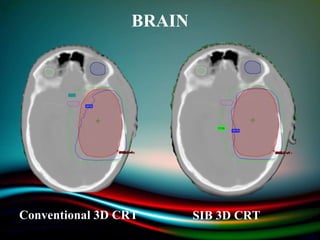
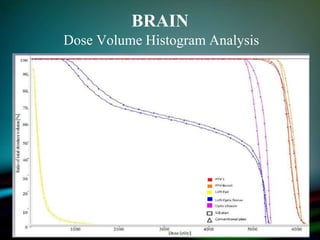
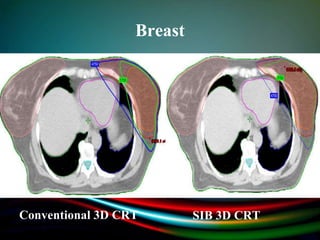
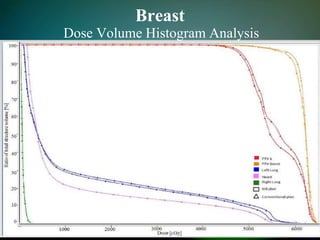
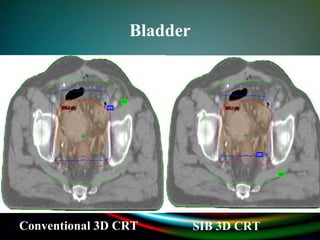
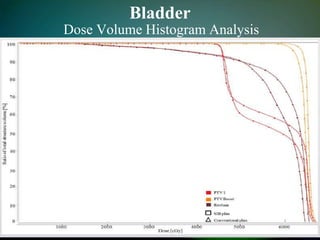
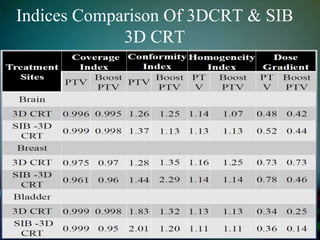
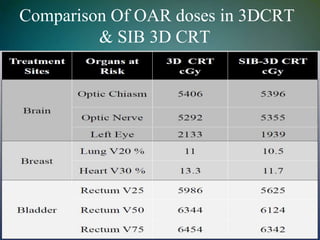
Simultaneously integrated boost (SIB) allows different doses to be delivered simultaneously to the planning target volume (PTV) and gross tumor volume (GTV), reducing the number of fractions needed. SIB provides a greater biological effective dose while allowing individual dose optimization to both targets in a single plan, overcoming limitations of conventional fractionation. An institutional study compared SIB to conventional 3D conformal radiation therapy in 30 patients with brain, breast, or bladder cancer, finding SIB reduced maximum doses to targets and organs at risk while shortening treatment duration by about a week.





![Biological Effective Dose
•BED is an approximate quantity by which different
radiotherapy regimens may be compared.
•BED = nd [1+d/(α/β)]
where n = no. of fractions
d = dose per fraction
nd = total dose](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sib-150530044839-lva1-app6891/85/Sib-si-6-320.jpg)