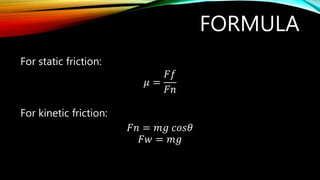
This document discusses the laws of friction and provides examples of how to calculate coefficients of friction and frictional forces. It defines key terms like coefficient of friction, normal force, static friction, and kinetic friction. Formulas are provided to calculate the coefficient of friction and frictional force. Two sample problems demonstrate how to apply the formulas to find the coefficient of friction or frictional force given values for normal force, applied force, mass, and angle of inclination. Finally, two practice exercises are presented.