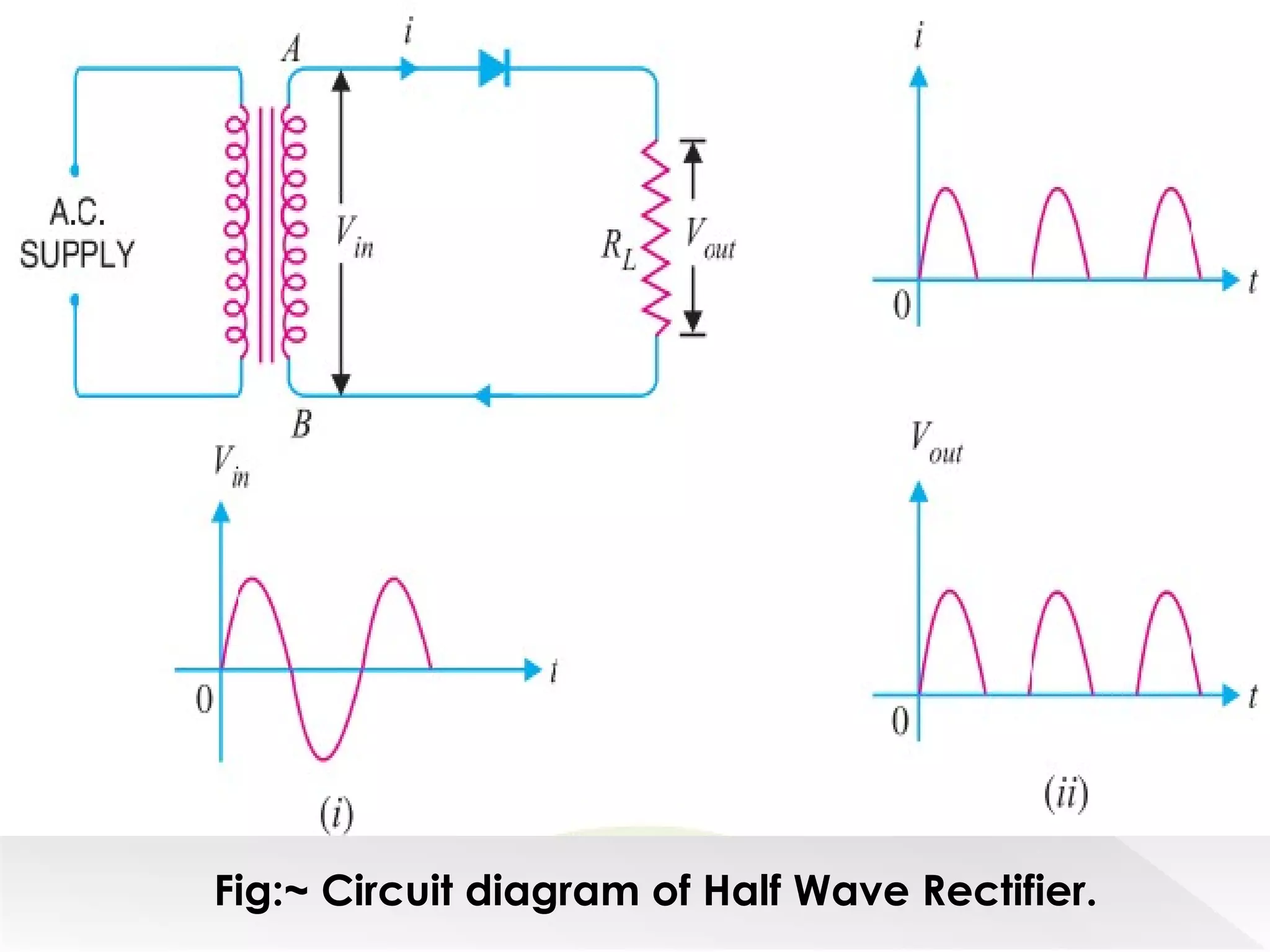
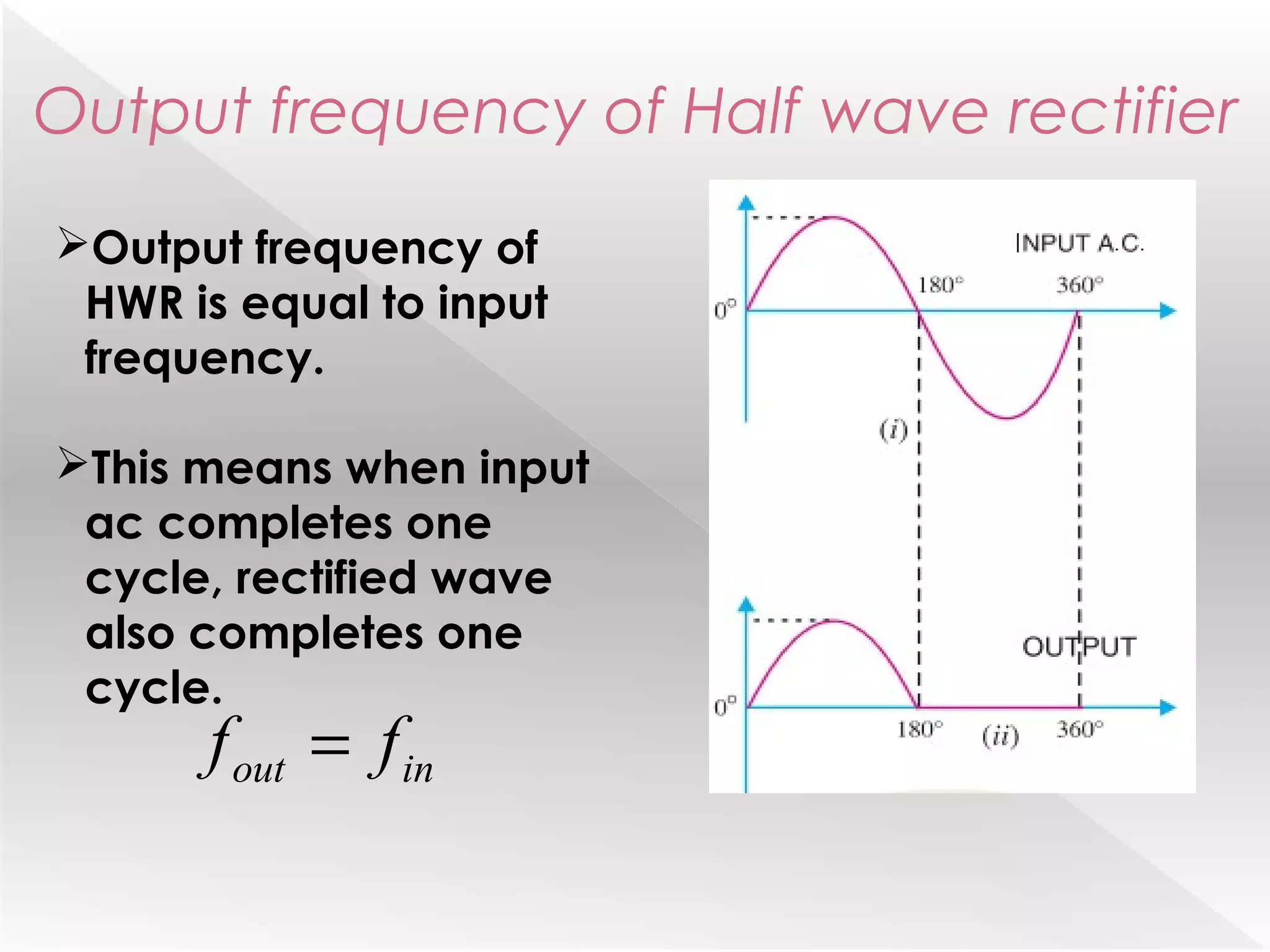
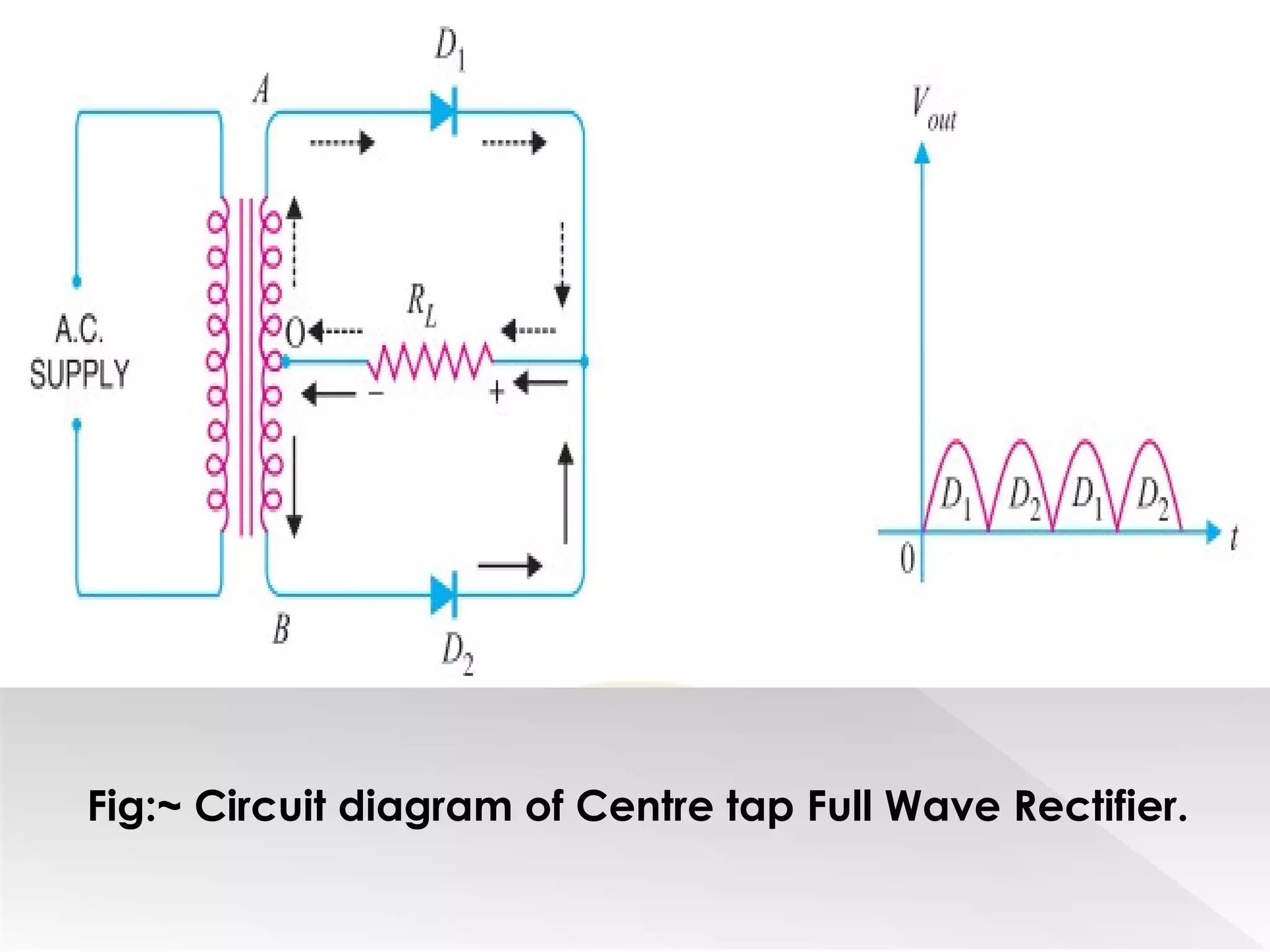
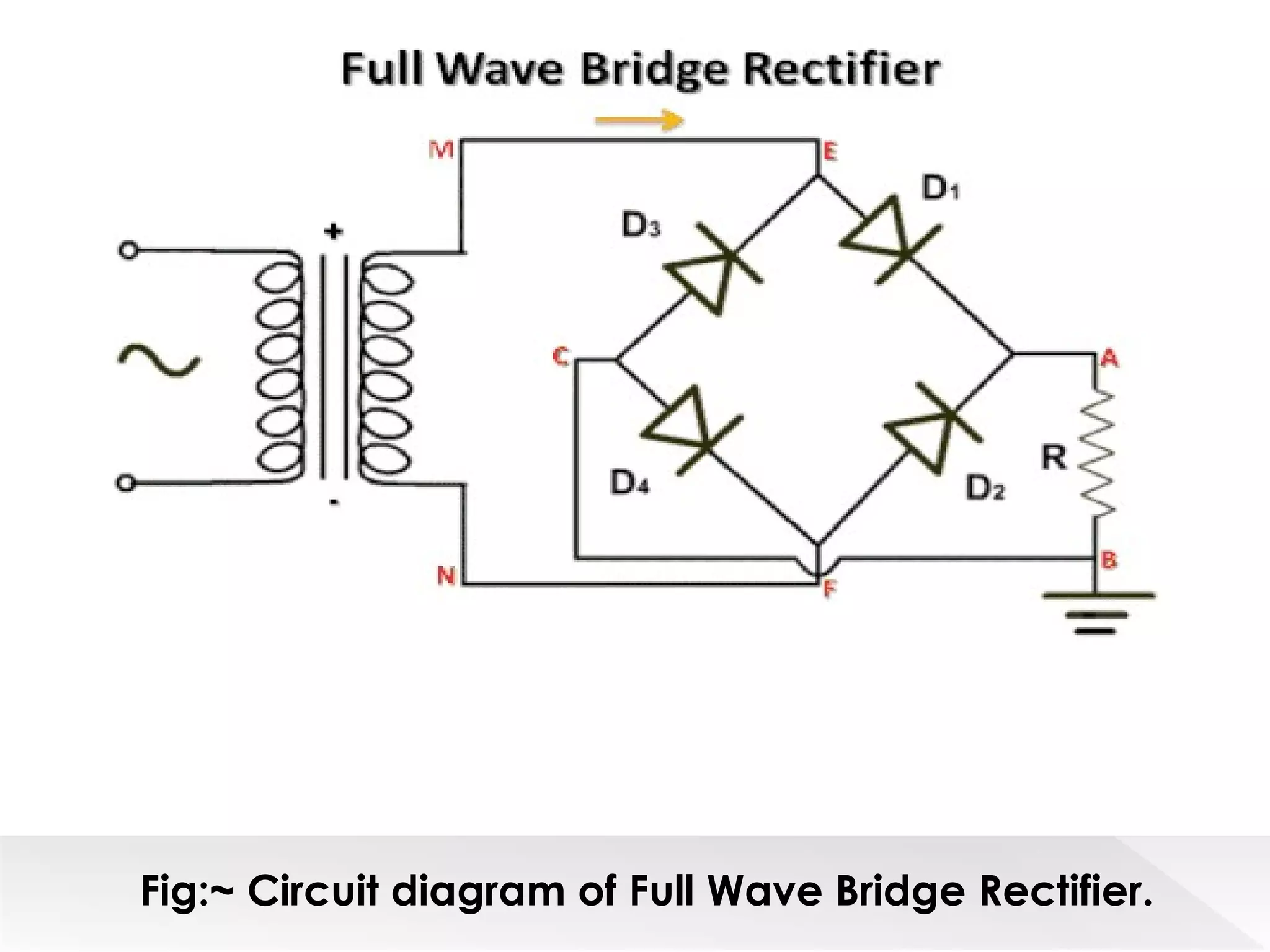
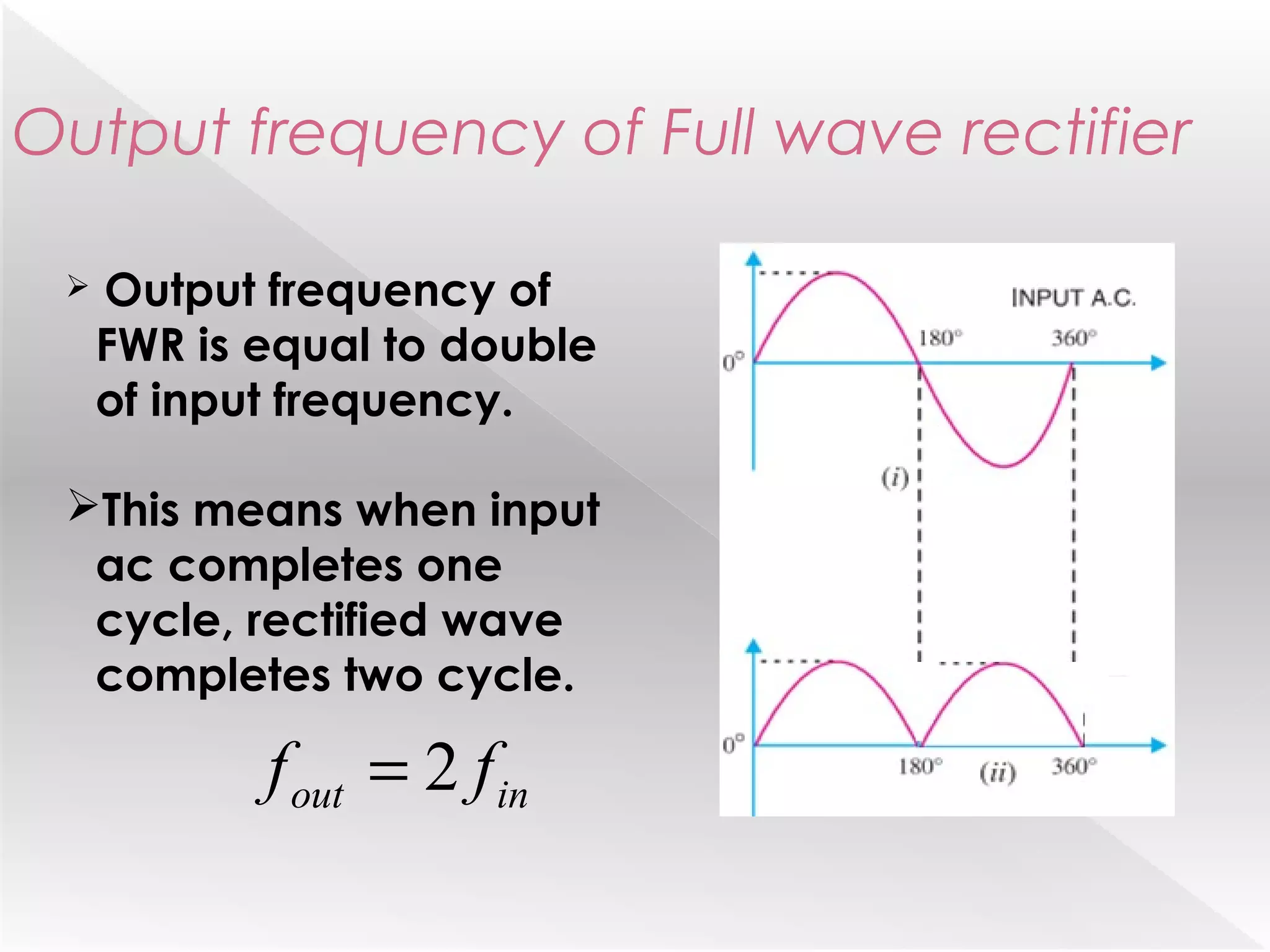
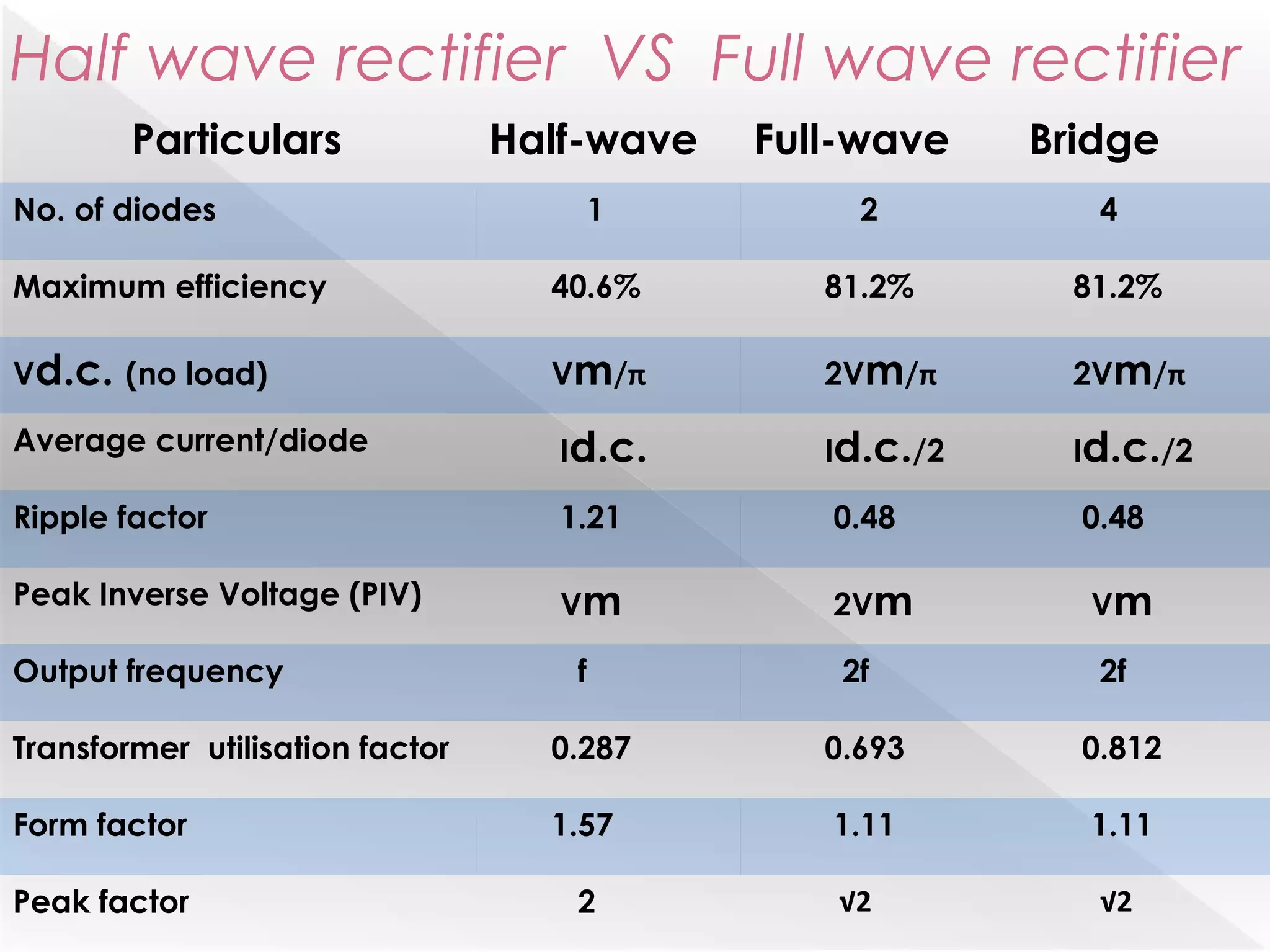
This document summarizes half wave and full wave rectifiers. It describes that a rectifier converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) through a process called rectification. There are two main types - half wave and full wave rectifiers. A half wave rectifier only conducts during the positive half cycle of the input AC signal, while a full wave rectifier conducts during both half cycles using two diodes or a diode bridge. Full wave rectifiers have higher efficiency and output than half wave rectifiers but require more diodes. The document provides circuit diagrams and explanations of operation for both half wave and full wave rectifier configurations.