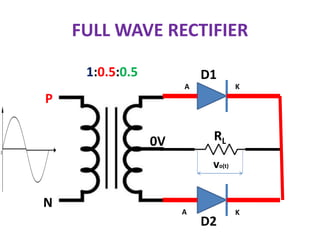
A rectifier converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) using diodes. There are two main types: half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. Half-wave rectifiers use a single diode and only conduct during one half of the AC cycle, resulting in lower output. Full-wave rectifiers use either a center-tapped transformer or diode bridge to conduct on both halves of the cycle, providing higher efficiency and output. Rectifiers are used in applications that require DC power such as battery chargers, DC power supplies, welders, and motor drives.