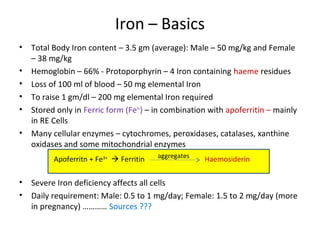
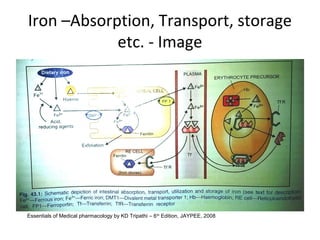
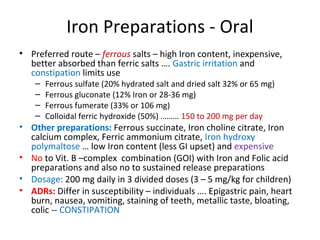
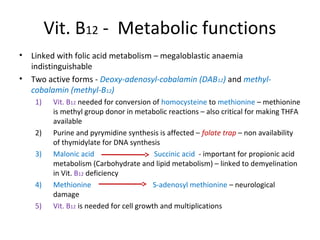
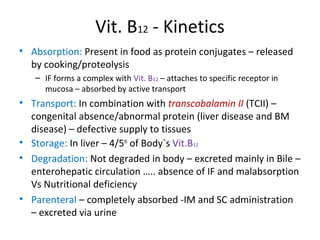
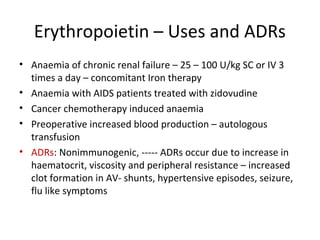
This document discusses haematinics, which are substances required for blood formation and used to treat anaemias. It focuses on iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid. Iron is essential for haemoglobin synthesis and is absorbed in the small intestine. Deficiencies can cause anaemia. Vitamin B12 and folic acid are also essential for red blood cell formation and preventing megaloblastic anaemia. The document provides details on the metabolism, deficiencies, and treatments of these important haematinics.