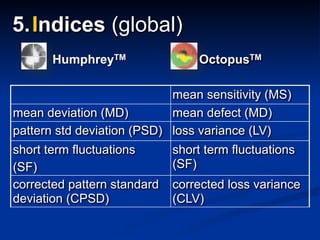
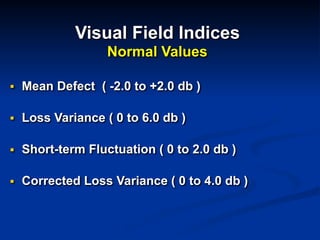
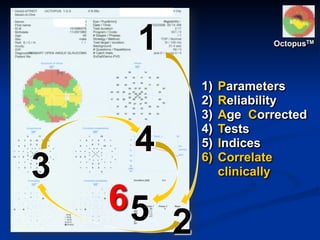
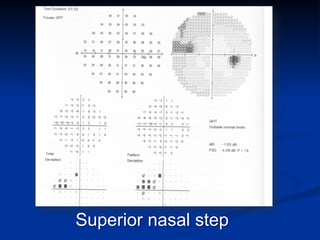
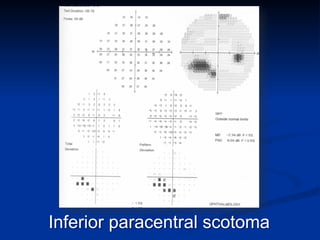
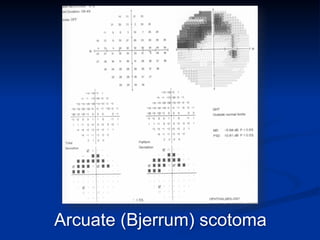
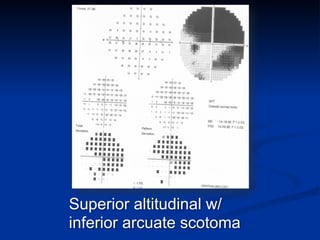
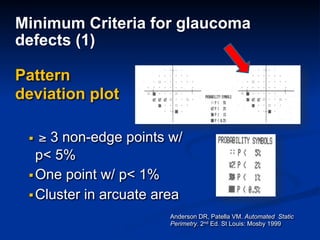
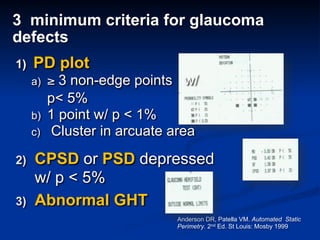
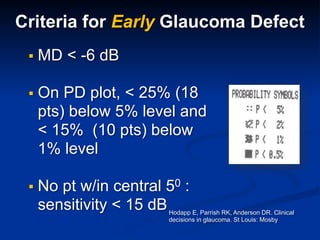
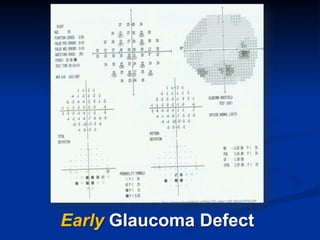
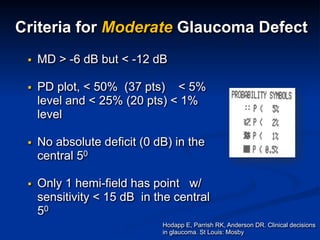
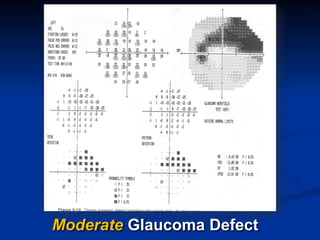
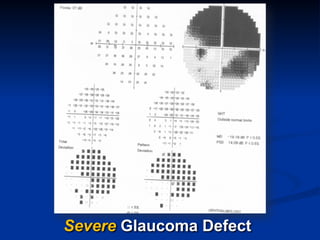
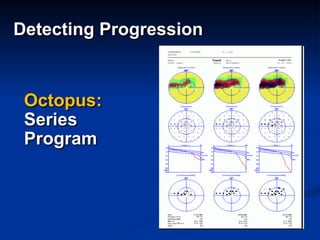
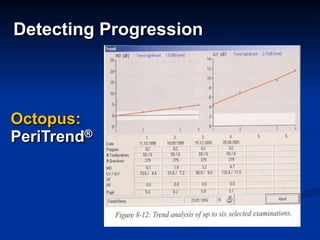
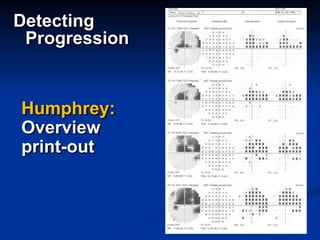
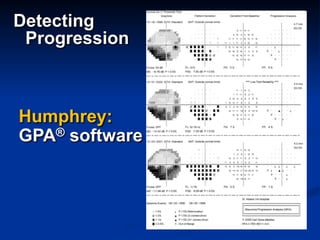
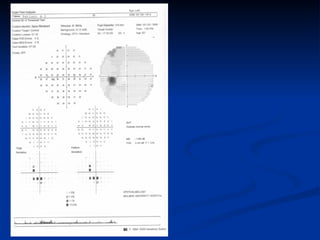
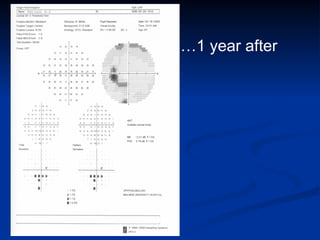
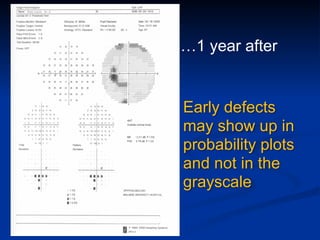
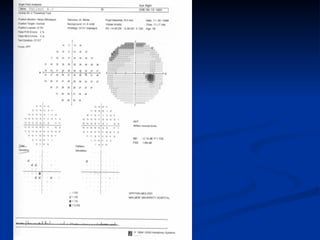
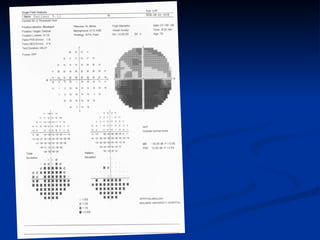
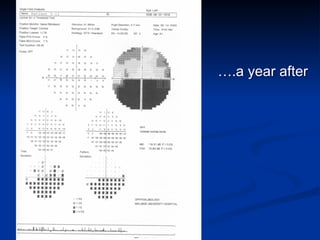
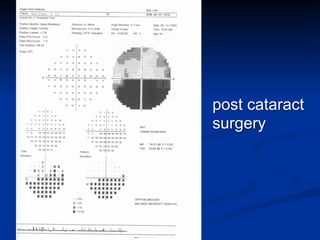
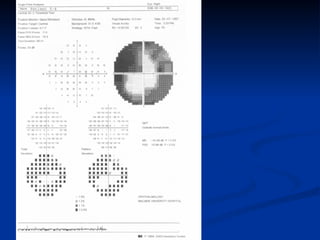
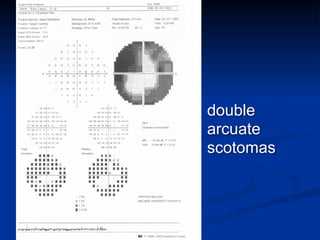
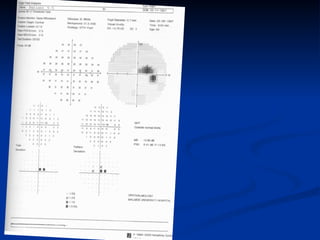
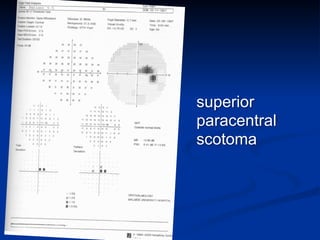
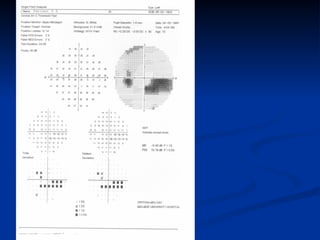
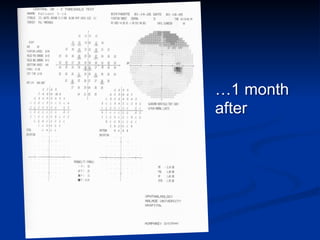
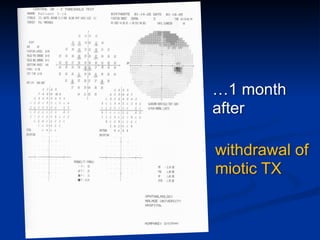
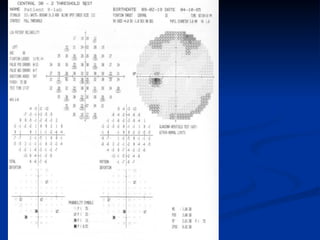
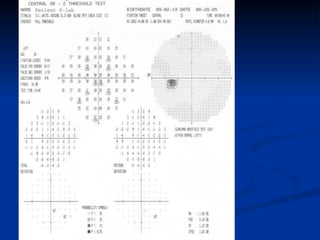
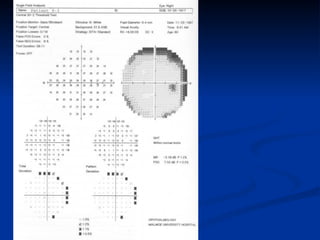
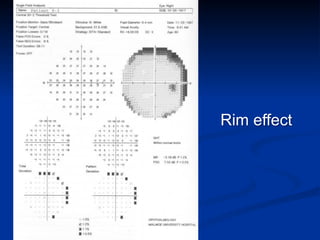
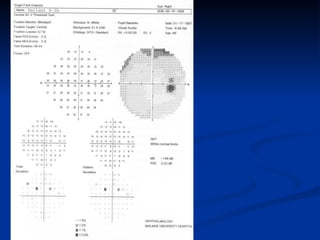
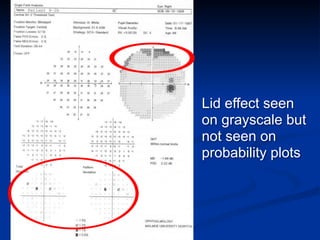
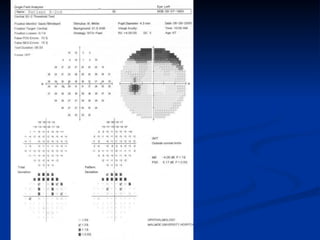
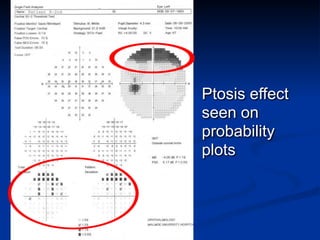
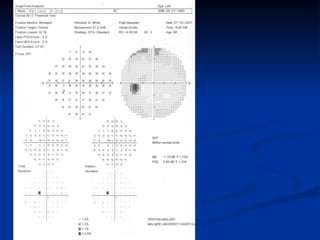
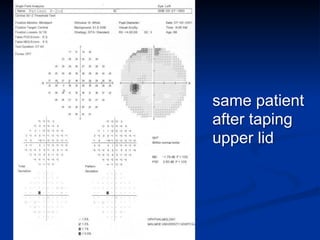
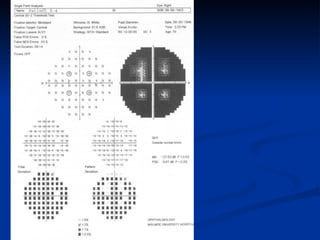
The document discusses visual field testing in glaucoma. It defines the visual field and perimetry, and describes the major types of clinical perimetry tests including full threshold, SITA standard, and SITA fast on Humphrey and normal, dynamic, and TOP strategies on Octopus. It explains parameters such as test patterns, reliability, age-corrected plots, tests like GHT and Bebie curve, and global indices including MD, PSD, SF, and CPSD. The purpose of visual field testing in glaucoma is to detect and monitor disease by measuring light sensitivity across the retinal field.