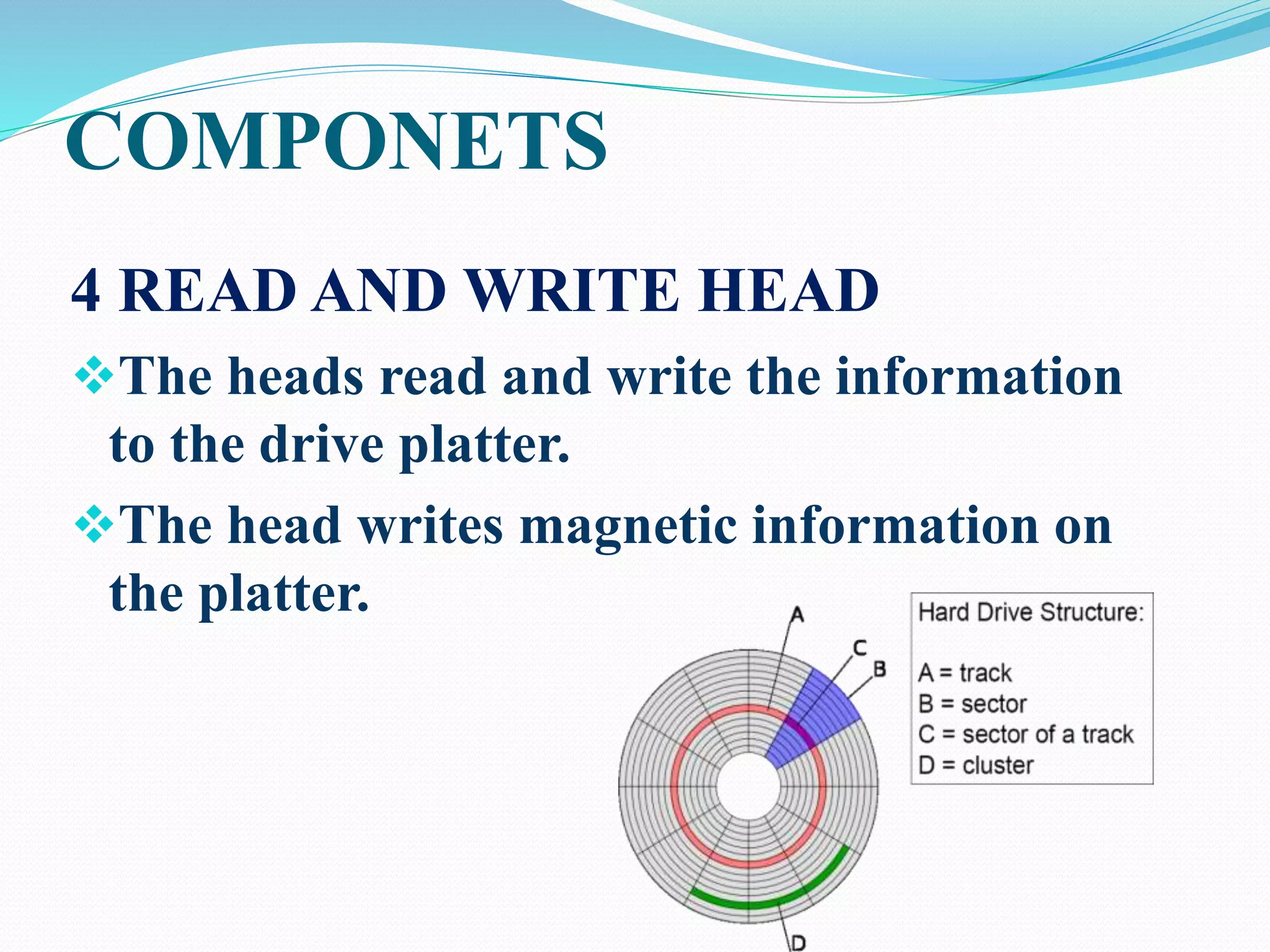
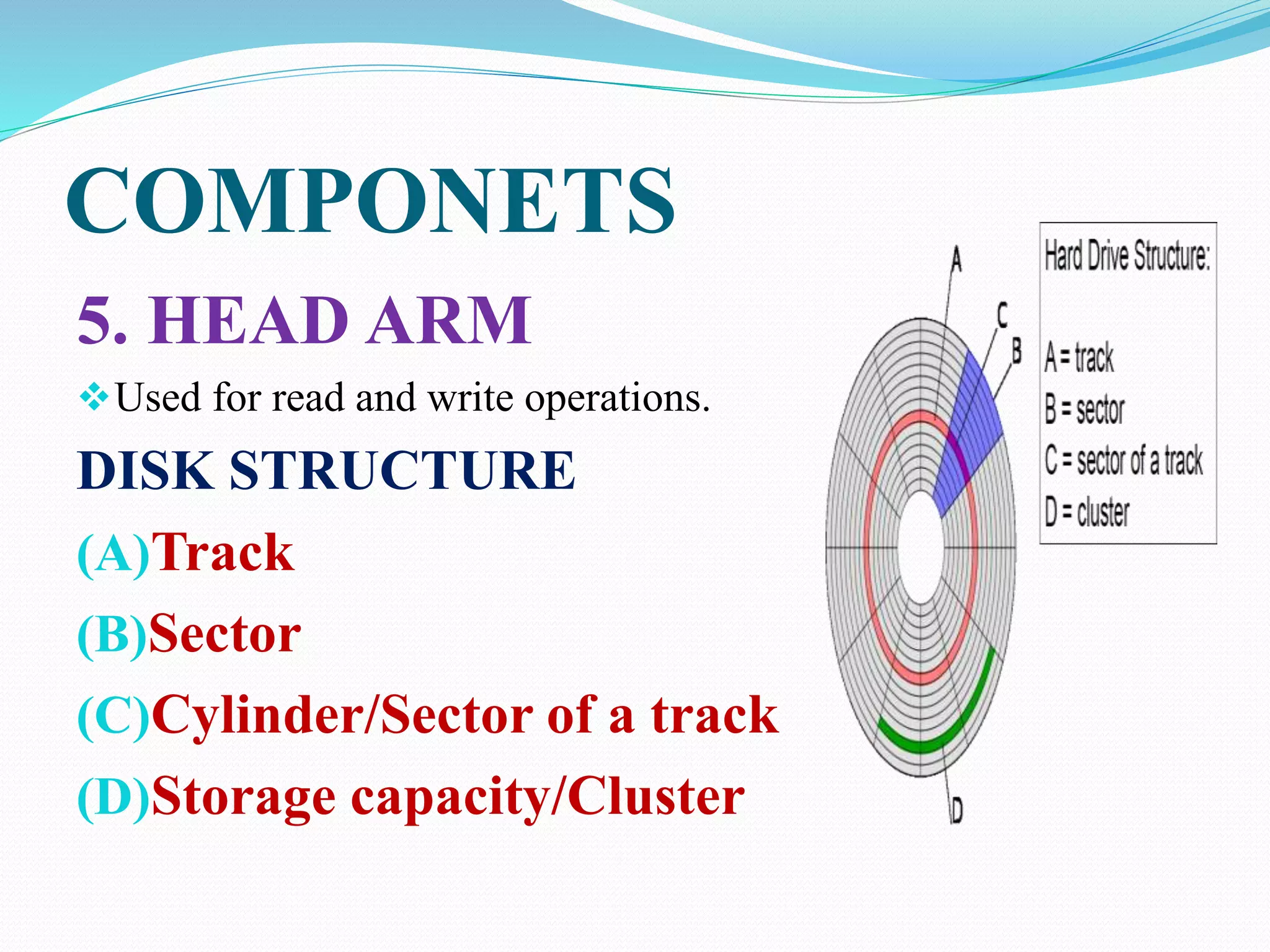
This document discusses the components and structure of a hard disk drive. It begins by defining a hard disk drive as a data storage device that uses rapidly rotating disks coated with magnetic material to store and retrieve data in a random access manner. The key components of a hard disk drive are then outlined, including disk platters, stepper motors, spindle motors, read/write heads, and arms. The document also explains the disk structure of tracks, sectors, and cylinders. It concludes by noting how hard disks have revolutionized data storage and the digital age.