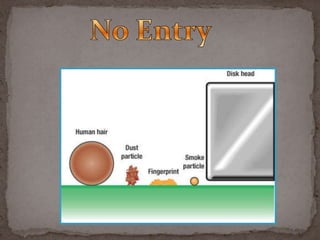
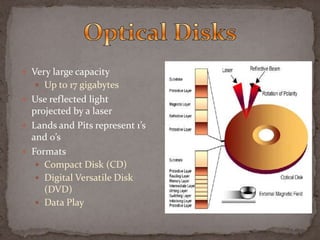
Primary memory, also known as main memory or internal memory, is directly accessible to the CPU and holds temporary data during program execution. It includes RAM, ROM, PROM, and EPROM. Secondary memory, also called external memory or auxiliary memory, provides larger storage and retains data when power is removed. Common examples are hard disks, CD-ROMs, magnetic tapes, and flash memory. Secondary memory is organized into files and directories for abstraction and includes additional metadata.