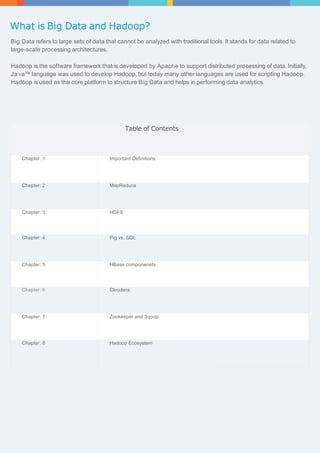
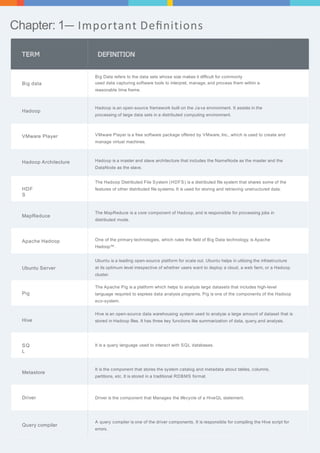
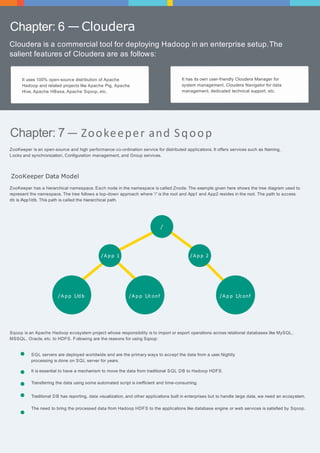
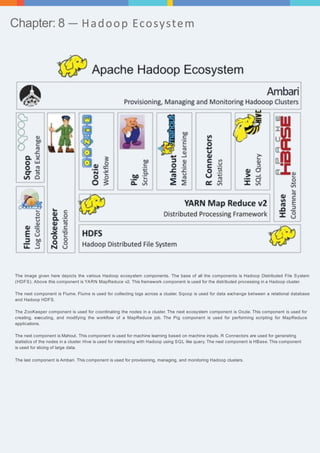
The document provides an overview of big data and Hadoop, detailing the definitions and functionalities of Hadoop as a framework for distributed data processing. It covers key components such as HDFS, MapReduce, Hive, and HBase, as well as tools like Sqoop and Zookeeper, which enhance the Hadoop ecosystem. Each chapter elaborates on specific aspects of these technologies, including architecture, data handling, and integration for managing large datasets.