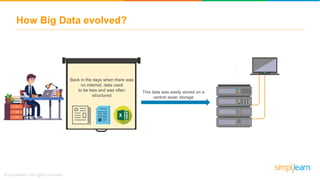
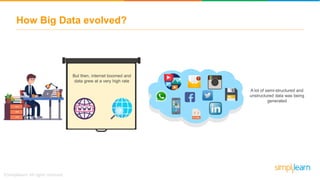
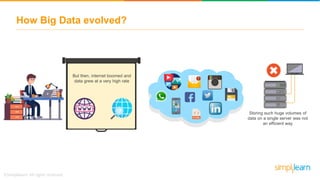
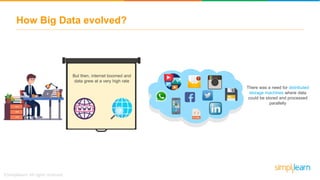
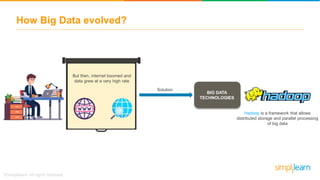
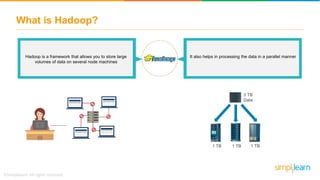
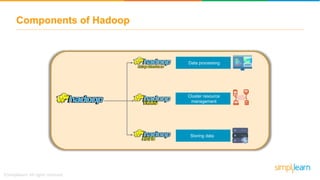
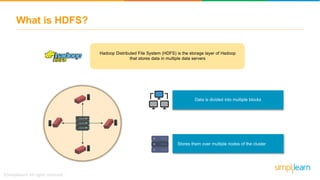
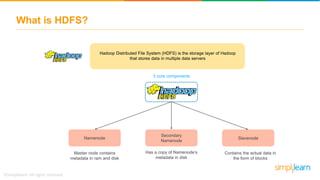
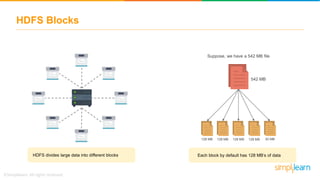
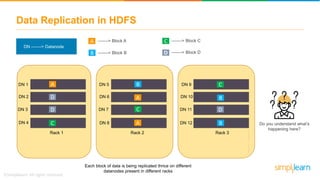
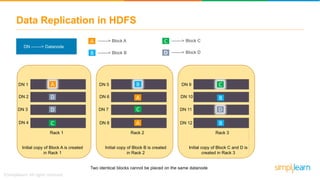
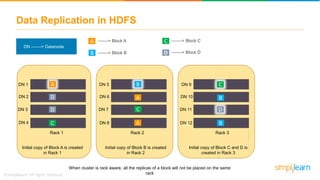
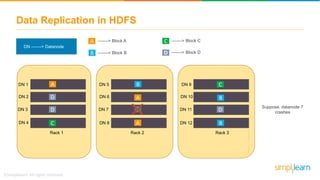
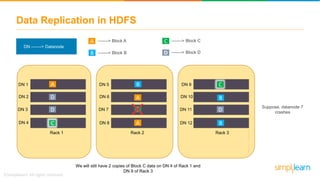
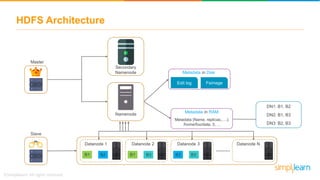
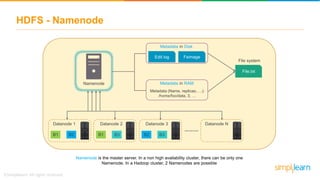
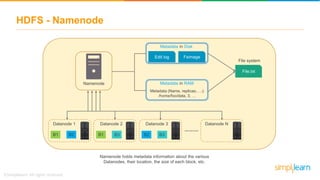
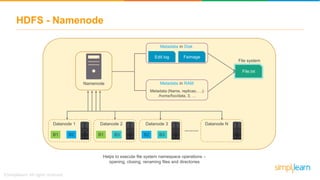
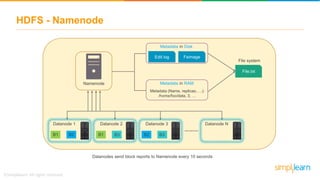
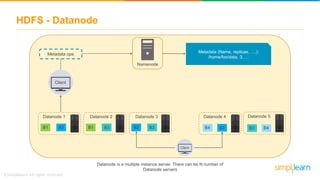
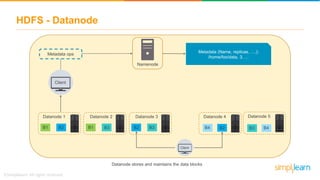
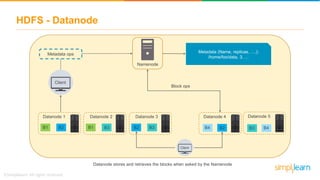
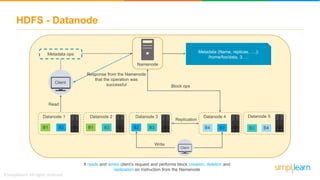
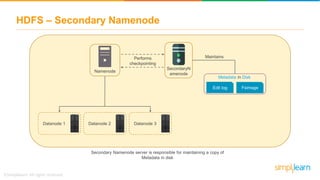
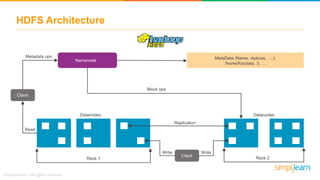
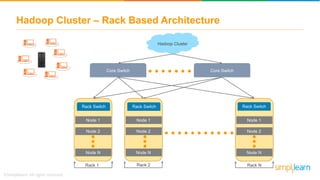
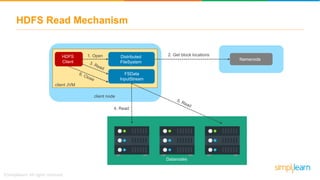
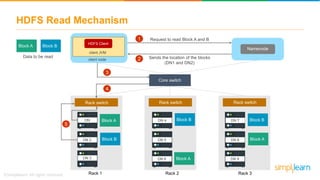
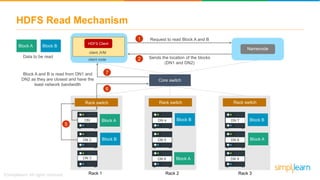
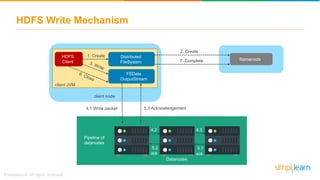
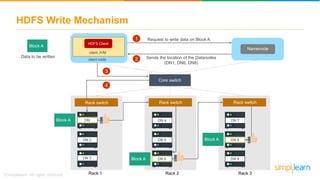
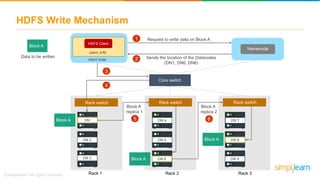
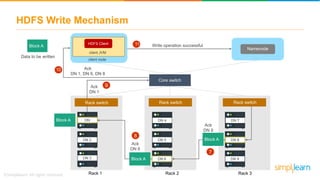
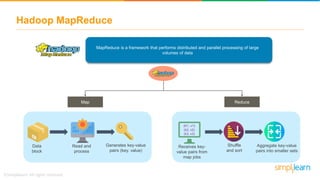
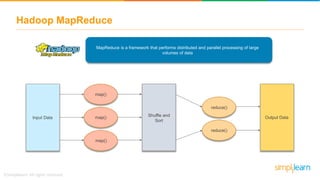
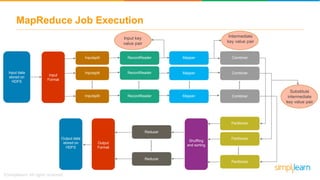
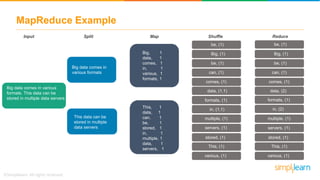
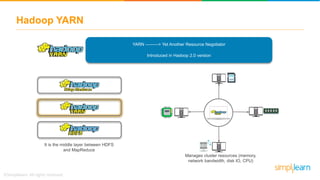
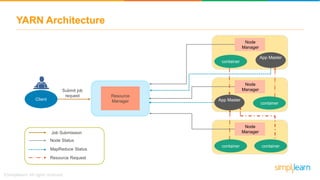
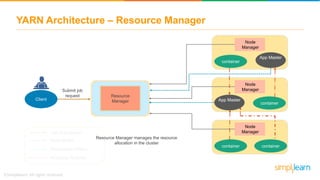
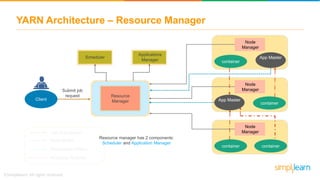
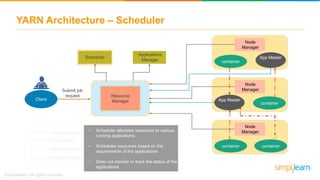
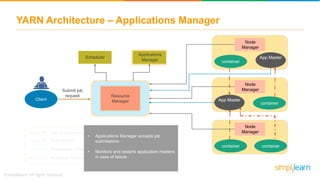
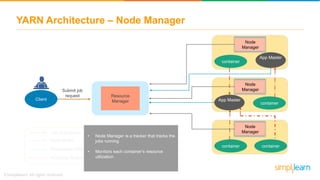
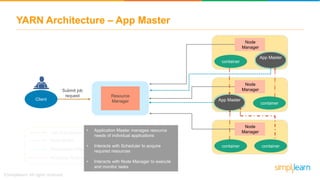
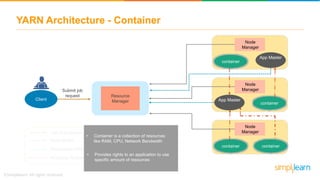
The document discusses the evolution of big data from a structured format stored on central servers to the distributed storage systems enabled by the internet, highlighting the role of Hadoop in managing large volumes of semi-structured and unstructured data. It explains the Hadoop architecture, specifically the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), which organizes data across multiple servers, and the processing capabilities through MapReduce and YARN. Additionally, it outlines the responsibilities of various components within the Hadoop ecosystem, such as namenodes, datanodes, and application masters.