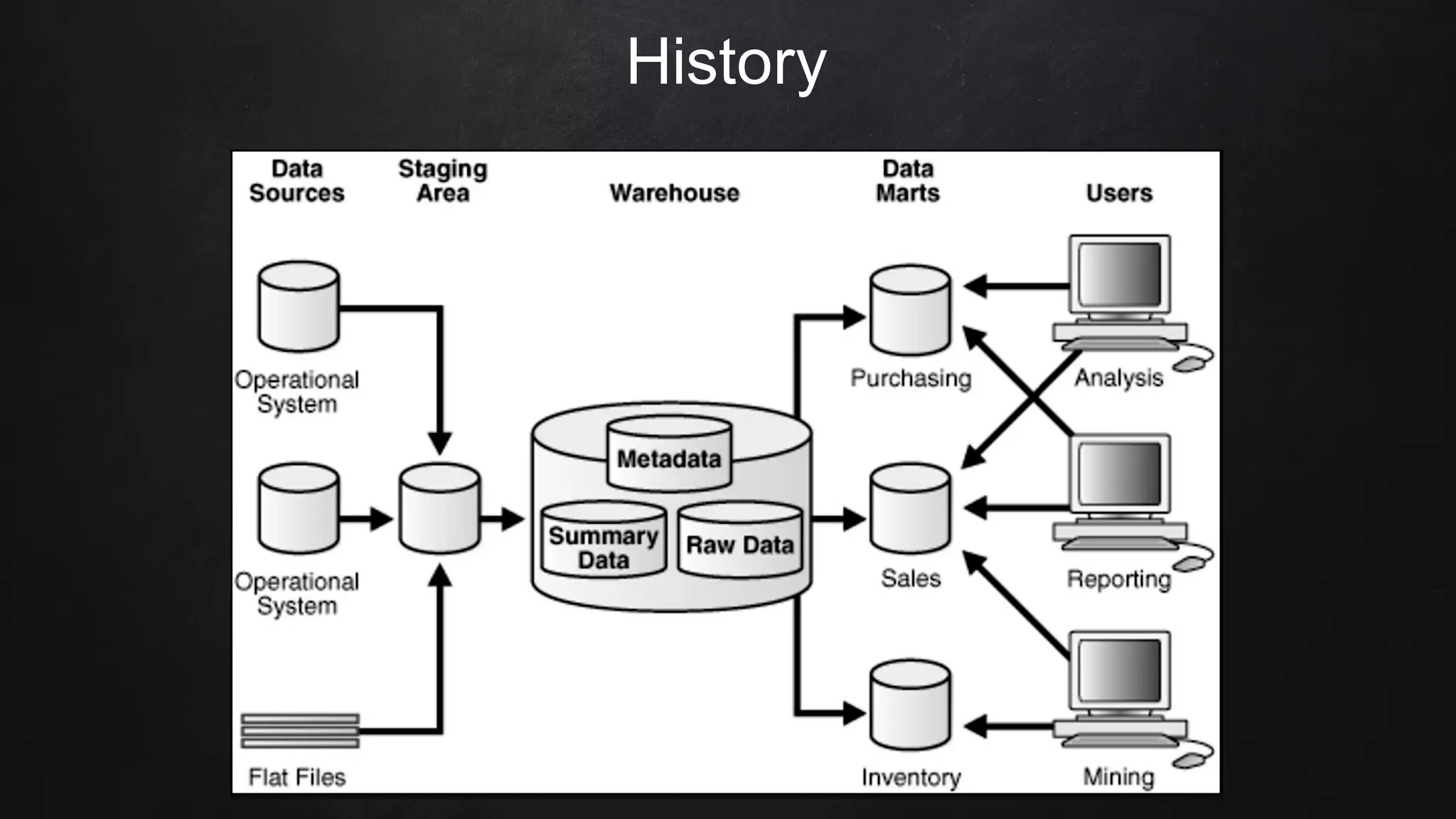
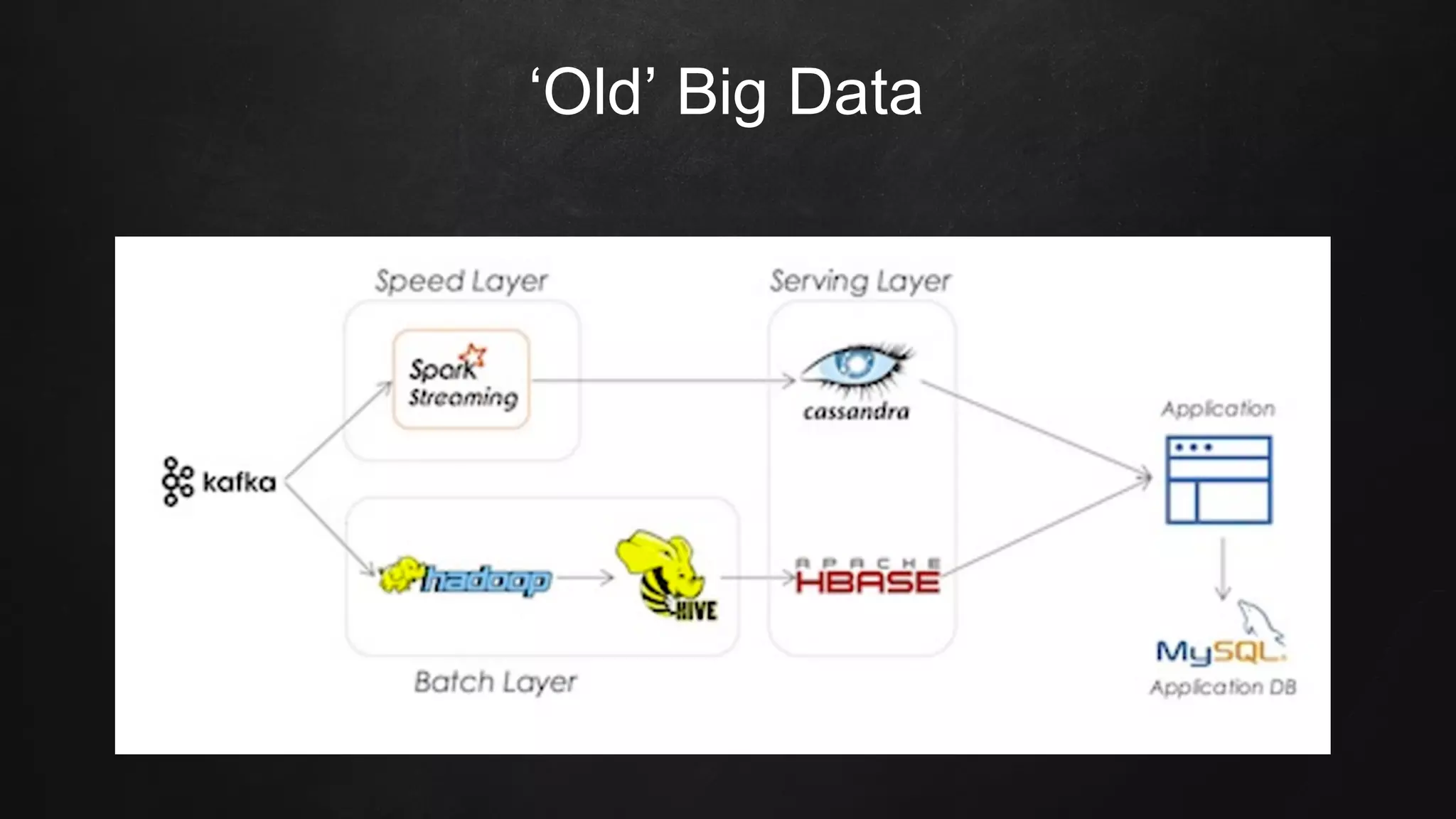
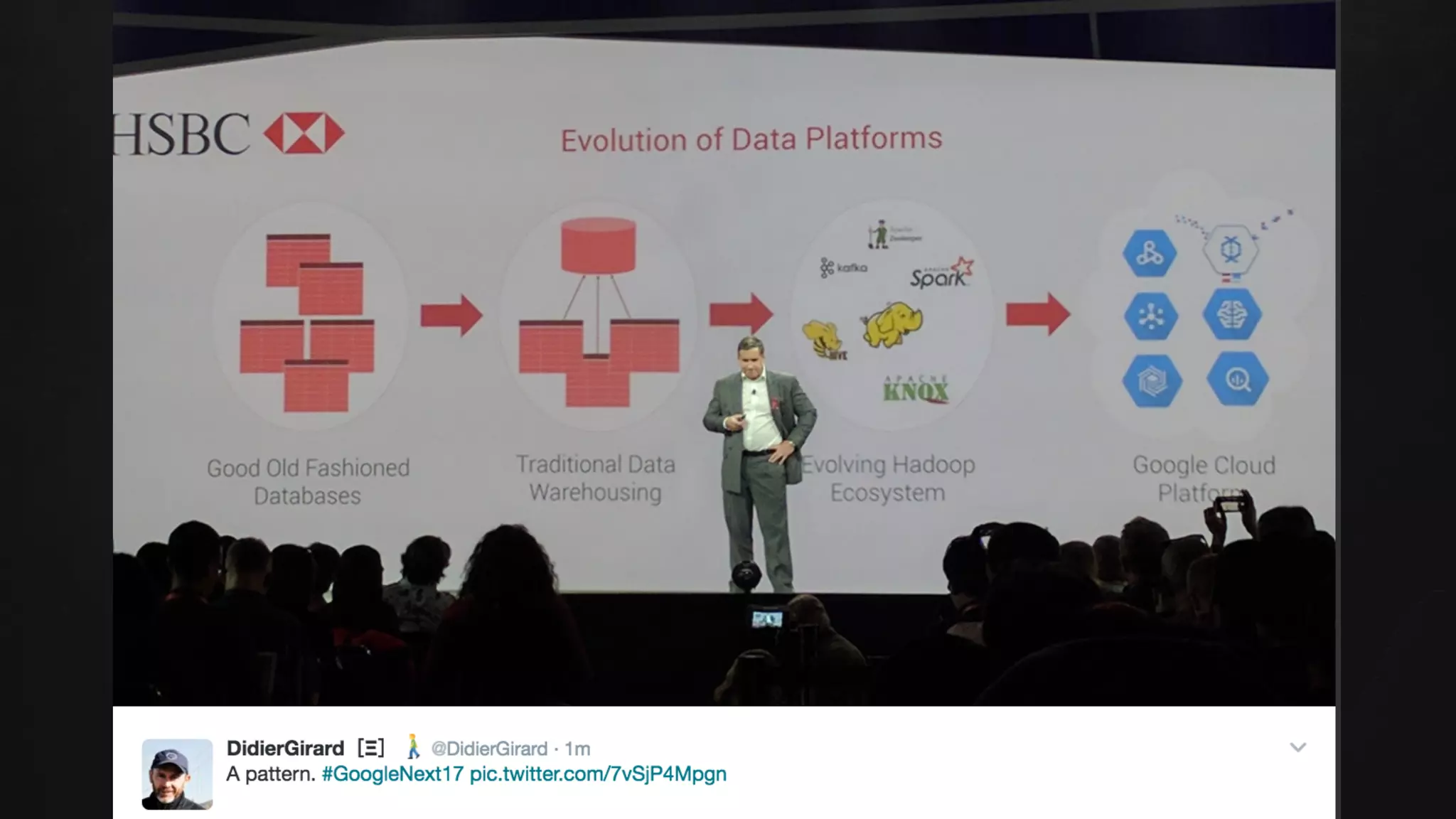
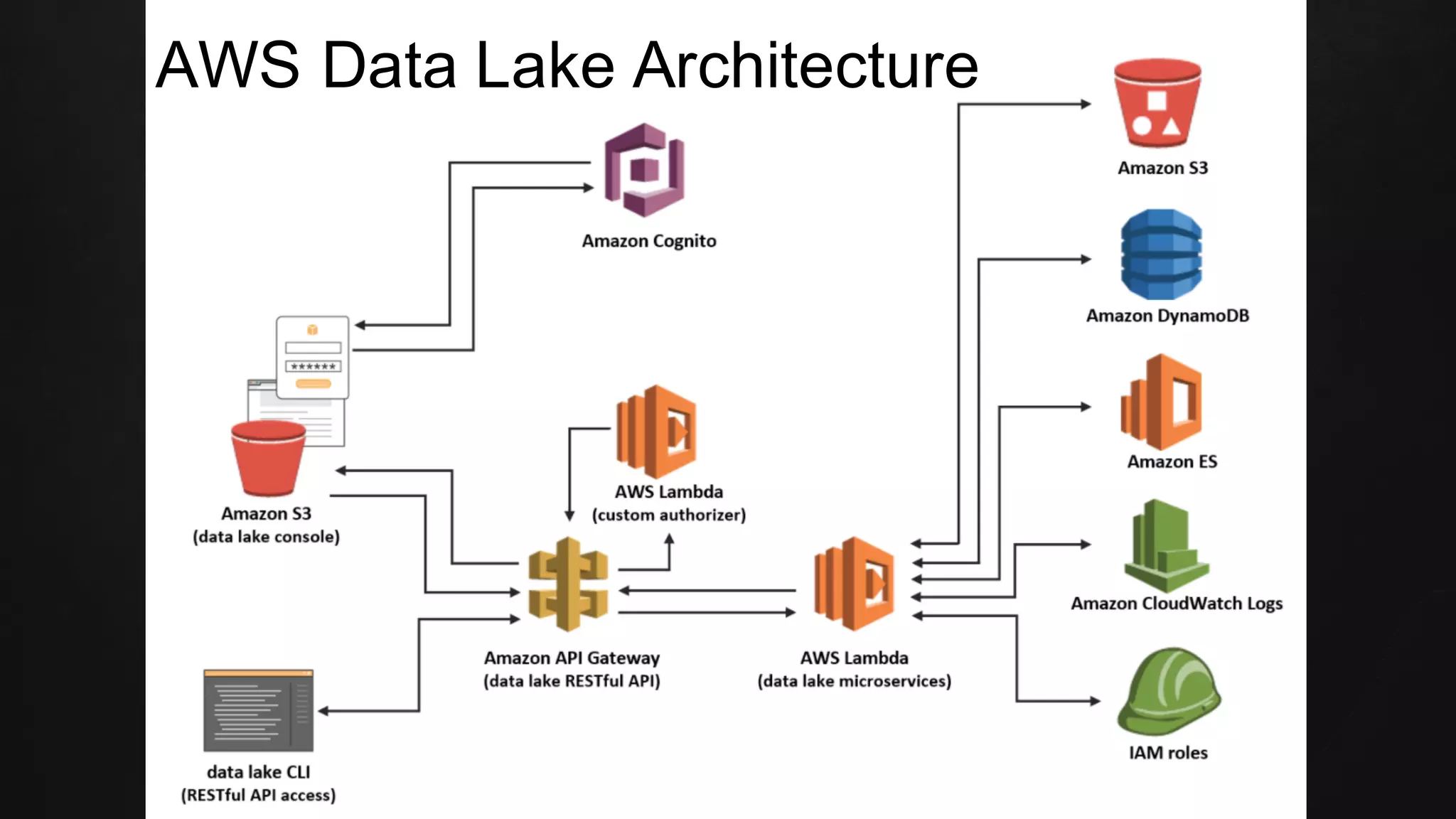
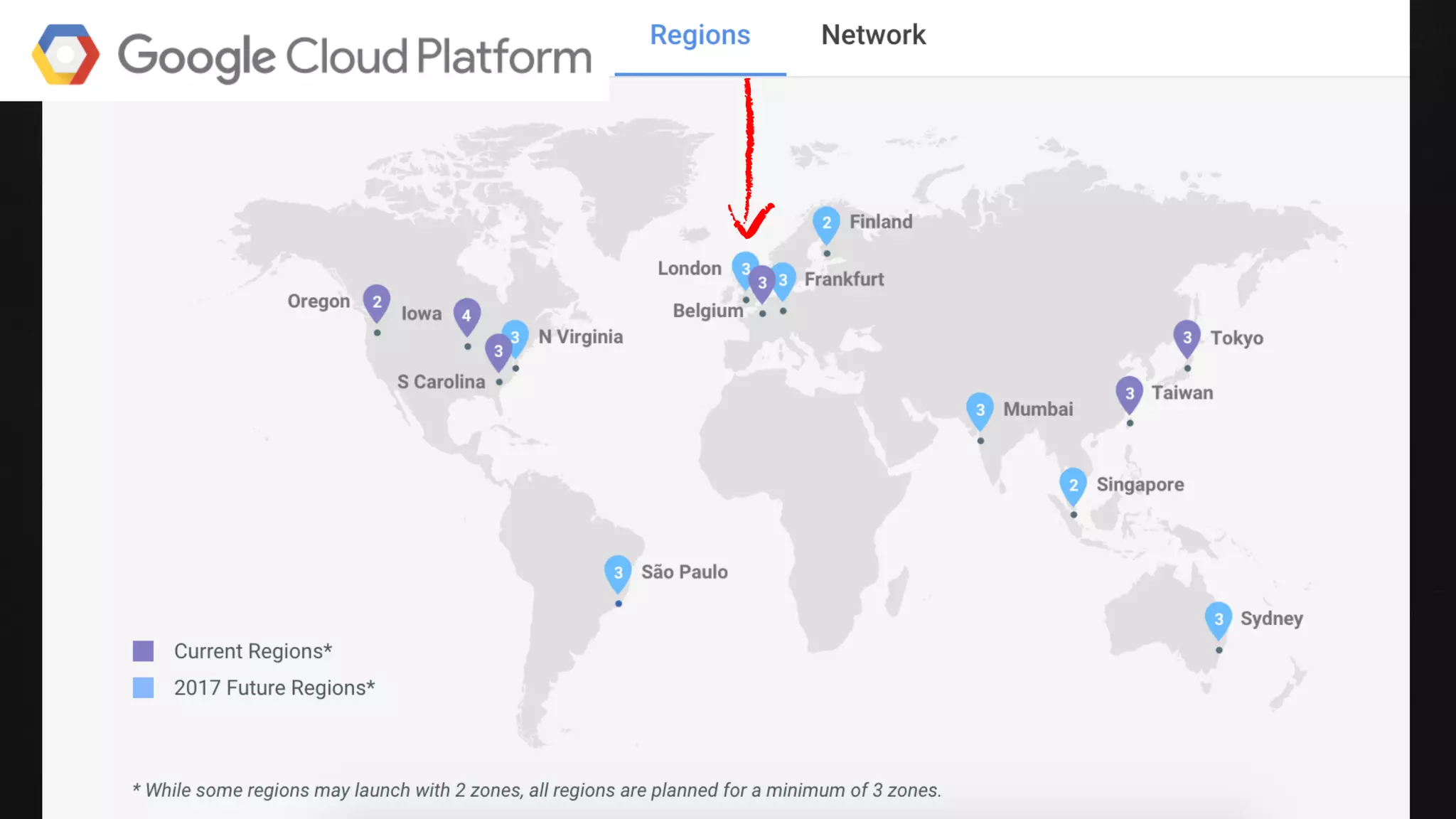
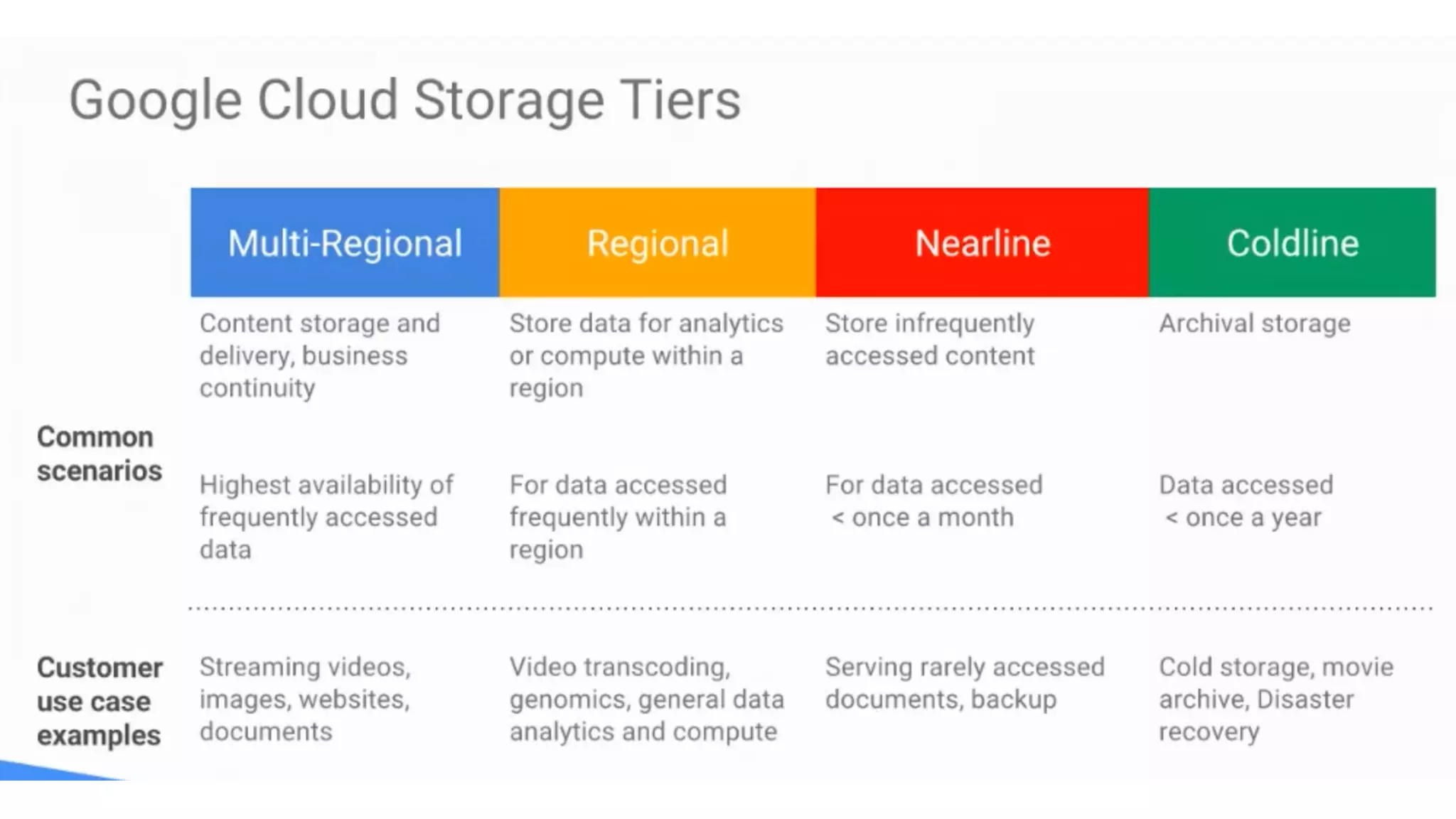
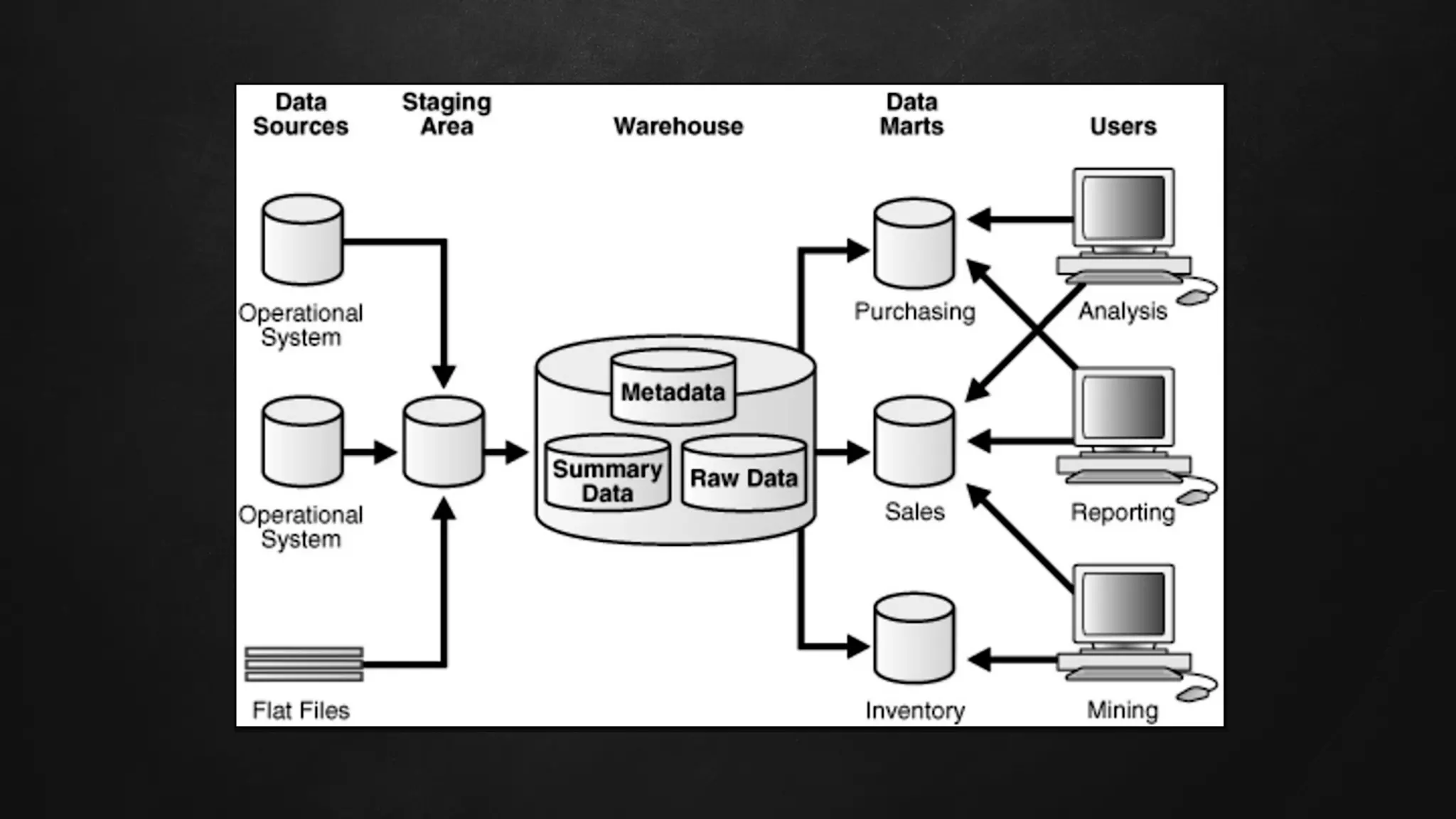
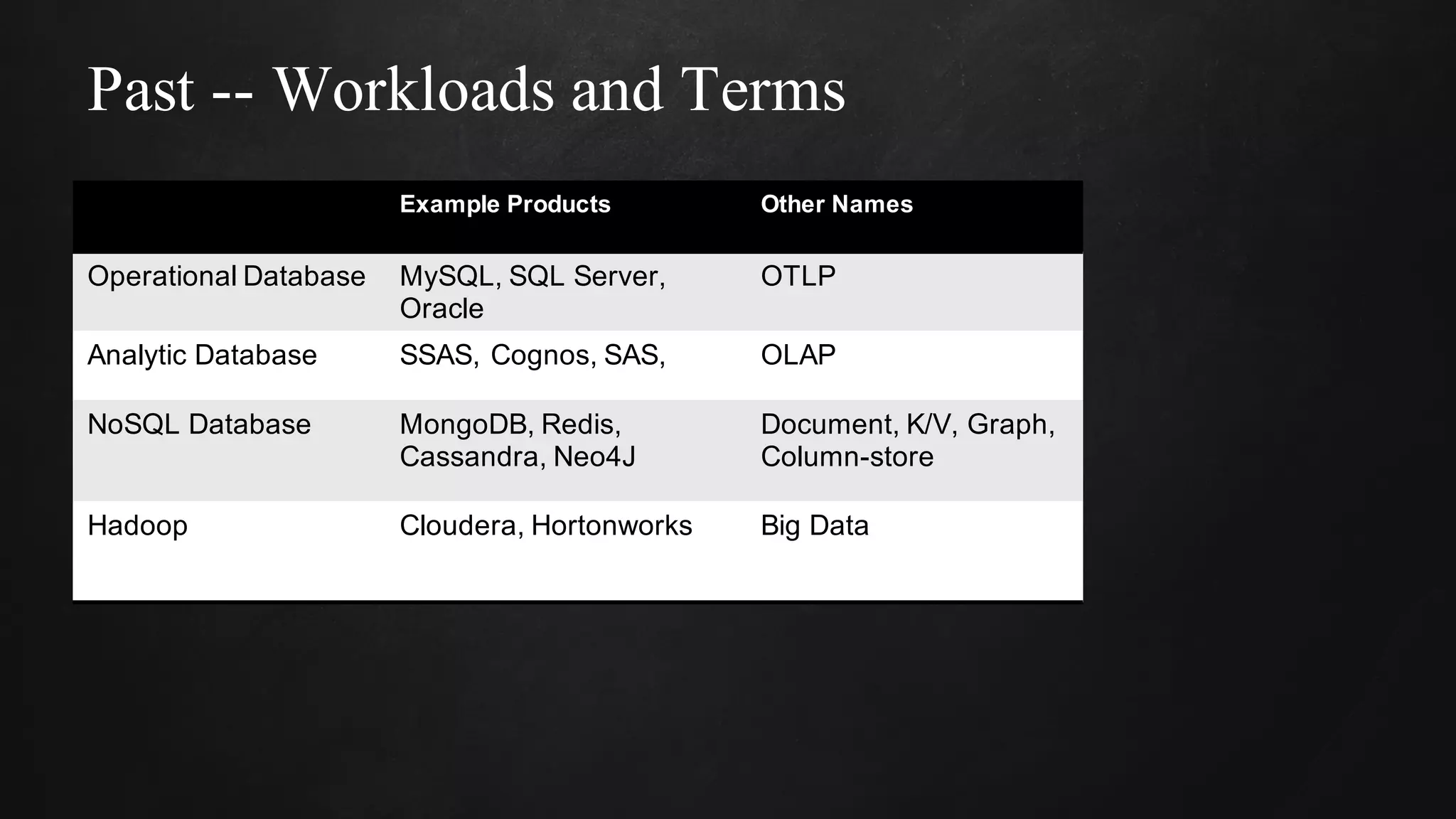
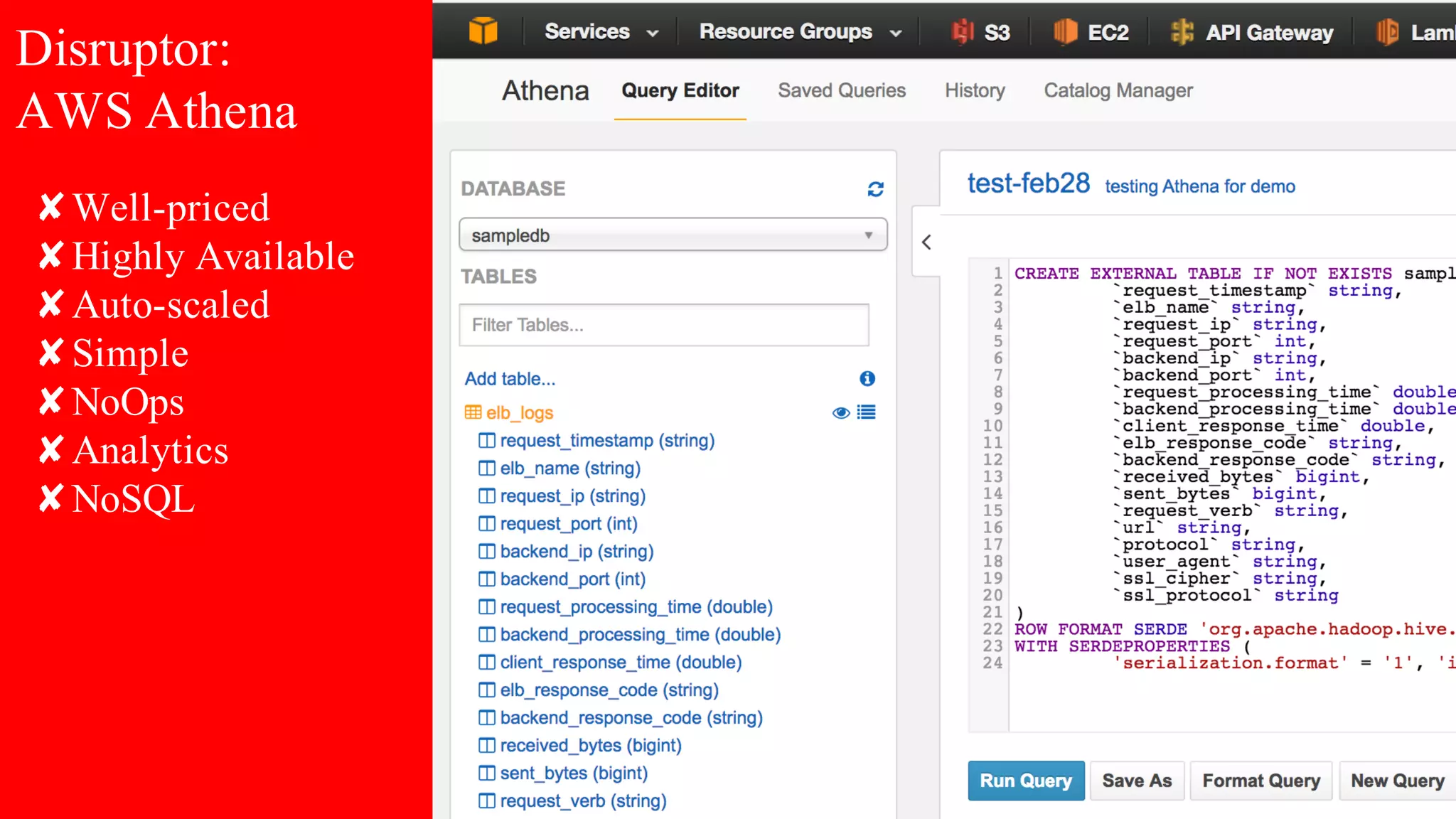
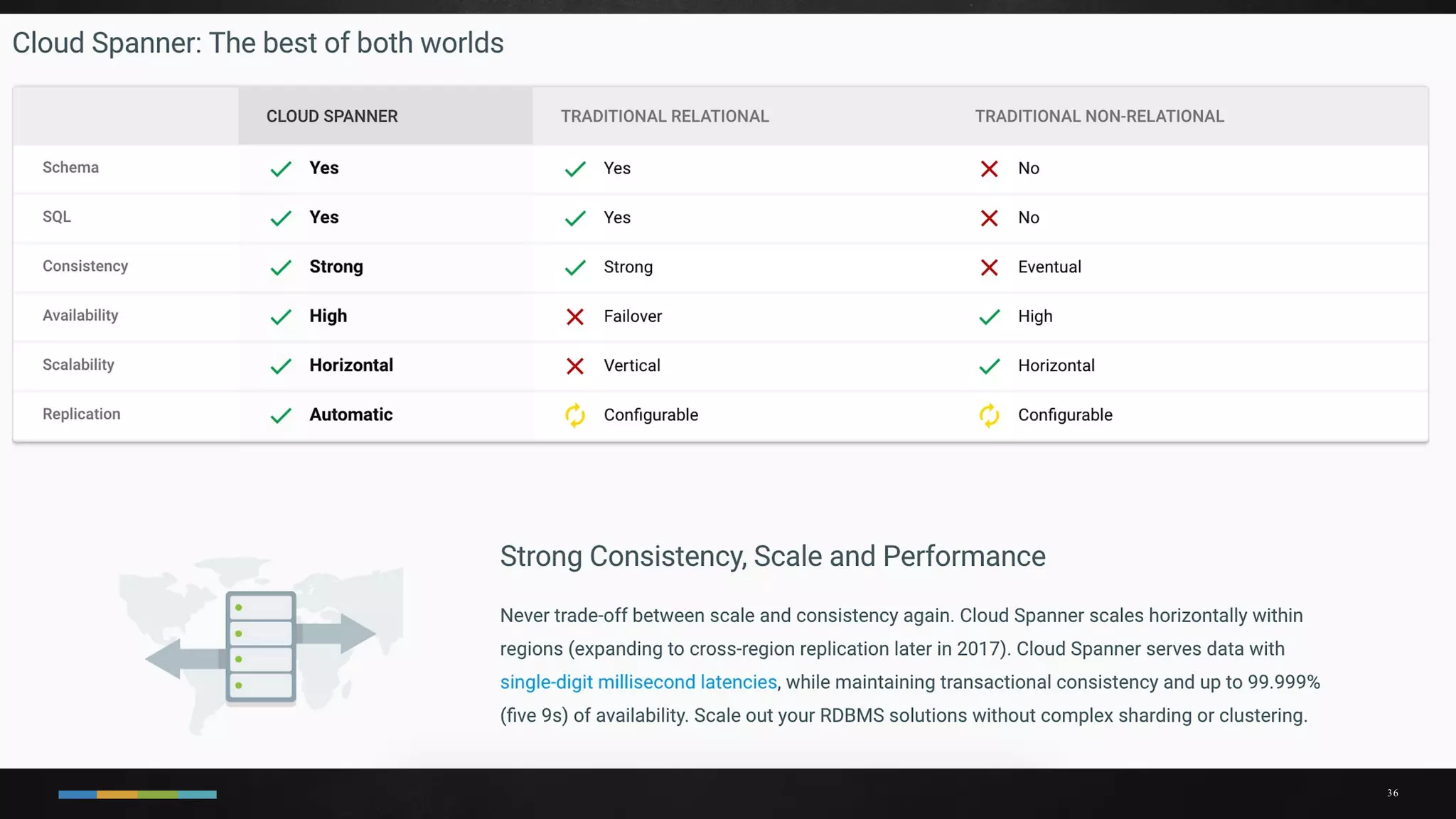
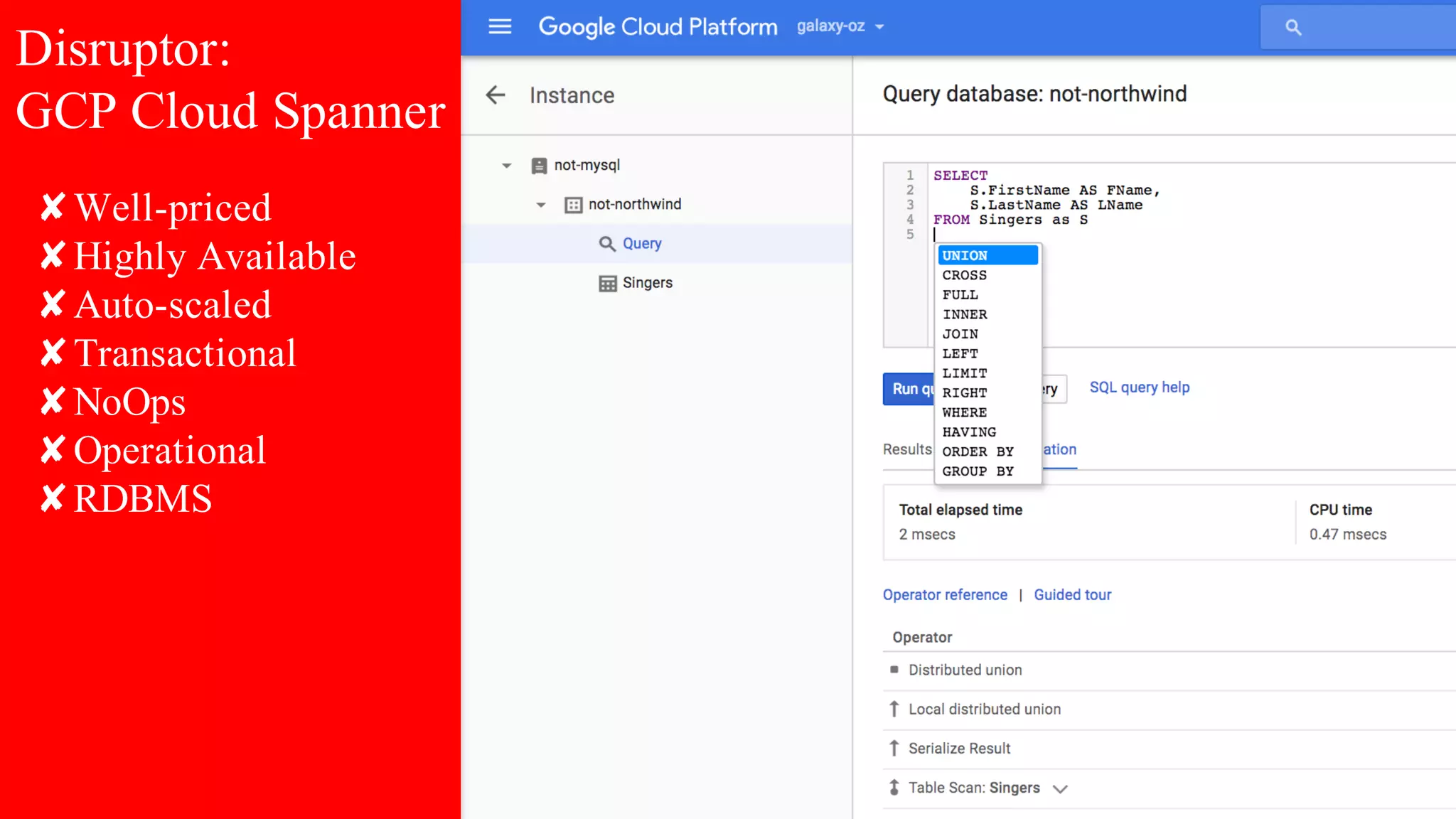
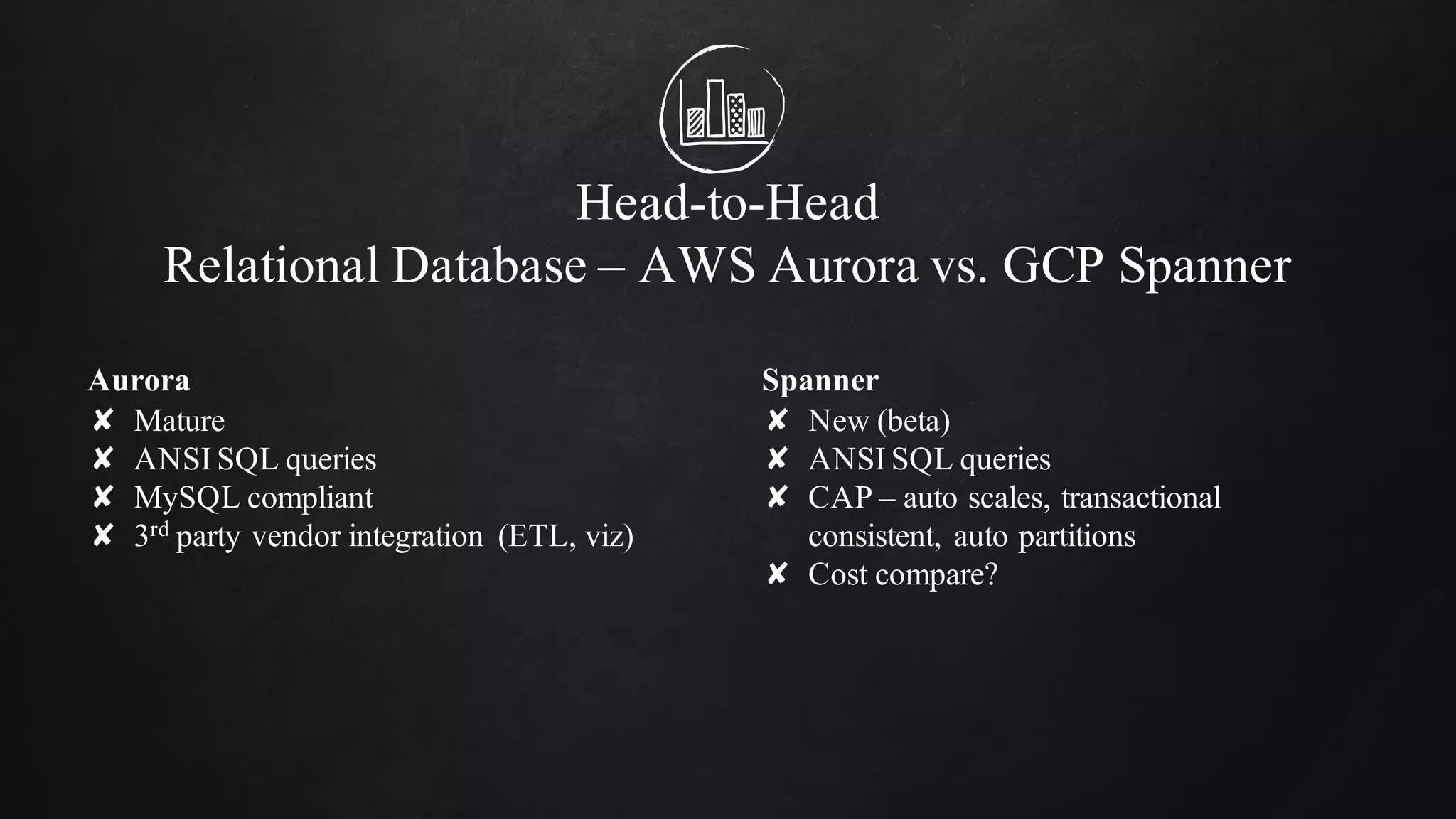
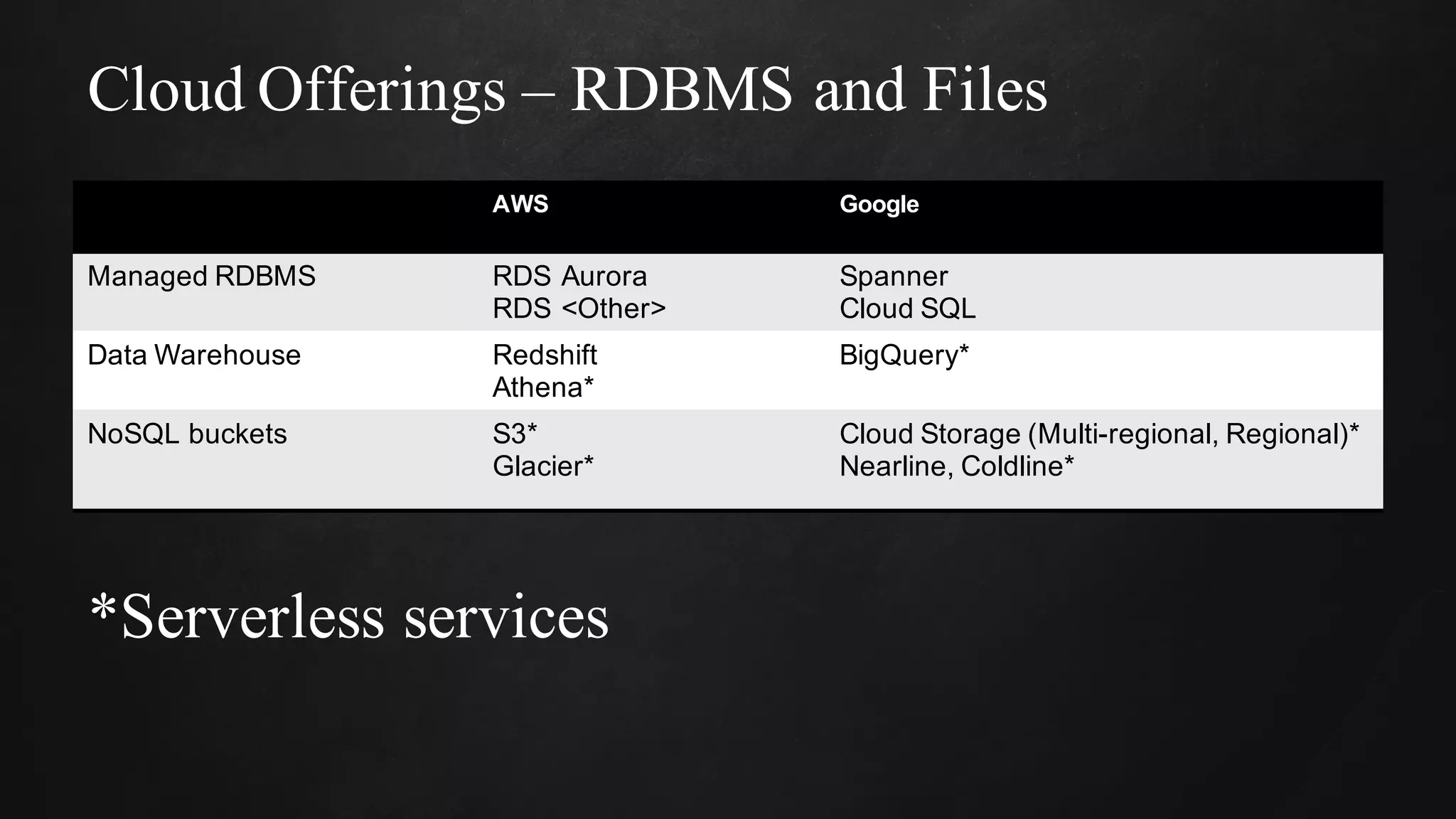
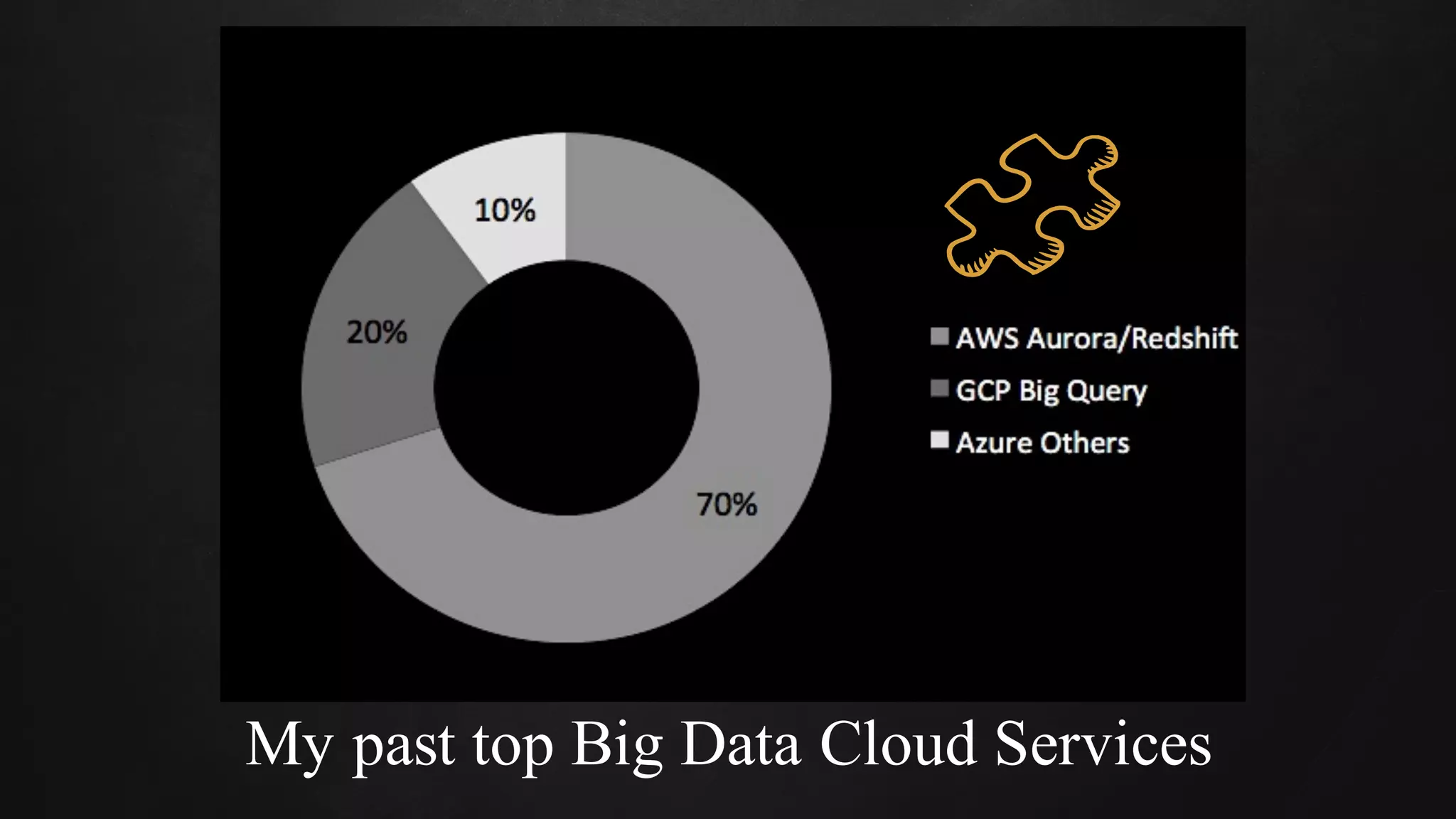
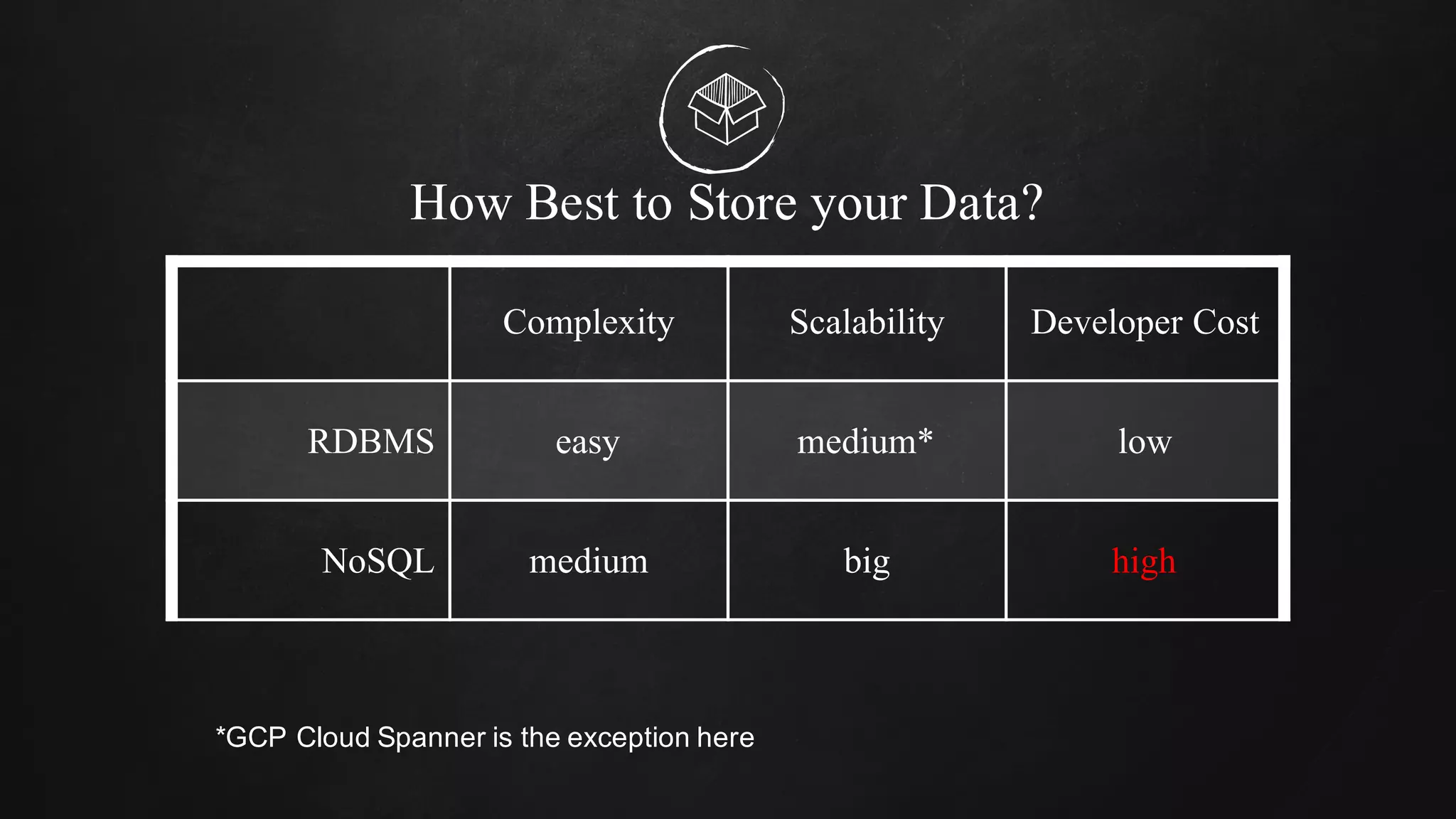
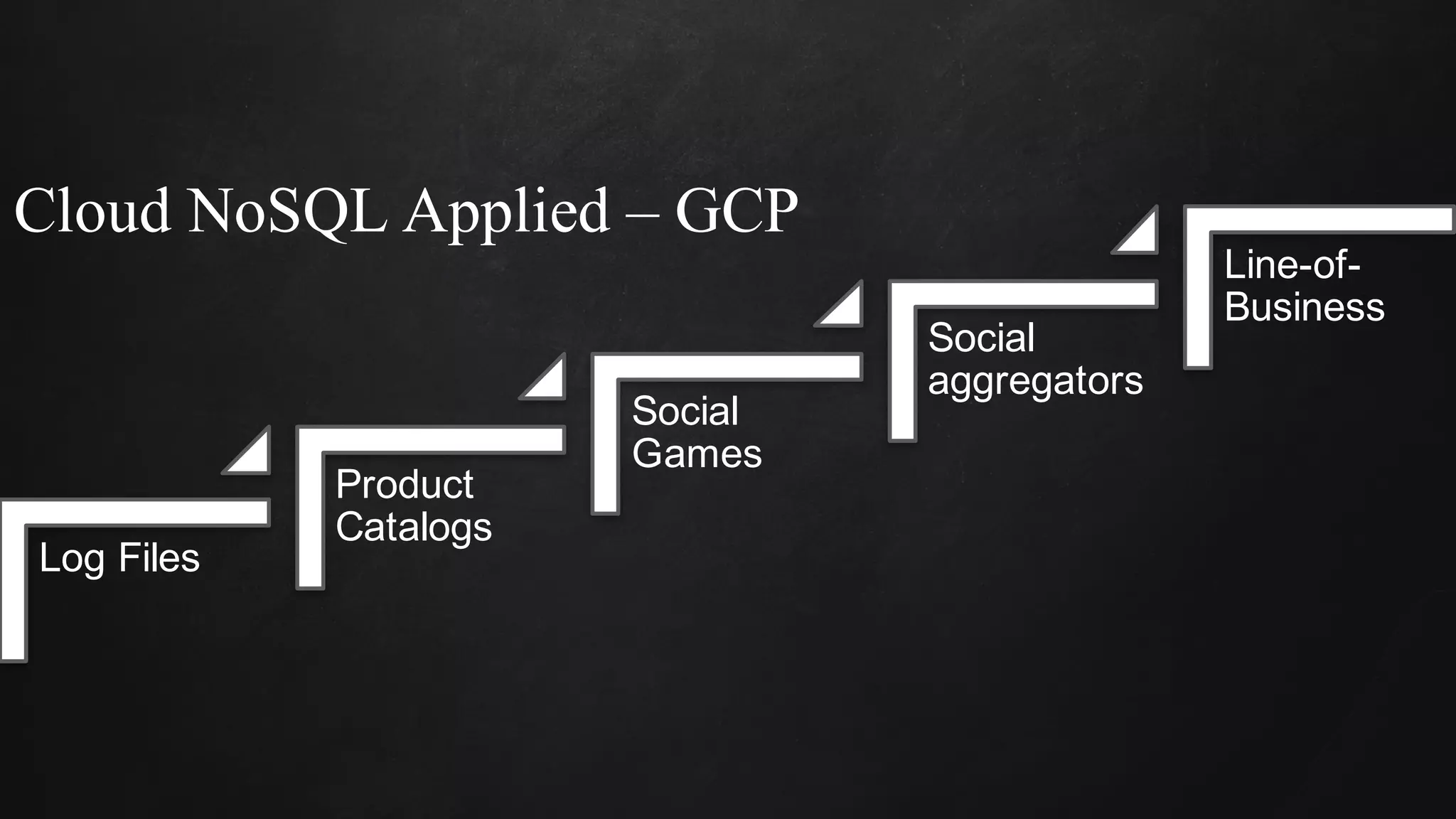
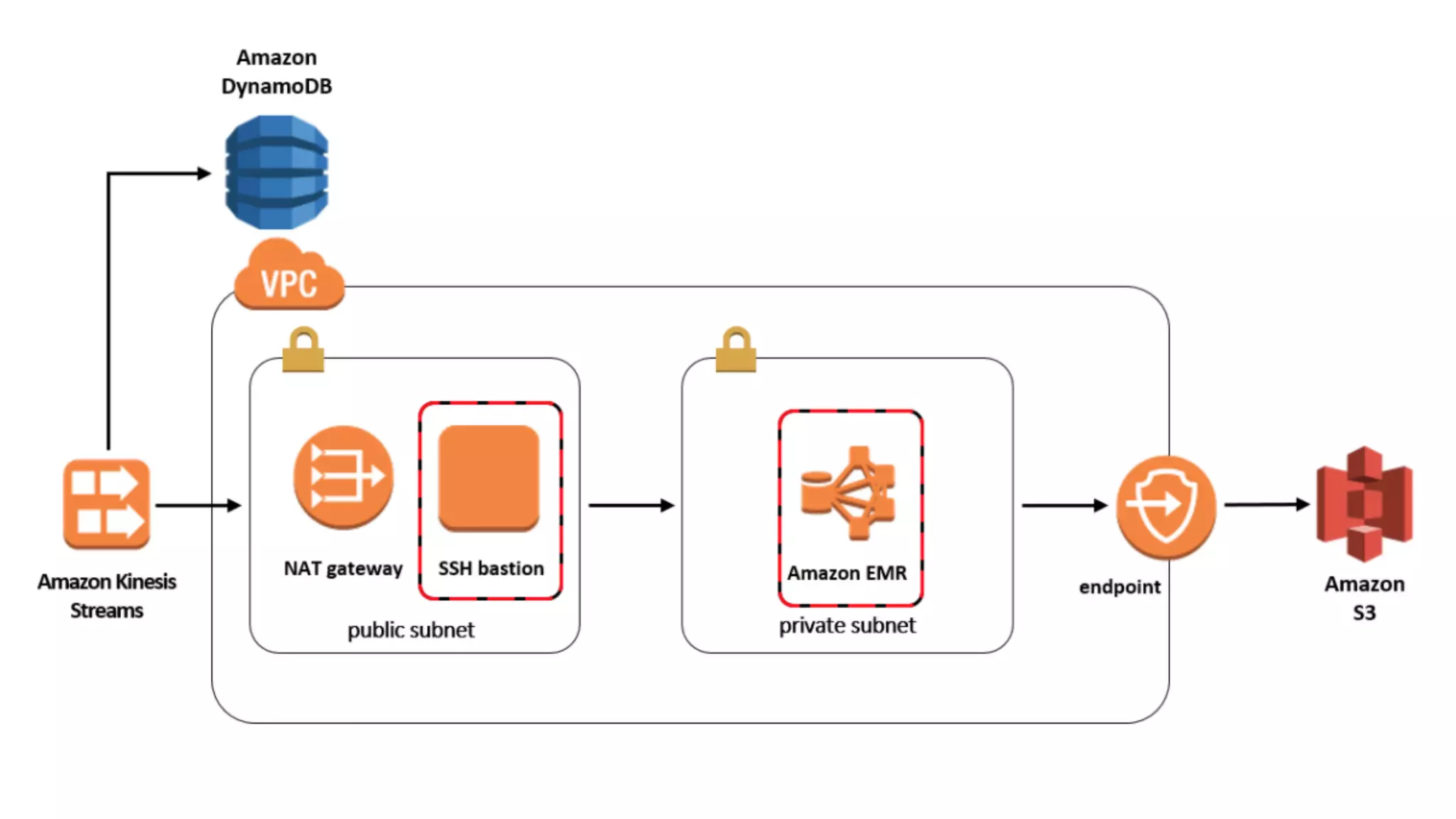
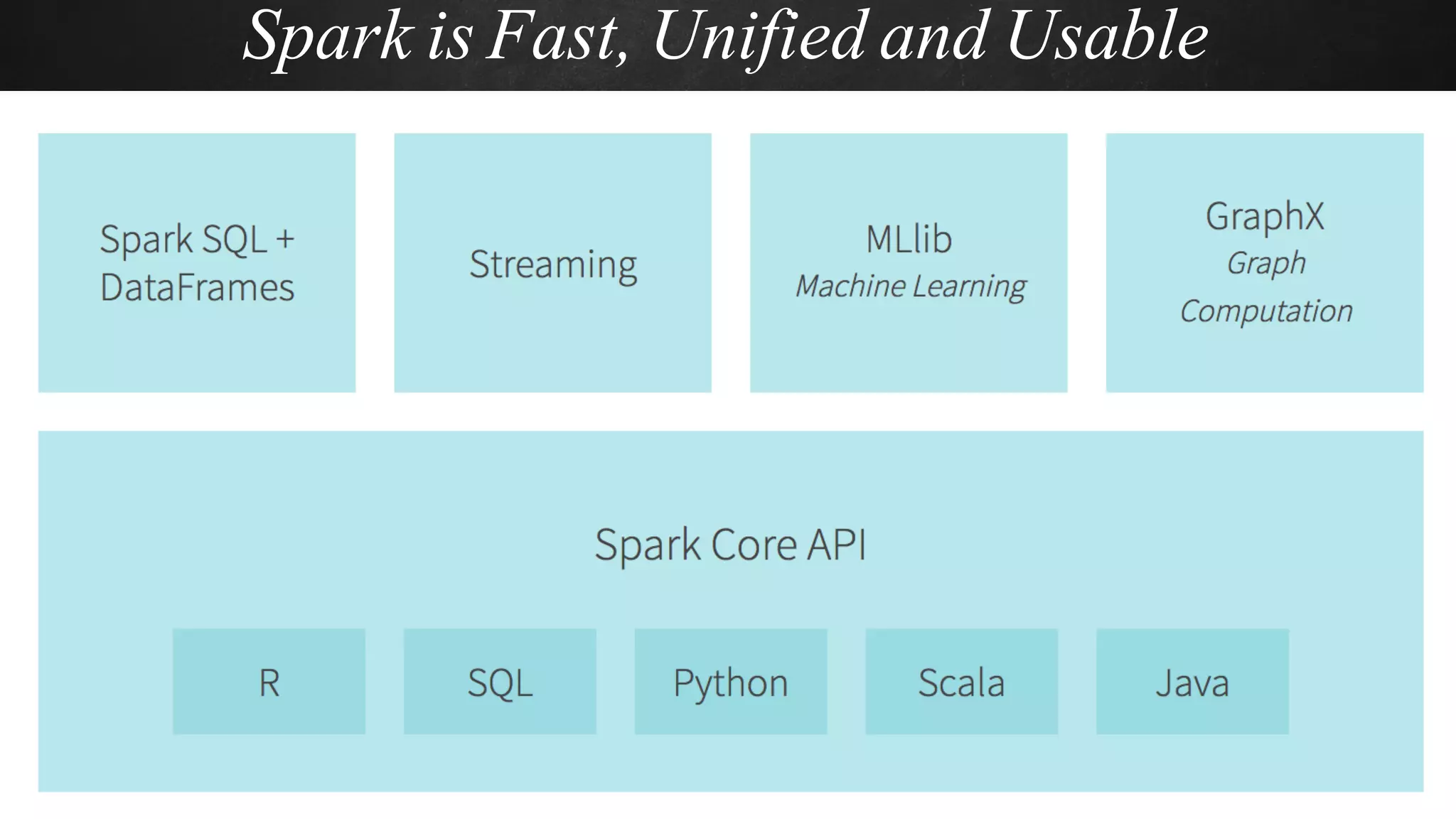
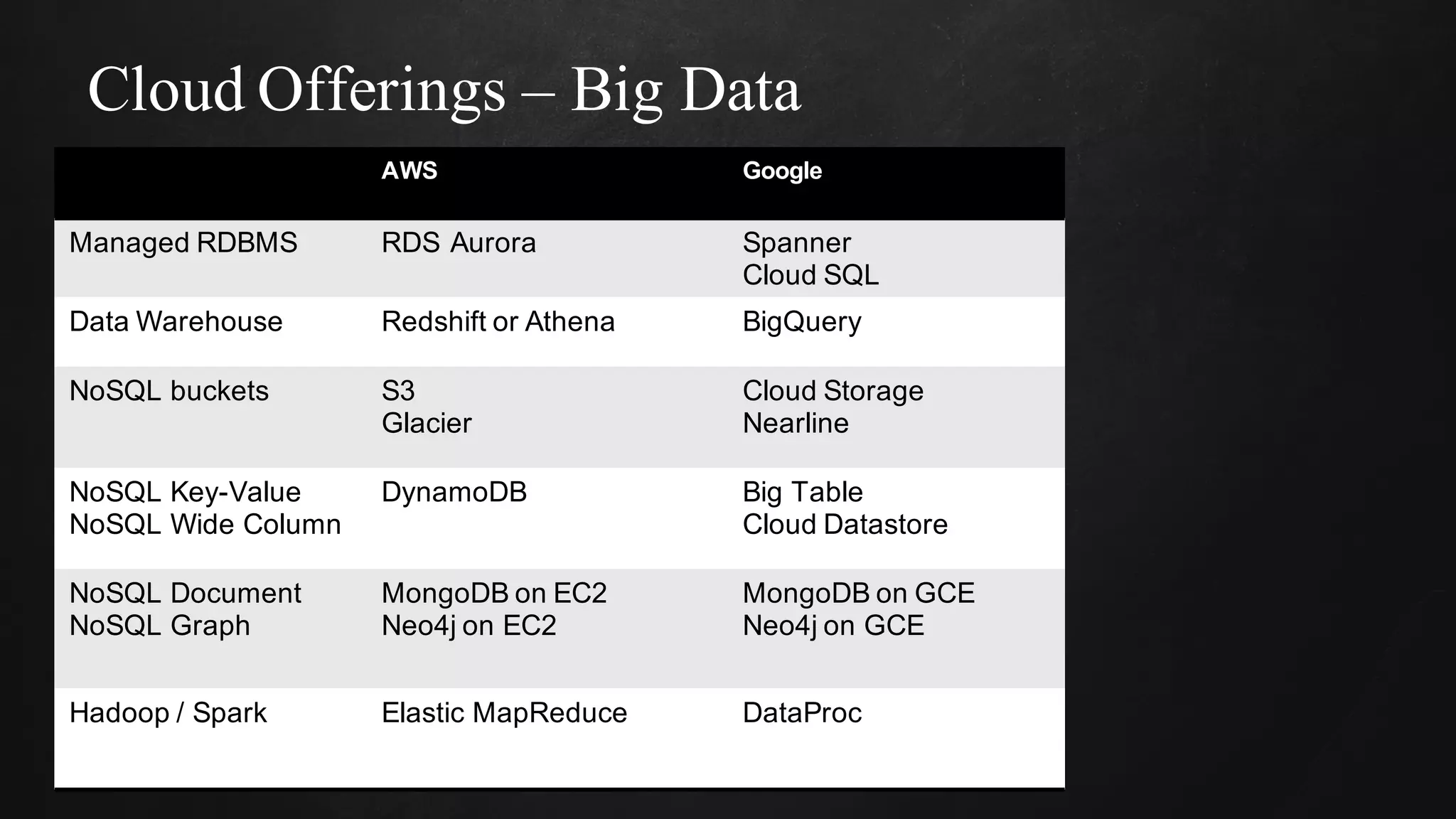
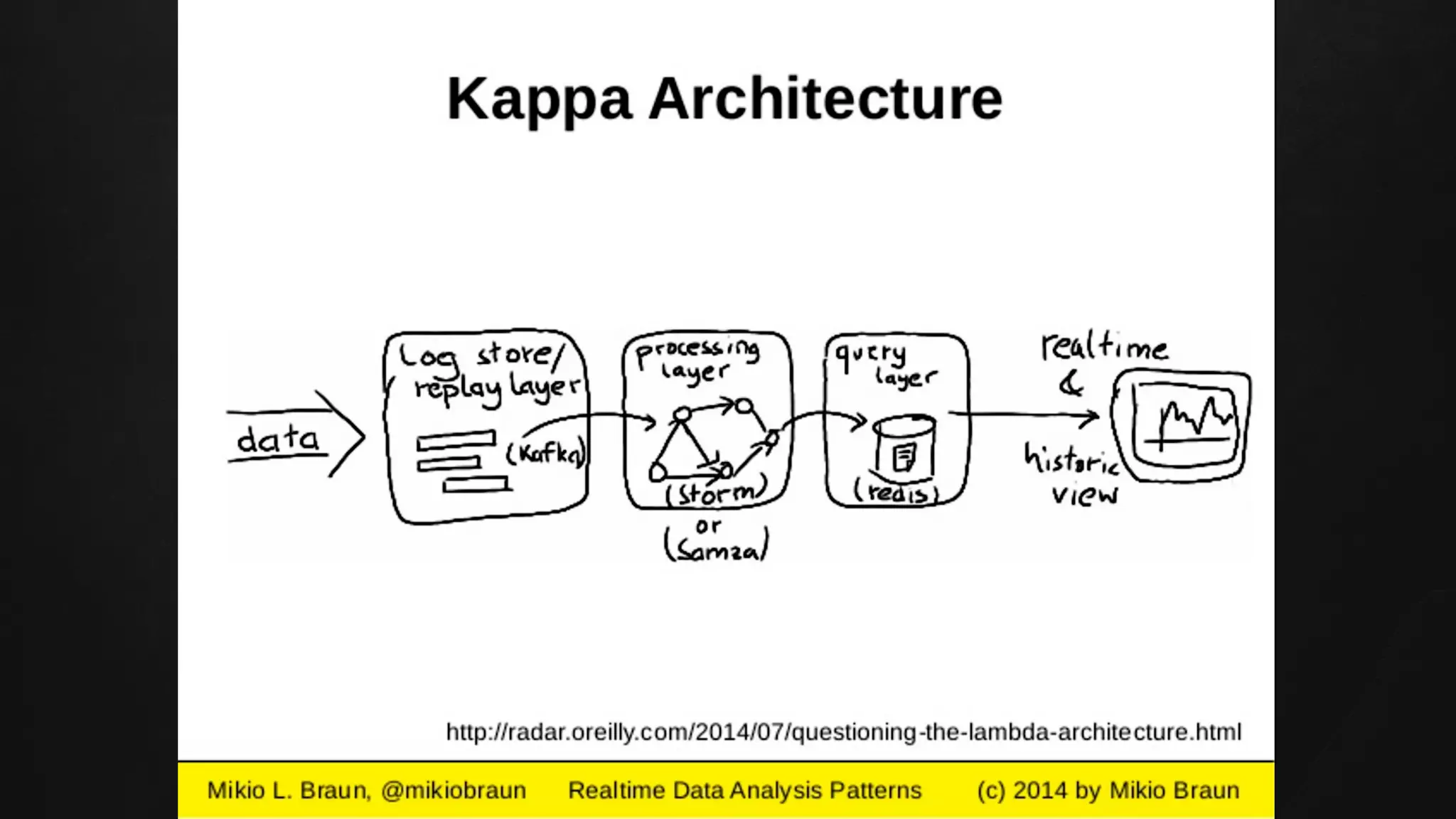
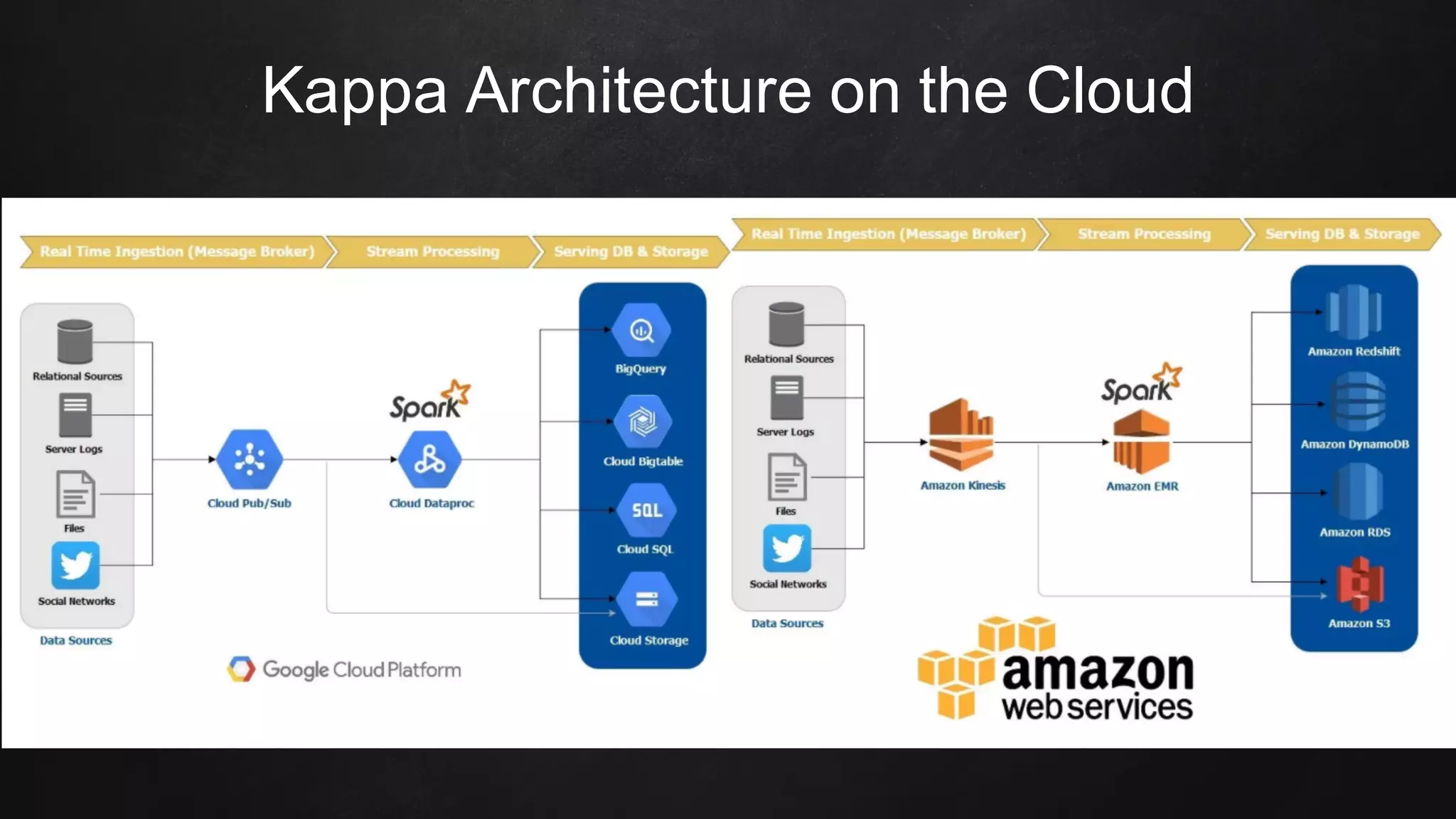
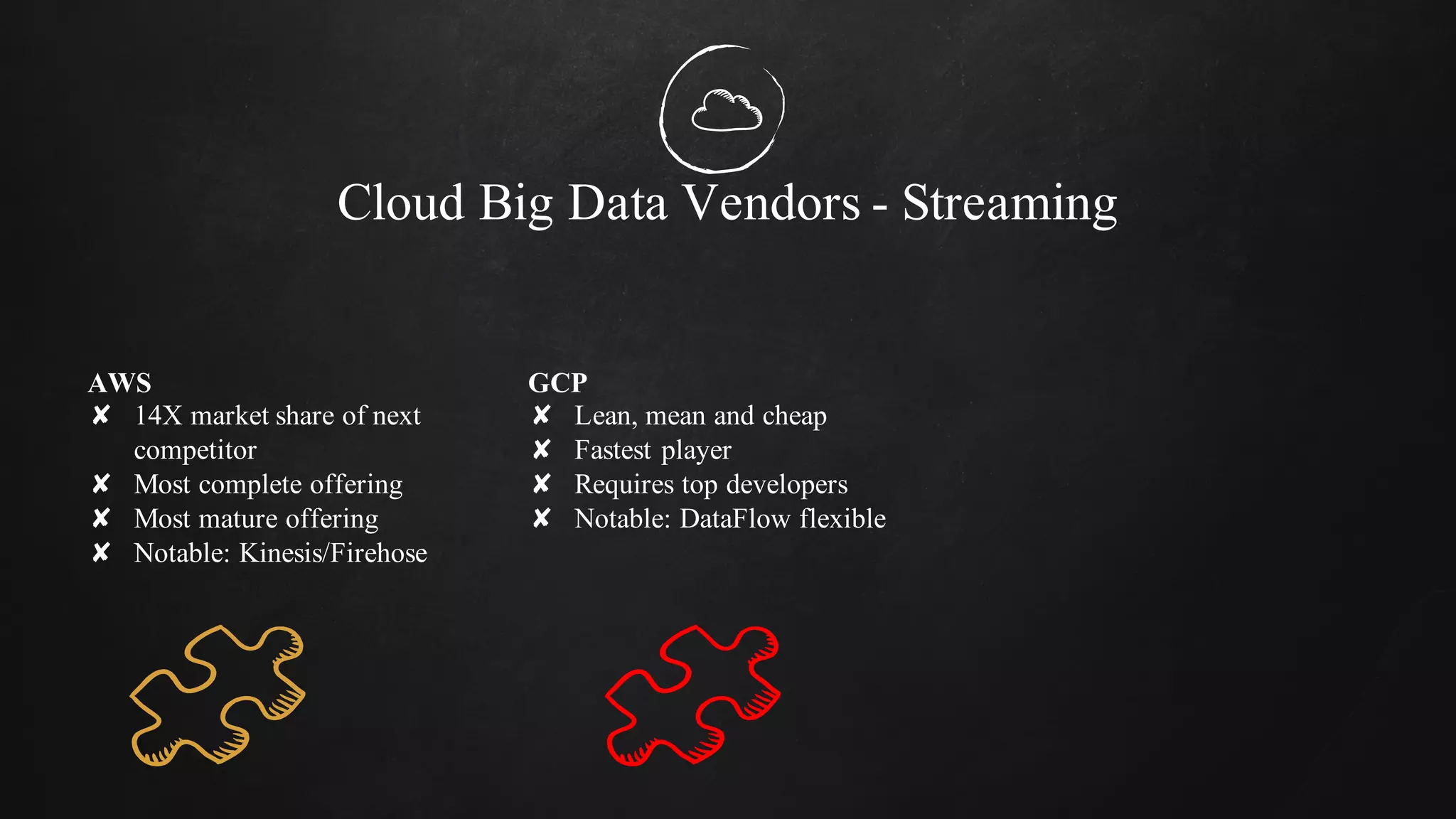
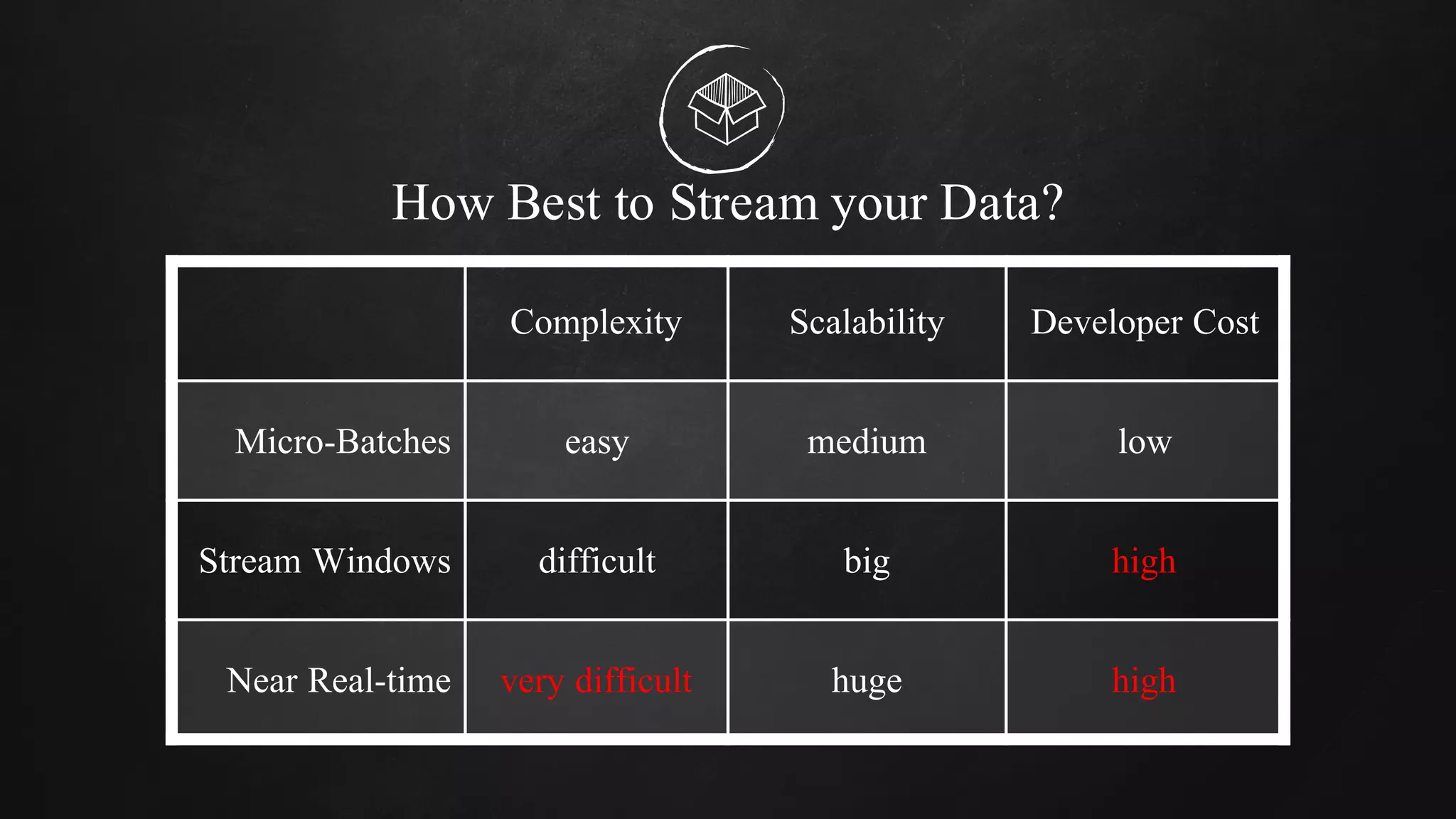
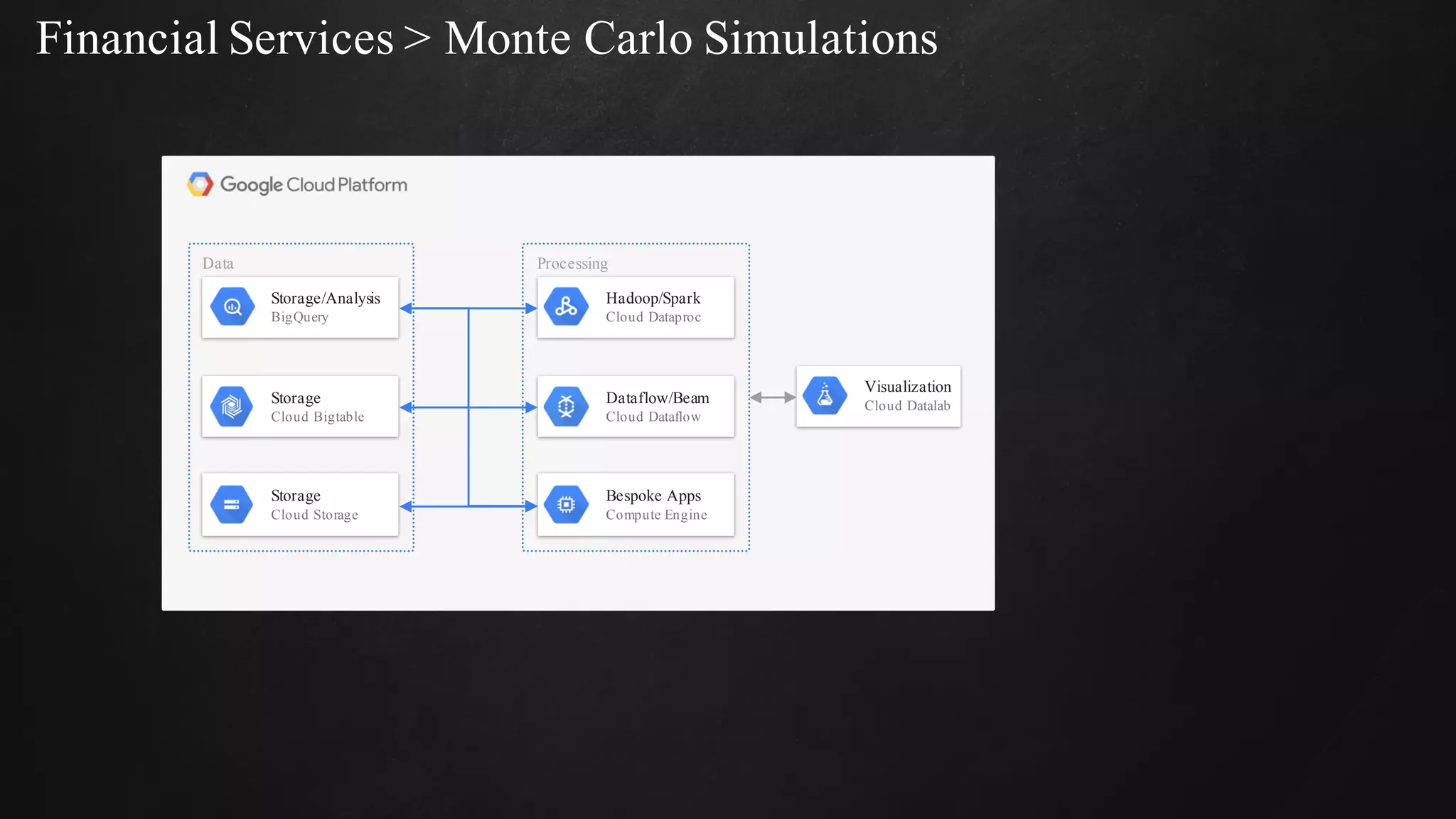
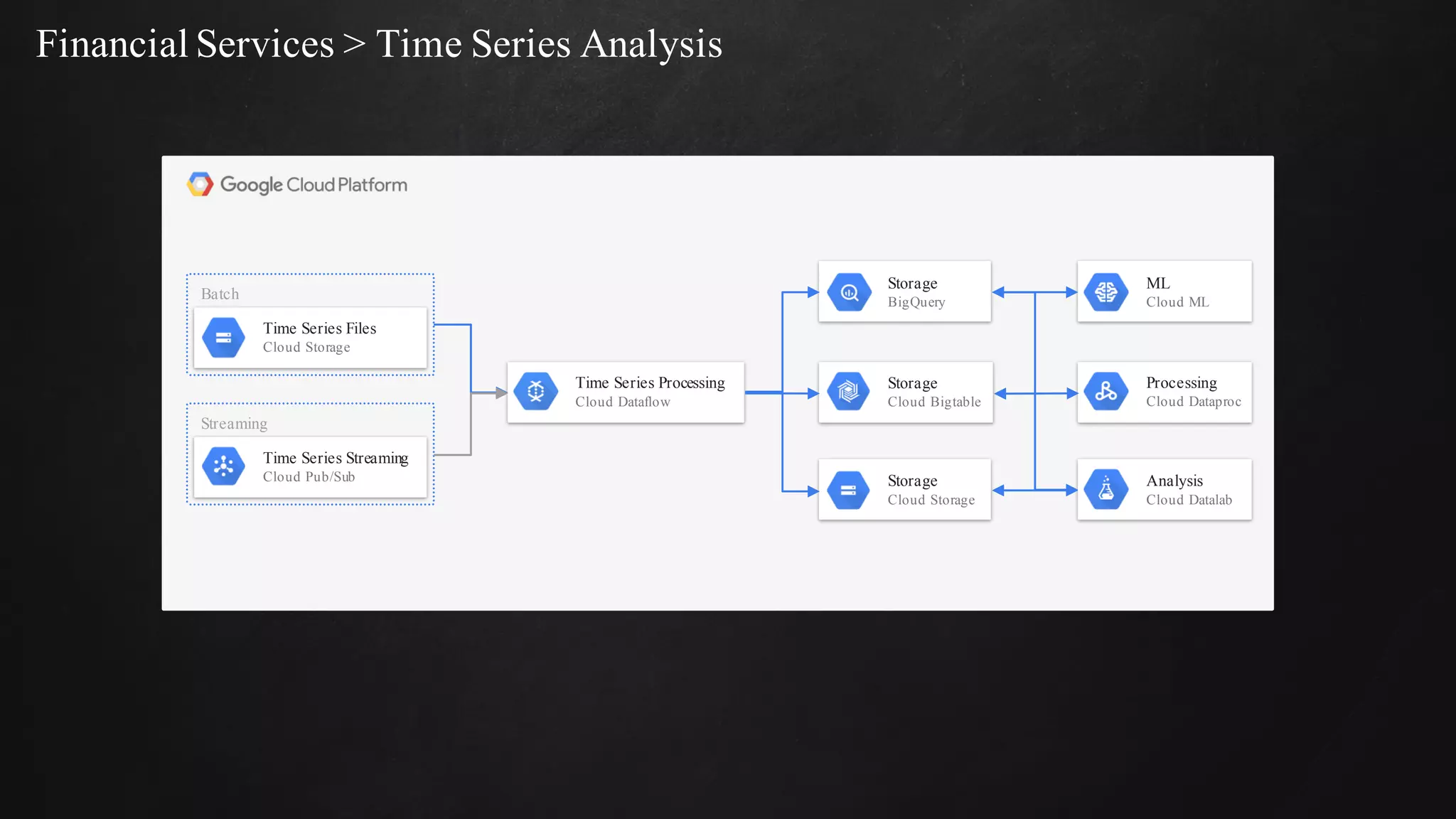
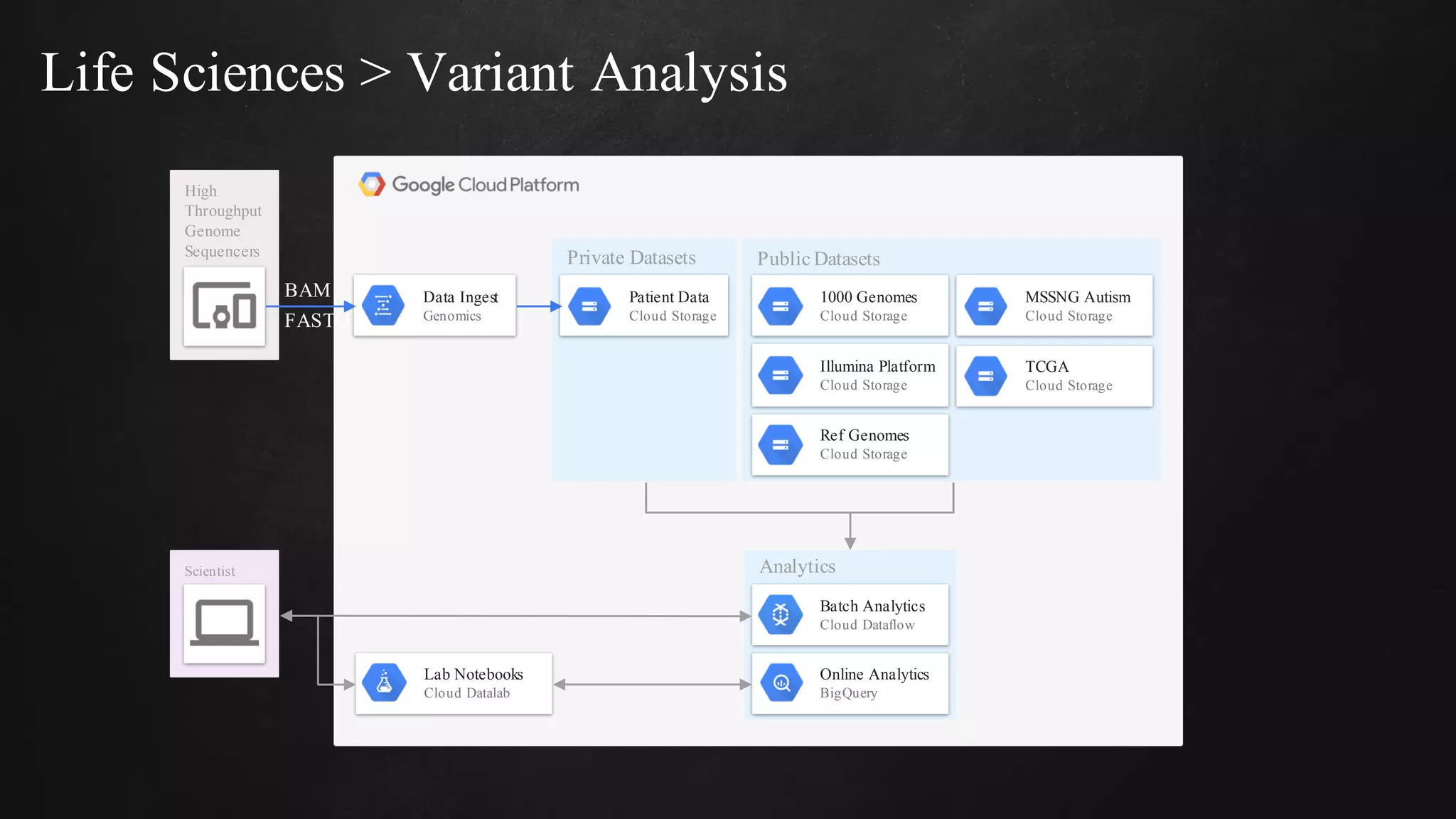
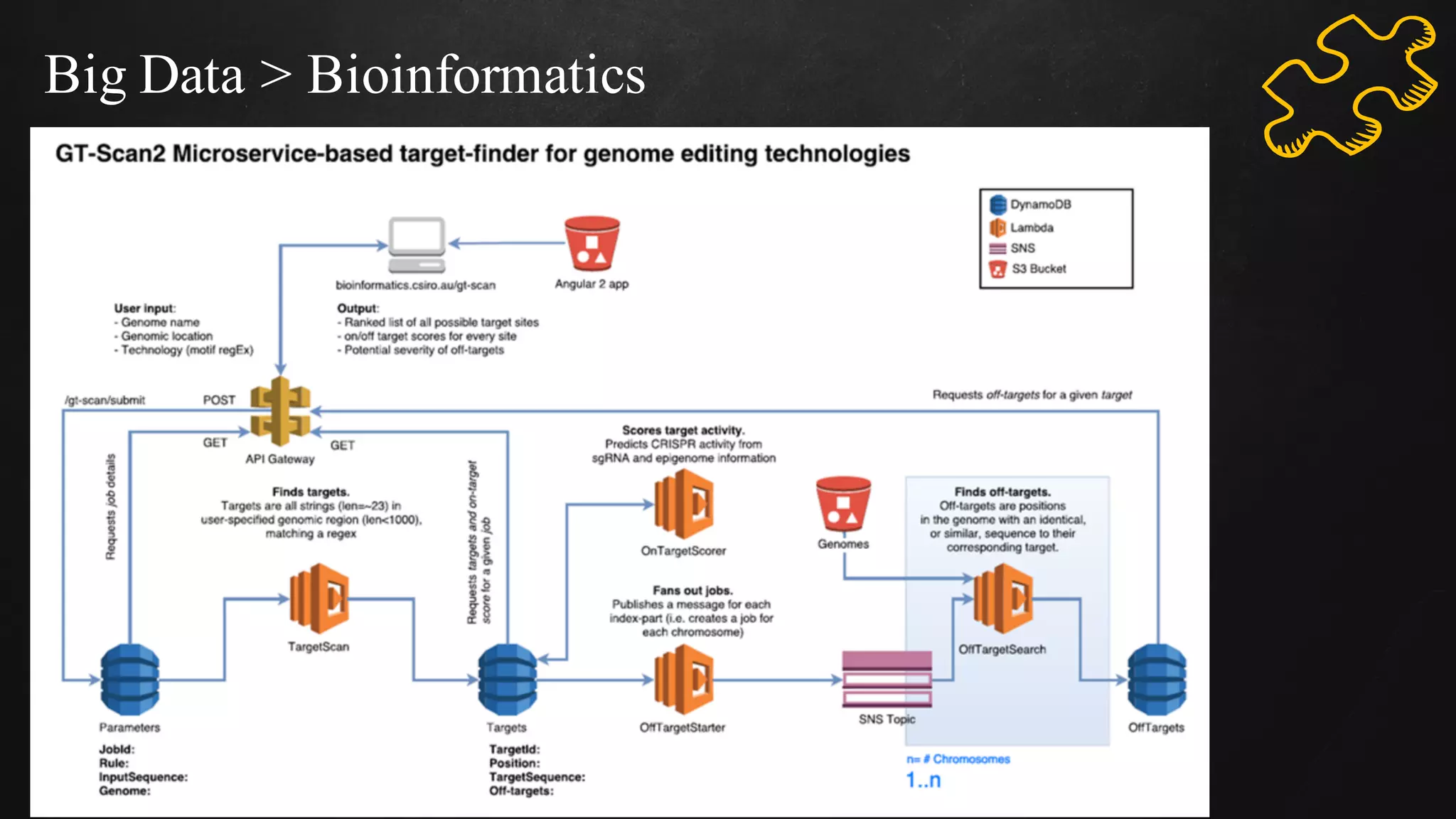
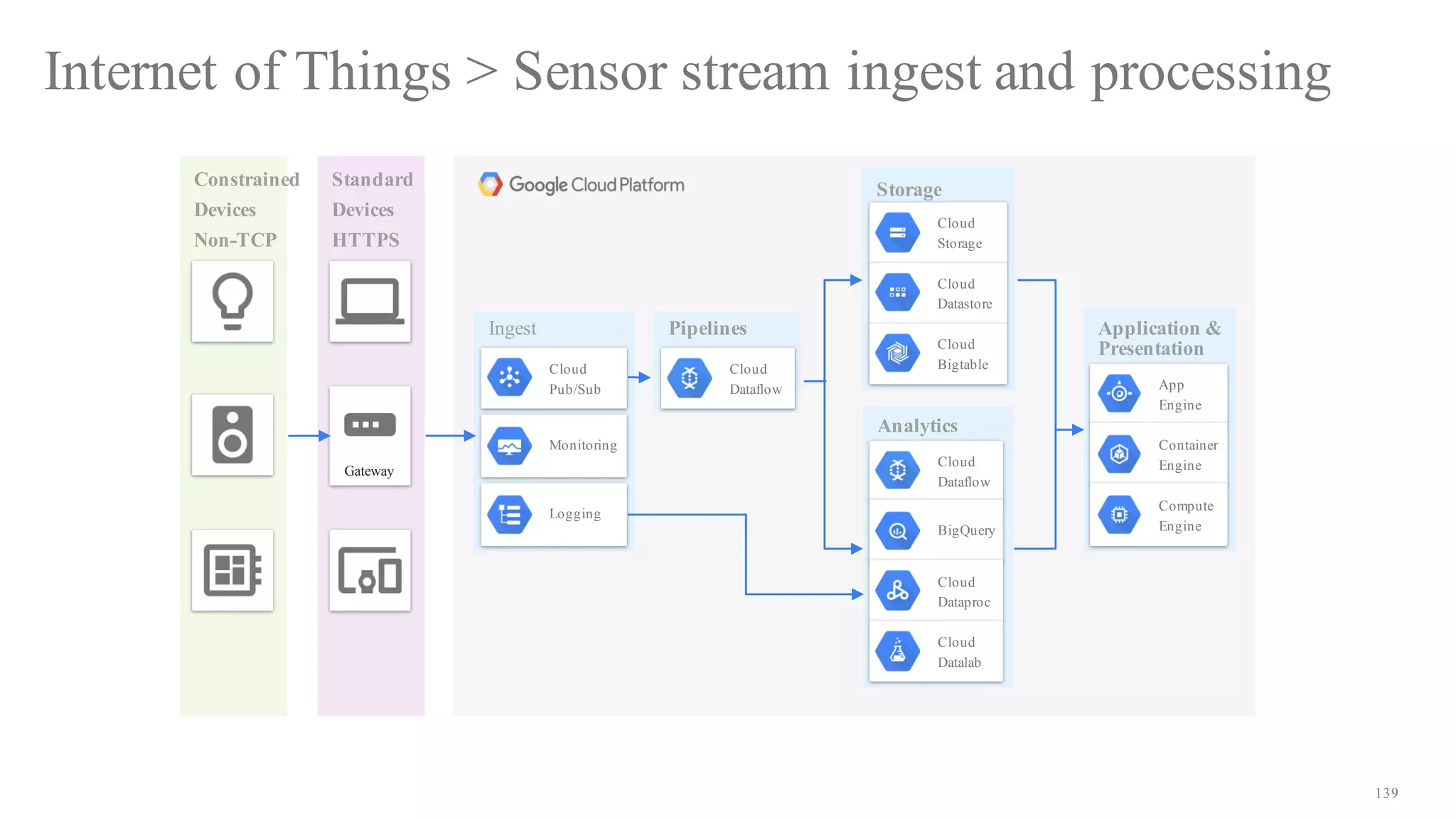
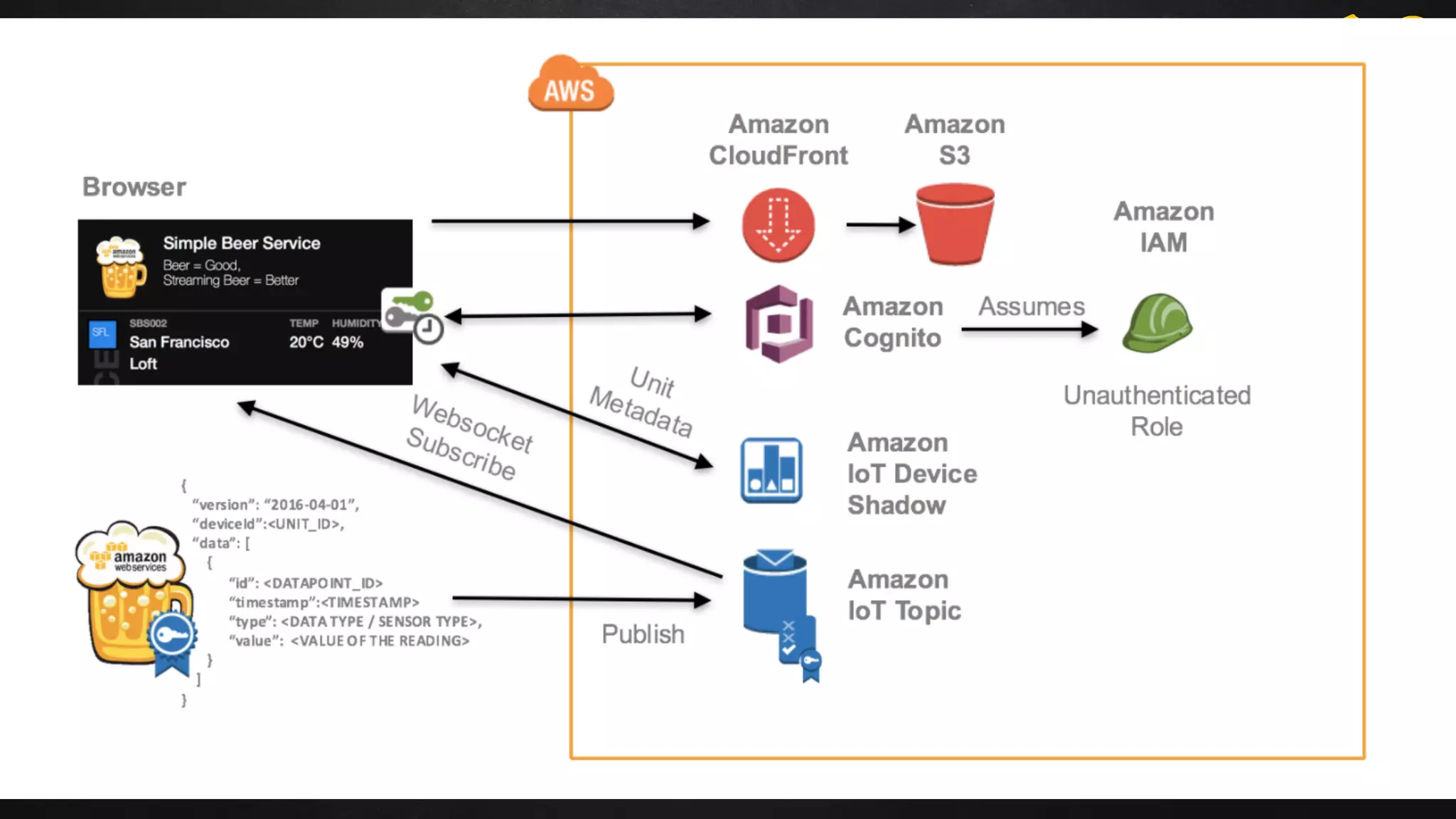
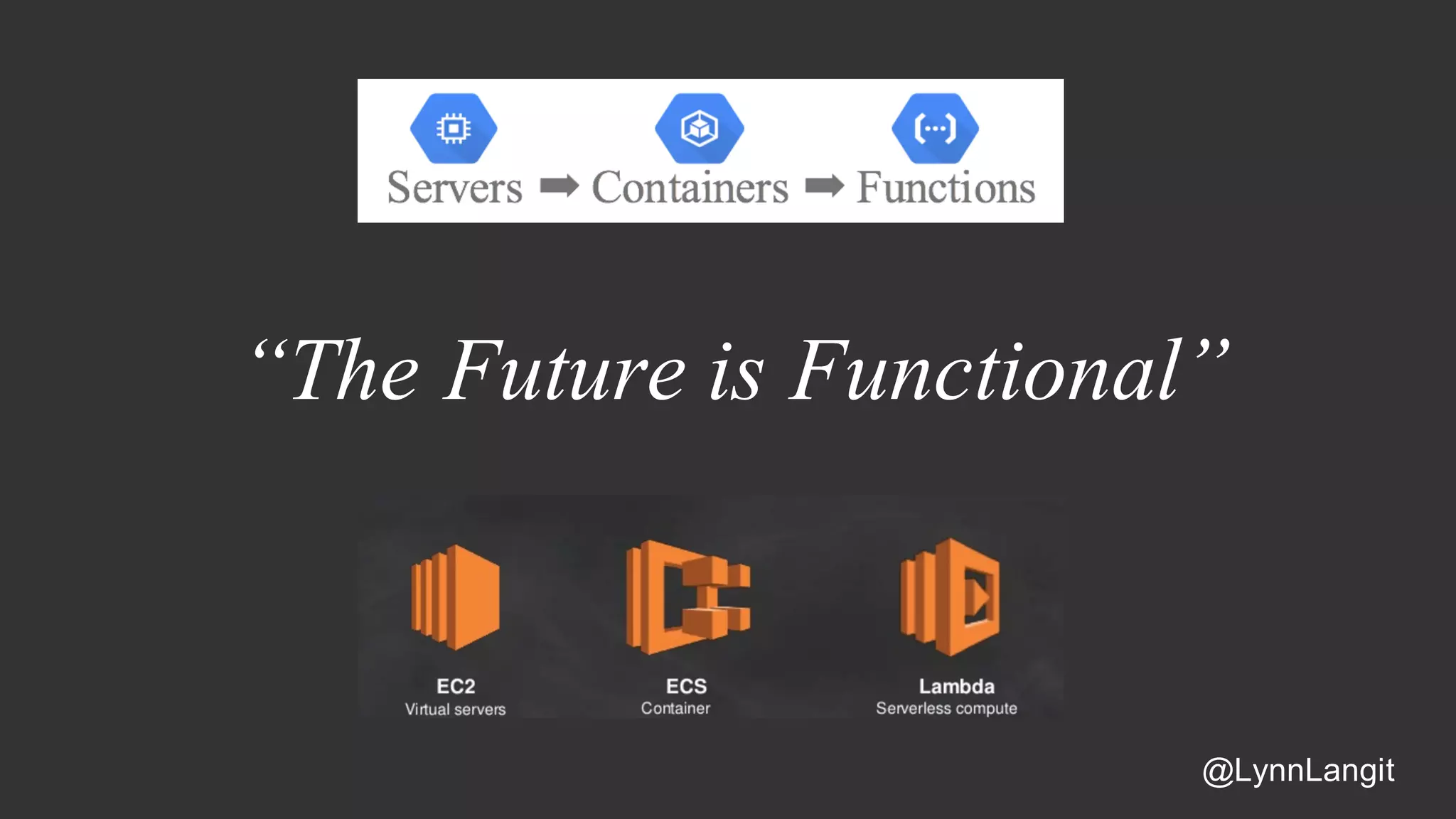
The document discusses building data pipelines in the cloud. It covers serverless data pipeline patterns using services like BigQuery, Cloud Storage, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Pub/Sub. It also compares Cloud Dataflow and Cloud Dataproc for ETL workflows. Key questions around ingestion and ETL are discussed, focusing on volume, variety, velocity and veracity of data. Cloud vendor offerings for streaming and ETL are also compared.