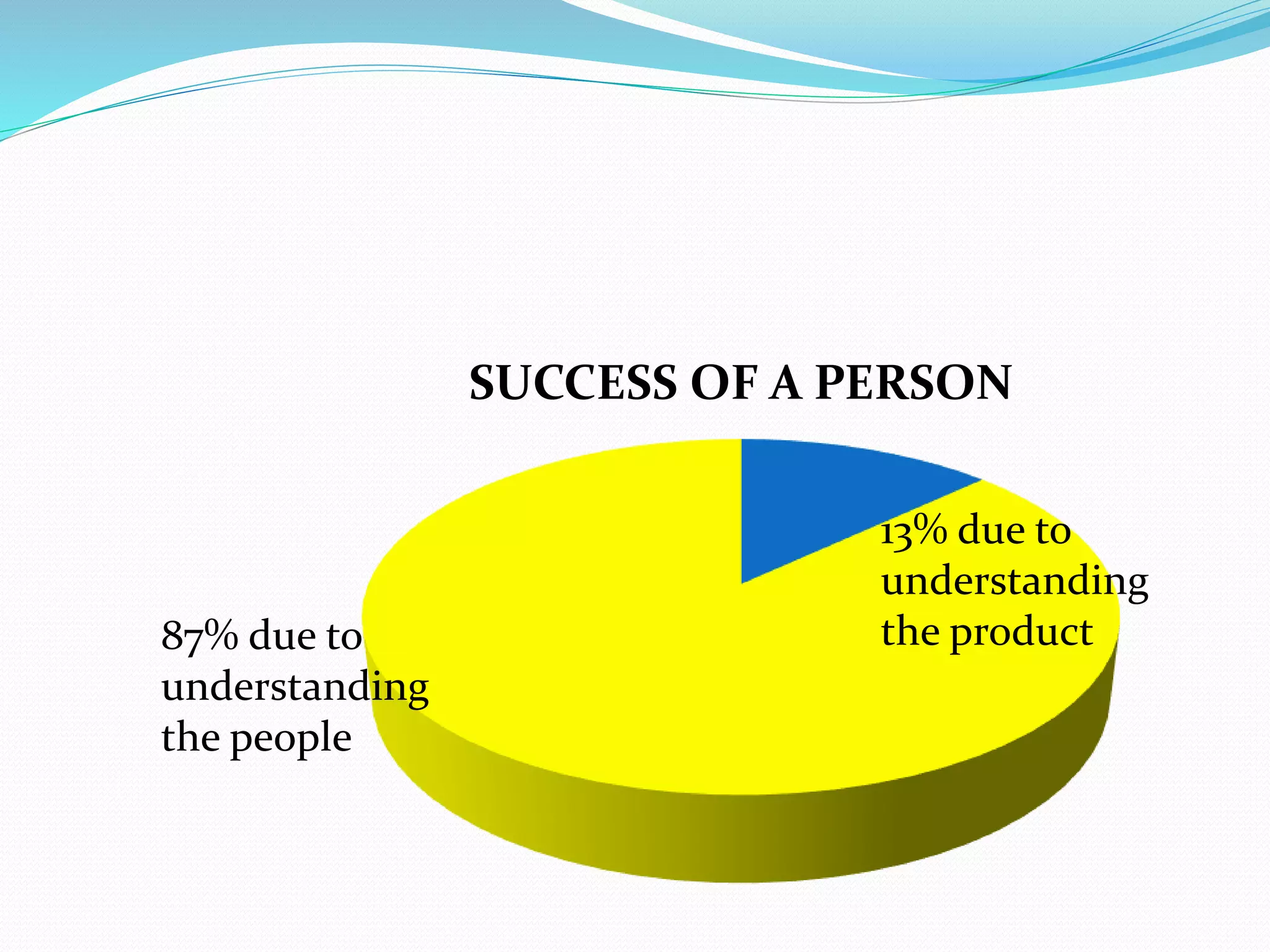
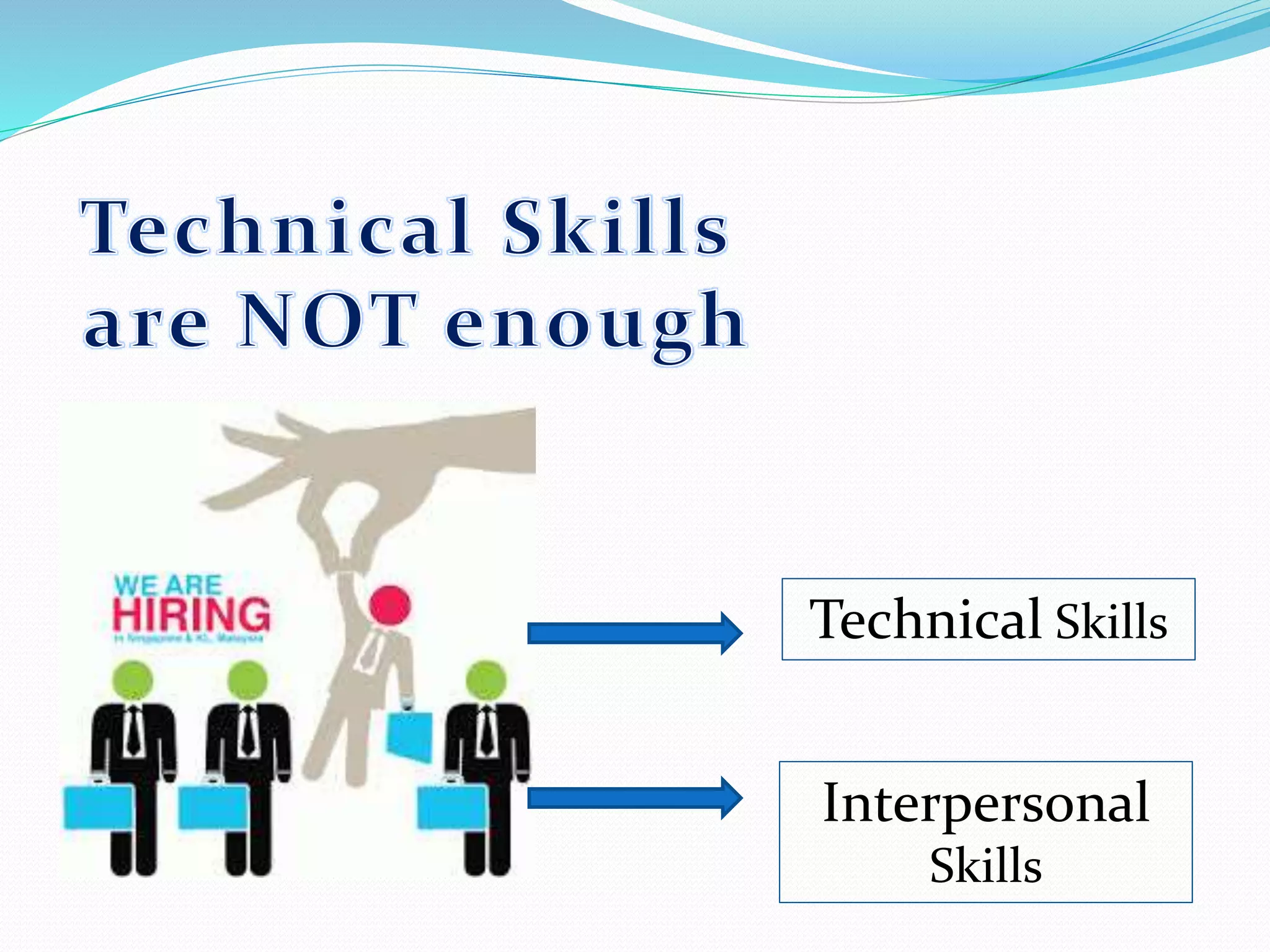
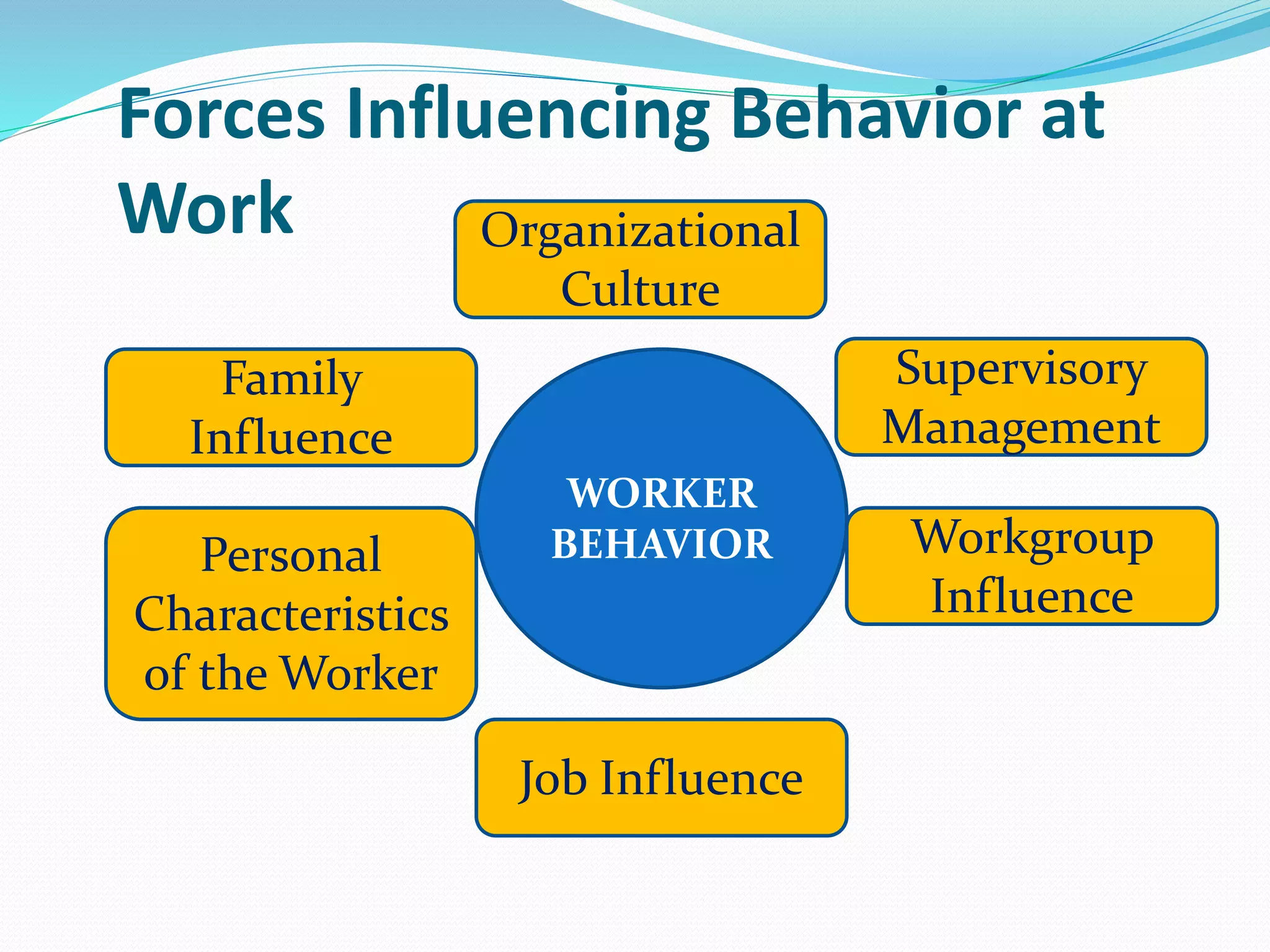
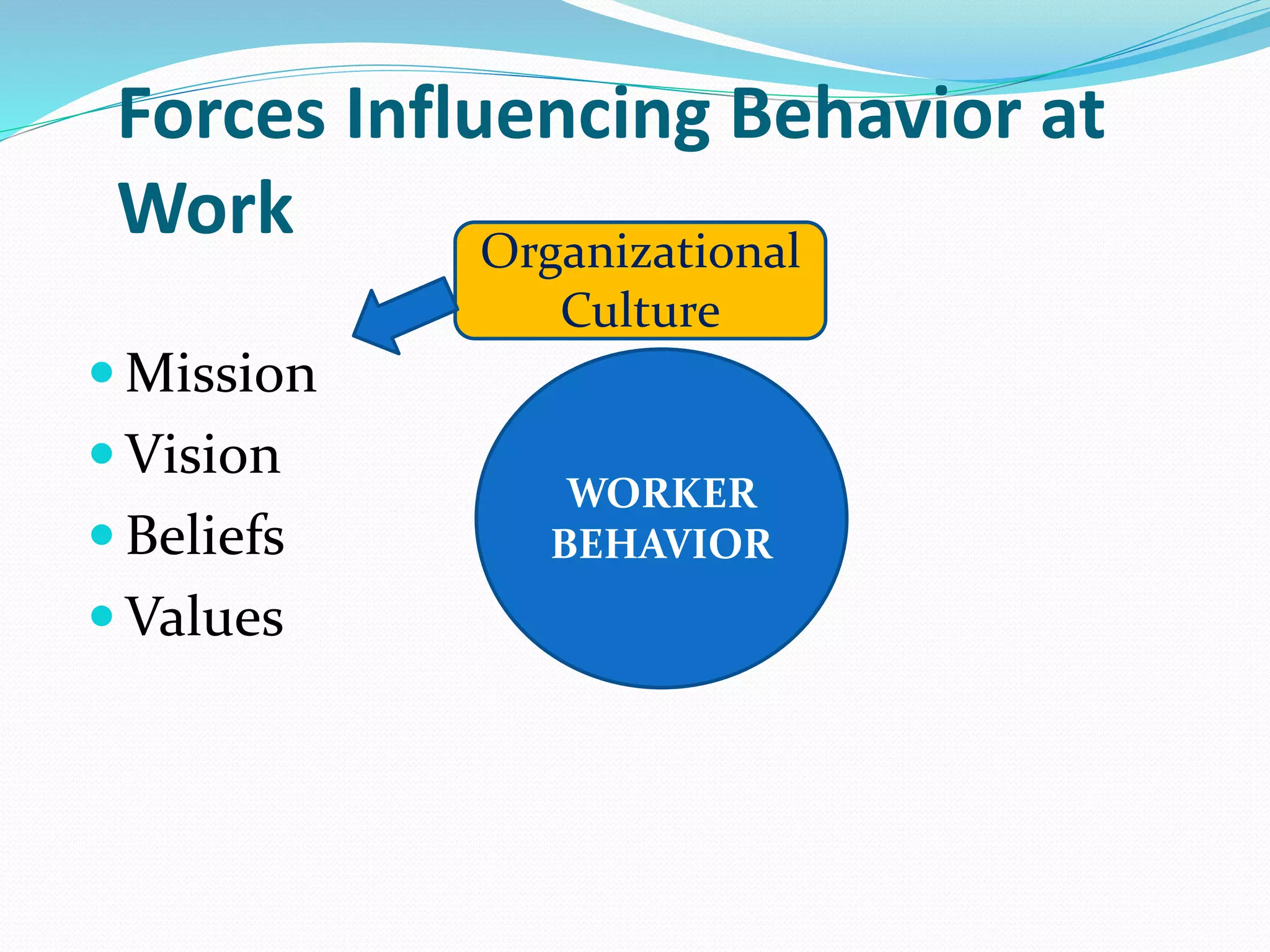
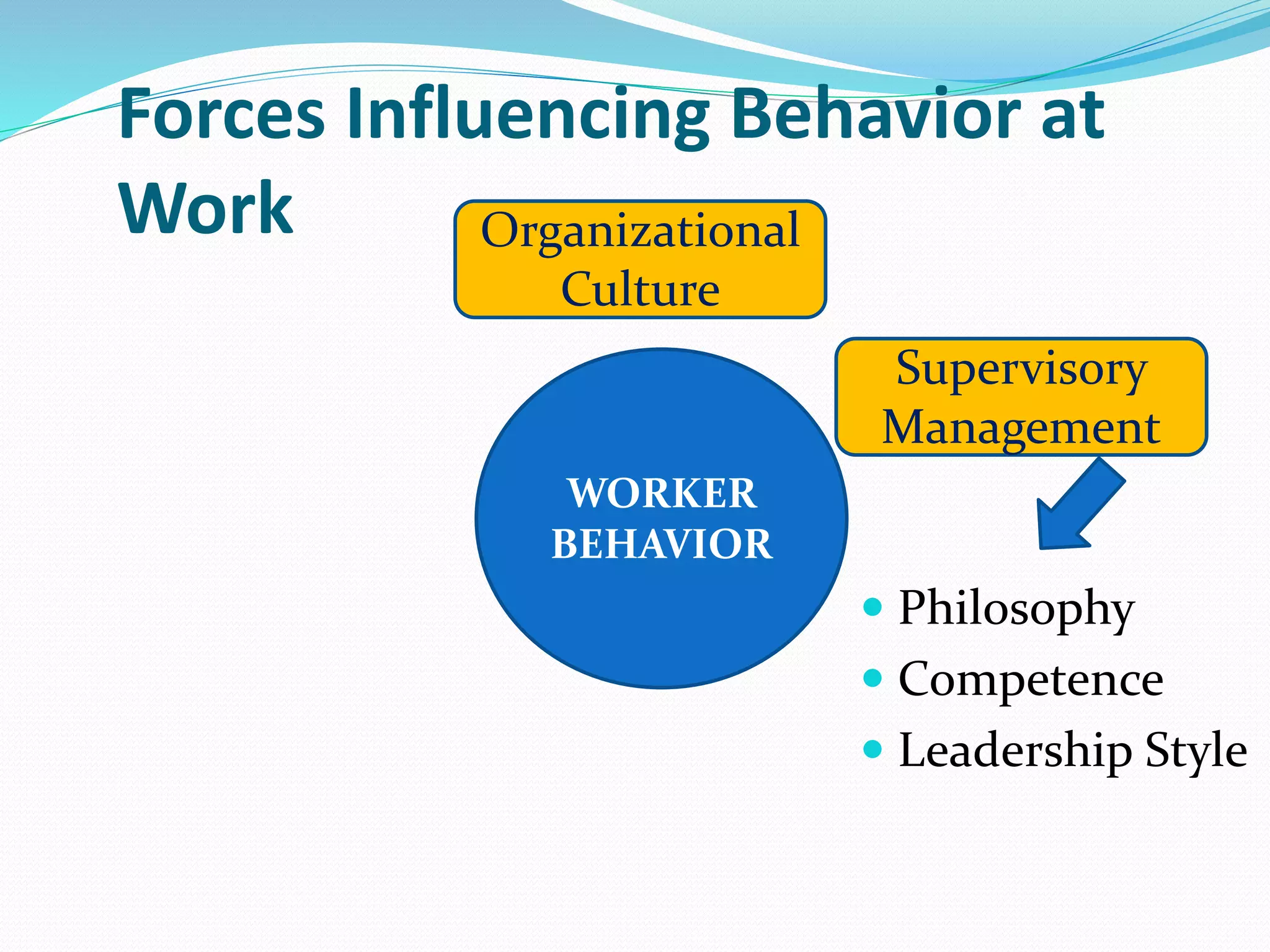
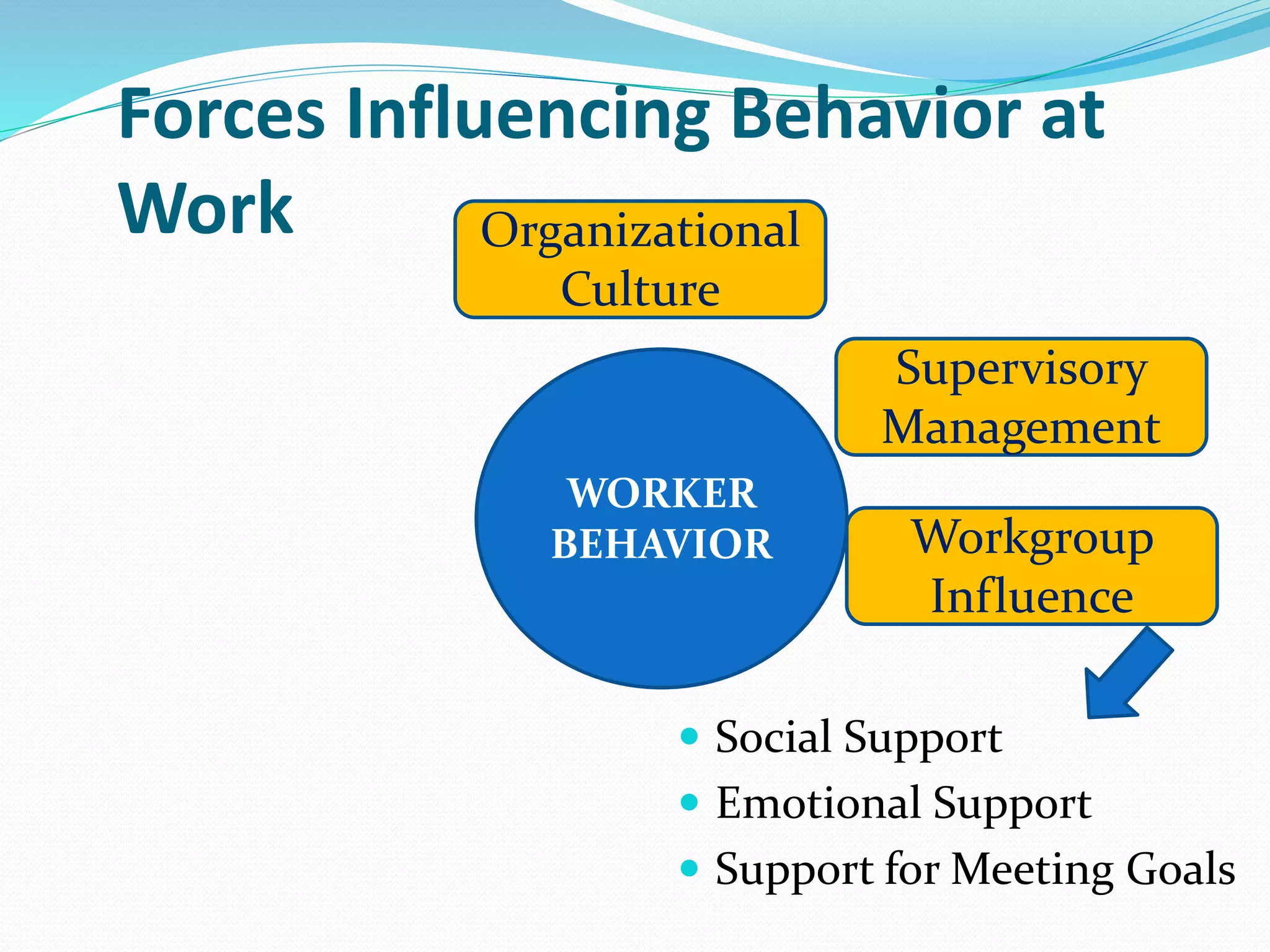
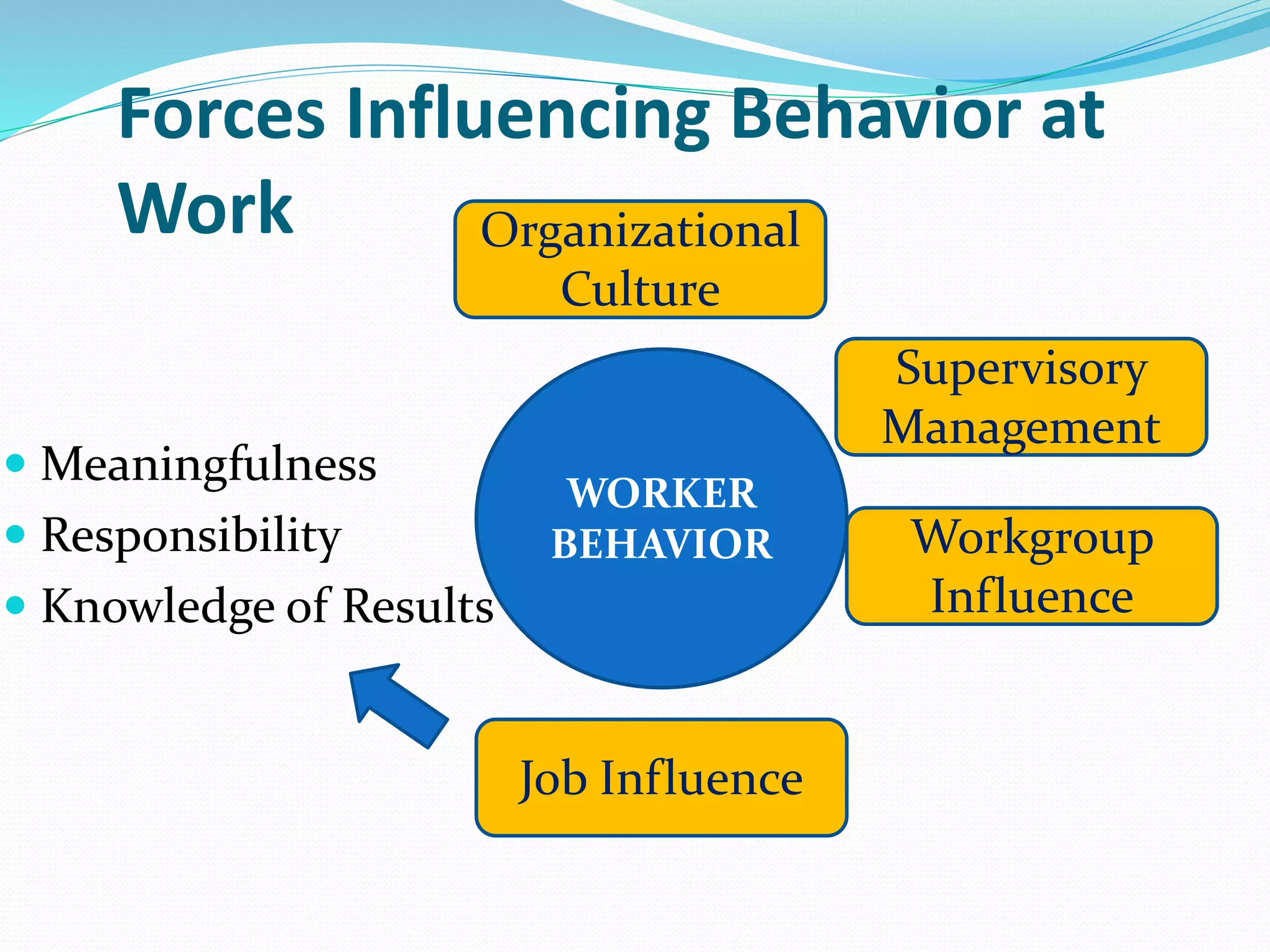
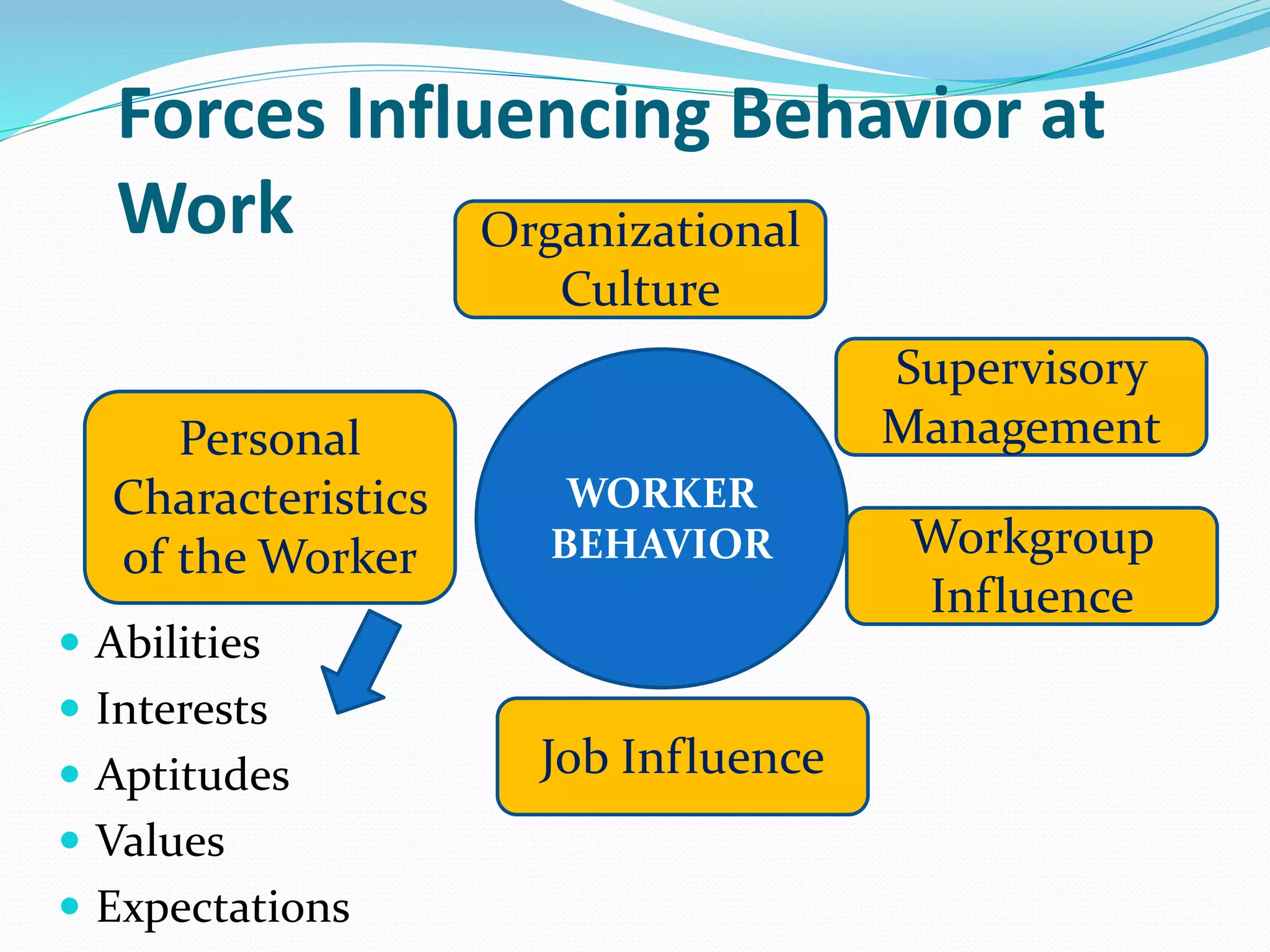
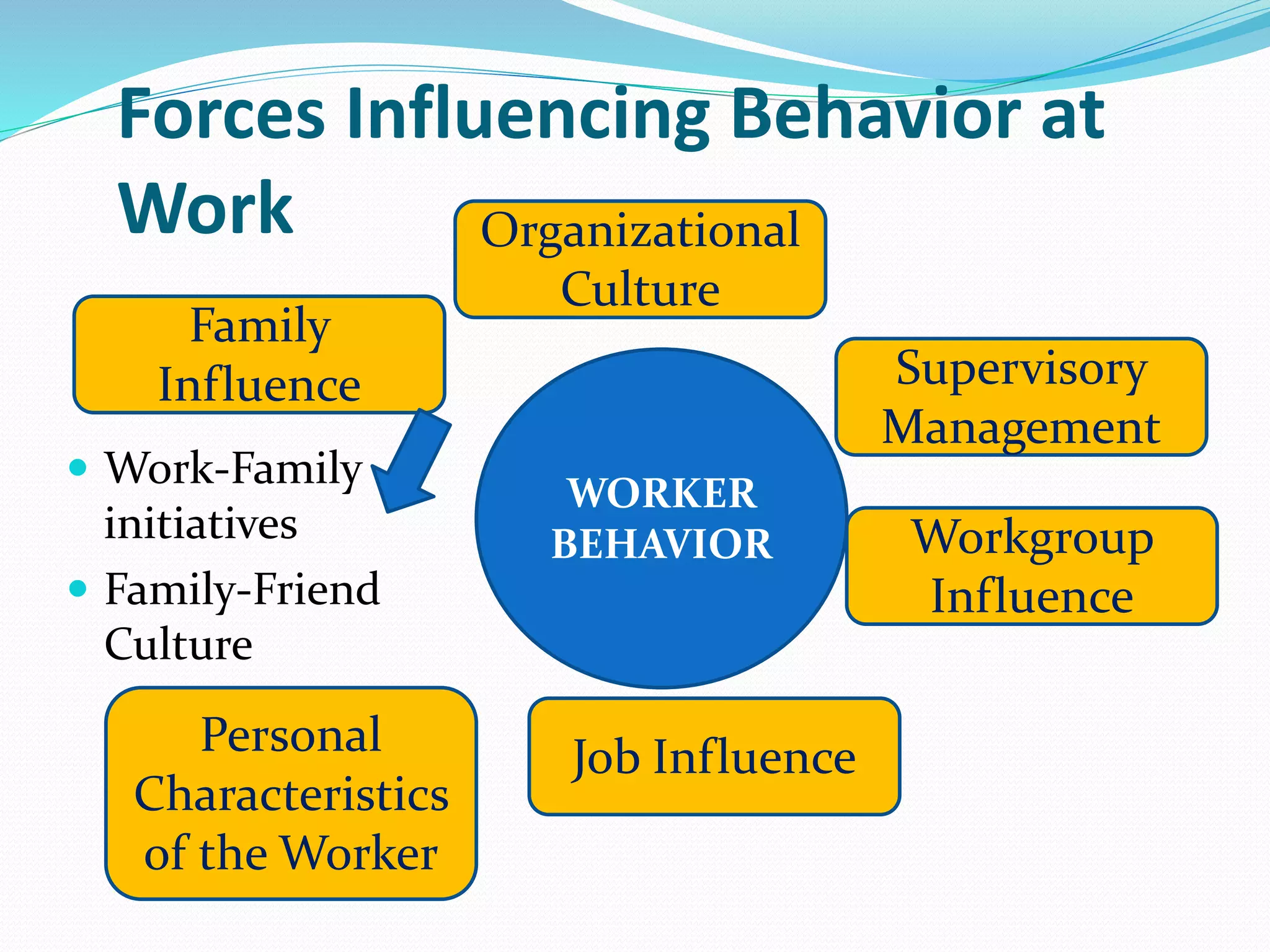
Human relations involves the study of interactions between people, including conflicts, cooperation, and group dynamics. It emphasizes analyzing human behavior, preventing problems, and resolving issues through self-development. Effective human relations combines cognitive and interpersonal skills like critical thinking, communication, and trust-building. It is important for respecting human rights in organizations, emphasizing employees as human resources, and helping diverse work groups. Multiple forces influence worker behavior, including organizational culture, management, work groups, job factors, personal characteristics, and family.