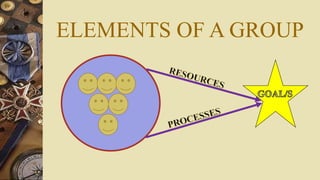
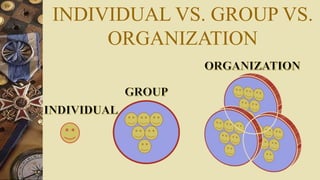
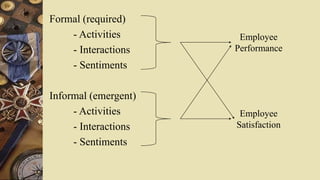
A group is defined as two or more individuals who interact with one another and work together regularly to achieve common goals. Groups have various types of resources like staff, funds, facilities, equipment, supplies, and time. Groups can be formal, arising from an organizational structure and purpose, or informal, emerging without official designation. Examples of formal groups are operations, finance, human resources, and marketing teams. Informal groups include command groups composed of those reporting to a manager, task groups working on jobs, interest groups pursuing objectives, and friendship groups with common characteristics. Both formal and informal groups impact employee performance and satisfaction in an organization.