Embed presentation
Downloaded 57 times







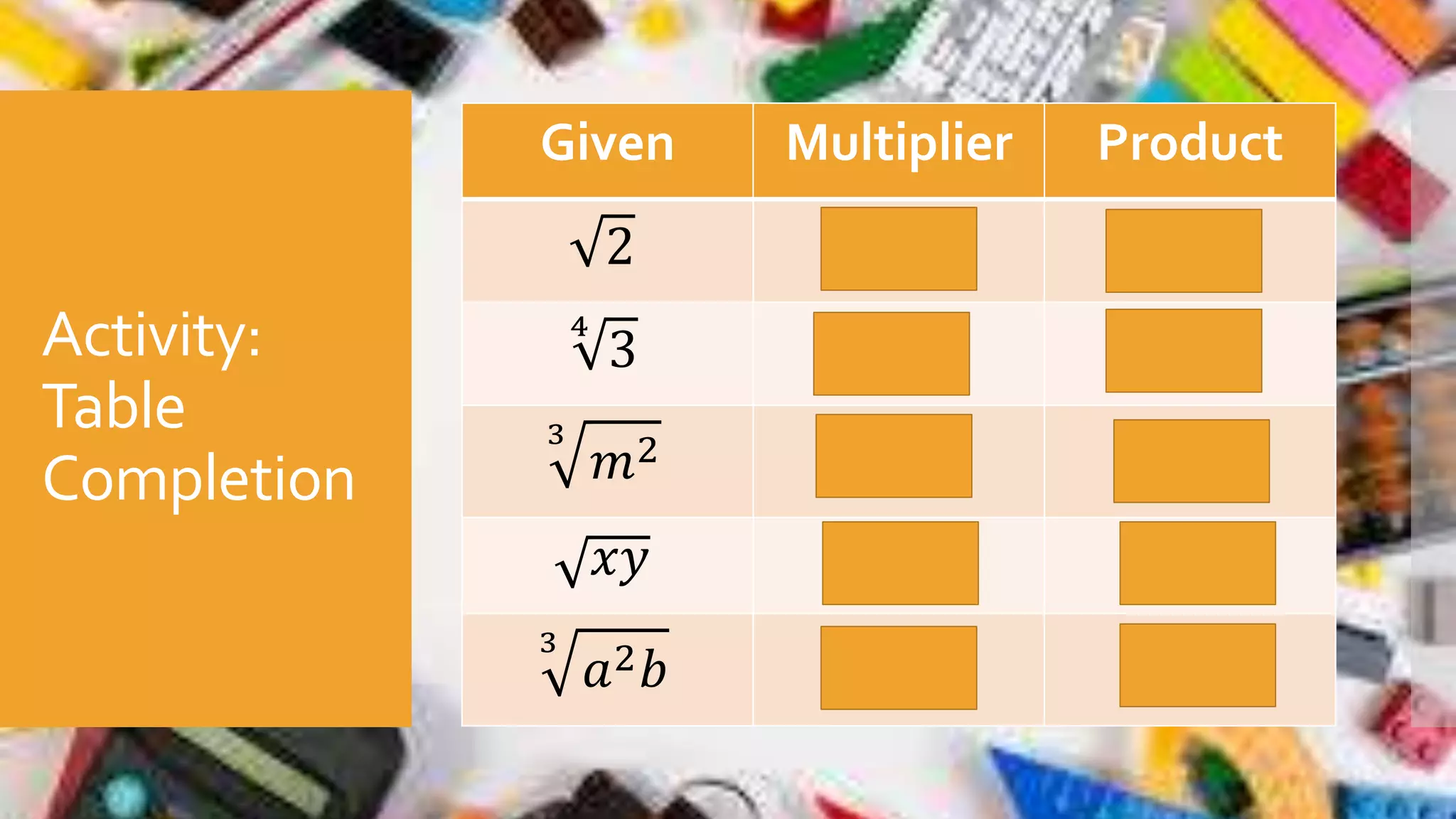








This document discusses dividing radicals and rationalizing radicals. It provides examples of rationalizing radicals by applying the law of radicals to make the denominator free of radicals. Examples of dividing radicals with the same index are also shown. The steps for dividing radicals are to divide the radicands and rationalize if needed to remove radicals from the denominator. An activity is included where students work in groups to solve radical expressions and present their work.















