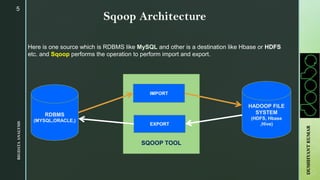
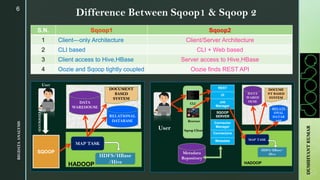
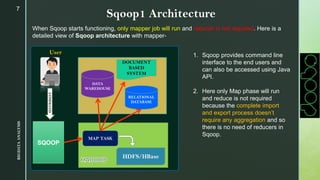
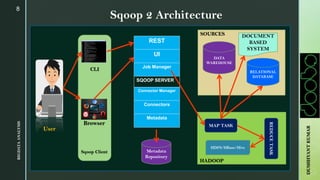
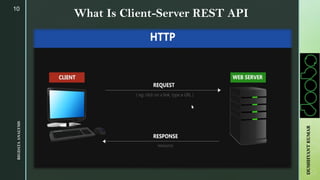
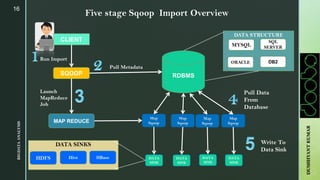
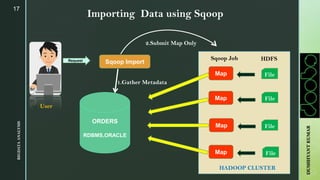
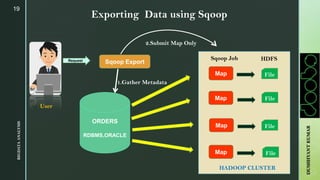
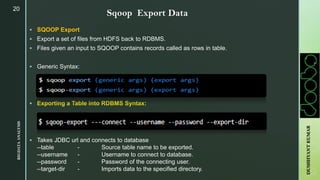
The document provides an overview of Apache Sqoop, a tool in the Hadoop ecosystem used for transferring data between HDFS and relational databases. It covers its architecture, features, the differences between Sqoop 1 and Sqoop 2, and the use of REST APIs for integration. Additionally, it discusses data import/export processes, including full and incremental loads, and highlights Sqoop's limitations.